Removing the background from an image allows you to move it to a different background, isolate small figures, or focus attention on certain elements of the photo. Whatever your intention, doing it is very simple.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Remove the Wallpaper Quickly
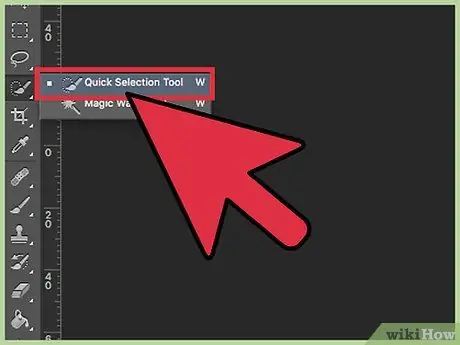
Step 1. Use the Quick Selection tool to quickly select the image elements you want to keep
The icon looks like a brush with a small dotted line. It should be the fourth from the beginning of the toolbar. Quick Select automatically detects edges near where you click, adding them to your selection.
If you can't find the tool, click on the Magic Wand and hold the mouse button down. Quick Select will appear in the small menu that opens

Step 2. Click near the edges of the most important objects in the image you want to keep
Click and drag the mouse cursor inside the image, in order to select all the elements to keep (those in the foreground). Keep clicking, until you select everything you want.
- If you make a mistake, hold down alt="Image" or ⌥ Opt, then click on the area you want to deselect.
- With [and] you will make the selection area larger or smaller.
- If the background is solid or rather small, select it, then press "Delete". Gone! If not, the most effective strategy is to select the image elements to keep.
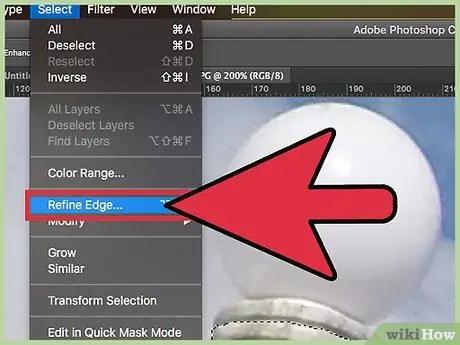
Step 3. Go to "Refine Outlines" to refine your selection
You will find this menu in the "Selection" section and you will have the option to preview the image without a background. At this point, you have several choices at your disposal. First, click "On White" in the preview field at the top of the Refine Outlines menu. Then, use the following tools:
-
Radius:
allows you to narrow the outline. Squeezing the field by 1-2 pixels will eliminate parts of the background without changing the image too much.
-
Round:
eliminates sharp edges for a smoother selection.
-
Feather:
makes the edges more blurry, allowing you to eliminate edges and improve the selection of parts that are impossible to isolate perfectly, such as hair.
-
Contrast:
creates sharper outlines. Performs the opposite action of "Round".
-
Move outline:
narrows the selection to a percentage of the original.
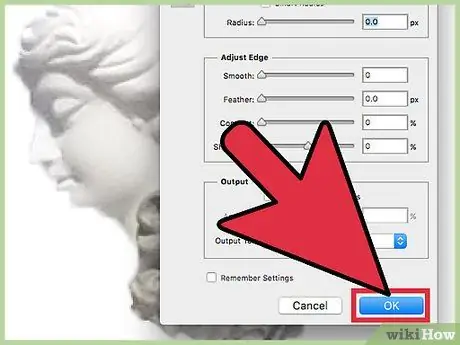
Step 4. Right-click on the selection to isolate it from the background
Click "Ok" on Refine Contours, then right click again on one of the areas you have delimited. Click on "Create Copied Layer" to separate the image from the background.
Make sure you've opened a selection when you right-click. If not, press "V" to get the normal cursor, then right click
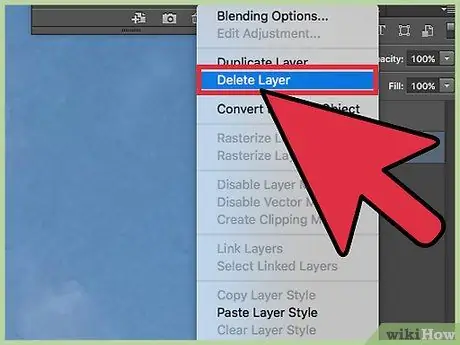
Step 5. Delete the background layer to isolate the image
You are now free to do whatever you like with the background layer. You can edit it in pieces, removing small parts and creating new "Create Copied Layer", or simply delete it with a single click. Either way, you'll isolate the image from the background.
