Computer networks are divided into subnets to allow for easier management and higher data transfer rates. Network devices such as routers are the devices that manage this division through the use of the subnet mask commonly known as "subnet mask" or "network mask". This is the data that indicates which part of the IP address refers to the subnet. In most cases, finding the subnet mask of a computer is a very simple task, while for other devices it may be a bit more laborious. If someone who wants to connect to the same network you are connected to asks you which subnet mask to use, you will need to provide them with the same one that your computer is currently using.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Windows systems
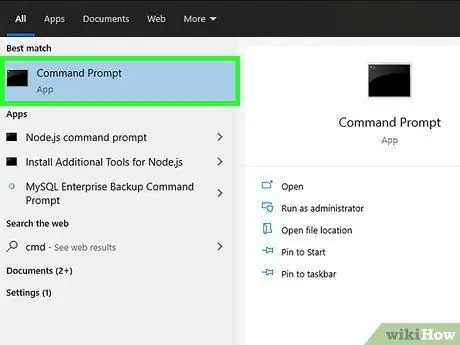
Step 1. Open the "Command Prompt"
Press the key combination ⊞ Win + R, type the keyword "cmd" in the text field of the appeared window and press the "Enter" key.
- If this procedure does not work, access the "Start" menu by clicking the Windows logo icon in the lower left corner of the desktop or press the "Windows" key on the keyboard, type the keywords "command prompt" all inside the search bar, then double-click the "Command Prompt" icon that appears in the list of results. You may need to select the Search icon first in order to view the search bar.
- If there is no icon in the lower left corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer to the lower right corner of the screen, then select the "Search" option. If you are using a touchscreen device, slide your finger across the screen to the left starting from the right side.
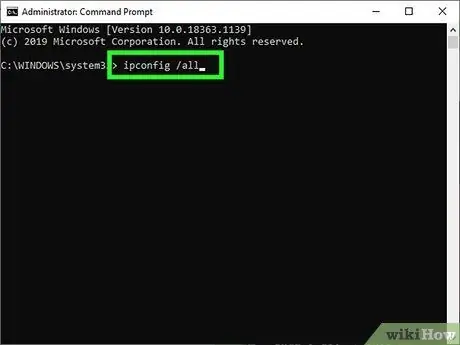
Step 2. View the network configuration
Type the command ipconfig / all (exactly as it appears without deleting the blank) within the "Command Prompt" window. Hit the Enter button. The Windows "ipconfig" program is the tool that allows you to view the configuration settings relating to all the system's network connections.
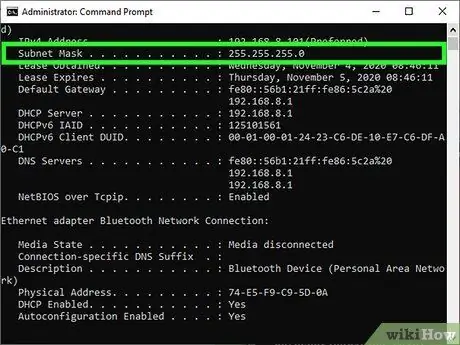
Step 3. Locate the subnet mask
It is shown in the "Ethernet Card Local Network Connection" section in the case of a wired network connection or in the "Wi-Fi Wireless LAN Card" section in the case of a Wi-Fi connection. Find the "Subnet Mask" field to find the subnet mask address. Most of the subnet mask addresses start with 255, for example "255.255.255.0" which is also the most used for connections to home LANs.
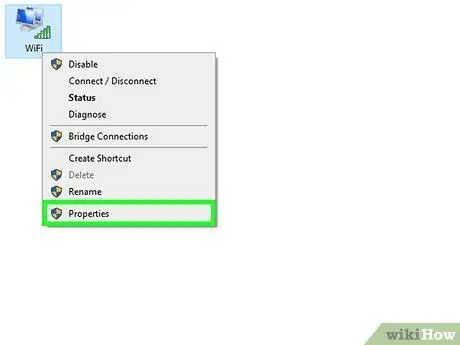
Step 4. Use the Windows "Control Panel"
If you don't want to use the "Command Prompt", you can find the same information by following this procedure:
- Open the Windows "Control Panel", choose the "Network and Internet" category, then select the "Network and Sharing Center" item;
- If you are using a modern Windows system, select the "Change adapter settings" link displayed on the left of the window. If you are using Windows Vista, choose the "Manage Network Connections" option.
- Select the network connection called "Local network connection" (Ethernet or Wi-Fi) with the right mouse button, then choose the "Status" option from the context menu that appeared. Press the "Details" button located inside the window that appears. Make a note of the address listed under "Subnet mask".
Method 2 of 4: Mac
Step 1. Select the "System Preferences" icon inside the Dock
If it is not visible, you can access the "Apple" menu in the upper left corner of the screen and choose the "System Preferences…" option.
Step 2. Click the "Network" icon
It is located inside the "System Preferences" window and is characterized by a gray globe. If you can't find it, type the keyword "network" into the search bar at the top right of the window.
Step 3. Select the active network connection from the list on the left of the new dialog box that appeared
Click the name of the network connection marked with a green dot and the words "Connected".
Step 4. If you are using a Wi-Fi network connection, press the "Advanced" button
It is located in the lower right corner of the window. In the case of most other types of network connections, the subnet mask will be visible in the right part of the window under "Subnet mask".
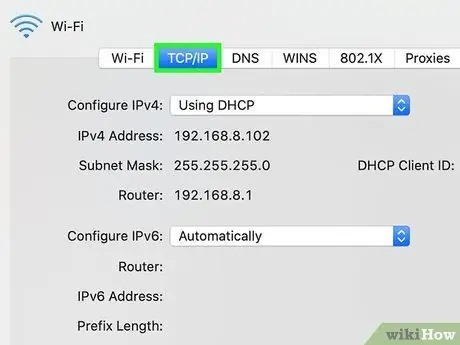
Step 5. Go to the TCP / IP tab of the window showing the "Advanced" network settings
This section specifies the protocols and information to be used to access the network.
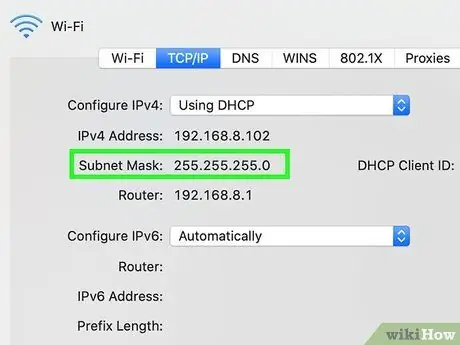
Step 6. Find the subnet mask address
It should be clearly visible within the text field labeled "Subnet Mask" and should start with the number "255".
If the only data visible in this screen are related to the "Configure Ipv6" section, it means that you are using the new IPv6 protocol which does not use the subnet mask. If you need to access the web, try selecting the "Using DHCP" option from the "Configure IPv4" drop-down menu, then hit the Renew DHCP Assigned button
Method 3 of 4: Linux systems
Step 1. Open the command console
If you are not an experienced user and are unfamiliar with this tool, you will need to follow the specific procedure related to the Linux distribution you are using. If you need more information about the Linux command line, do an online search or read this article.