Method 2 of 2: Using Other Tools and Techniques
Step 1. Make a duplicate of your image, especially the most important elements, before deleting any details
For example, imagine you need to edit a photograph of an elephant in the desert. Your goal is to remove the background and replace it with another one, but the Quick Selection tool continues to delete parts of the animal as well. Fortunately, there are other more effective tools and techniques for difficult areas.
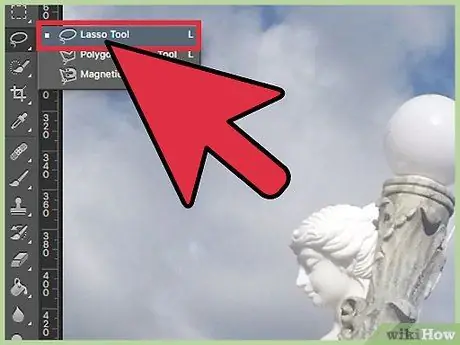
Step 2. Use the Lasso to draw small areas by hand
This tool follows the mouse cursor, creating a selection as you return to the starting point. It's not easy to use for large images, but it's effective when the job needs to be done precisely. Zoom in on the figure, then use Ctrl / Cmd + click to add small sections to your selection that the automatic tool did not detect, or Alt / Opt + click to remove small areas.
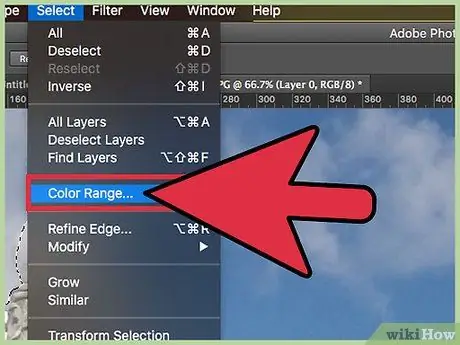
Step 3. Use "Color Range" to remove areas with a predominant color from the background
This tool easily selects large, solidly colored areas, such as a lawn, sky, or wall. However, if the image you want to keep has a similar color to the background, it will not be effective. To use it:
- Click on "Selection" in the top menu.
- Click on "Color range".
- Use the dropper to choose the color you want. You can also find specific colors in the "Select Colors" menu at the top.
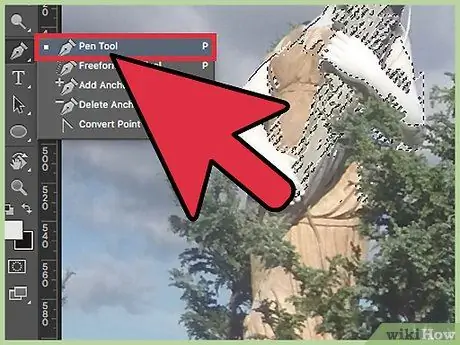
Step 4. Use the Pen to make exact and precise selections around a figure
This is the simplest and most useful tool for delineating an area. Of course, it takes some time to learn how to use it. Just click around the figure to create anchor points, which the program will join to draw a selection line. Click and hold the Pen icon in the toolbar, then choose the "Free Pen" item to draw curved lines. When done, right-click on the line, then click Create Selection. The line will be transformed into an area, which you can copy and separate from the background.
- If you make a mistake, Ctrl / Cmd + click to change the selection.
- With Alt / Opt + click you can remove a point from the line.
- With Shift + click you can draw a perfectly horizontal or vertical line starting from the last anchor point.
Step 5. Use layer masks to make the background invisible, but keep it in the image
These are very powerful tools that allow you to edit a file, without deleting any original information. To use them:
- Select the area to remove using the previous techniques.
- In the layers section, click on the "Add a mask" icon. It looks like a rectangle with a circle inside, at the bottom of the layer palette.
- Click on the black and white thumbnail. Now, use the Brush or Pencil tool to refine the image, drawing on top of the mask layer. Any black marks you add will "remove" the background. Draw over the blank mask to make the image "reappear".






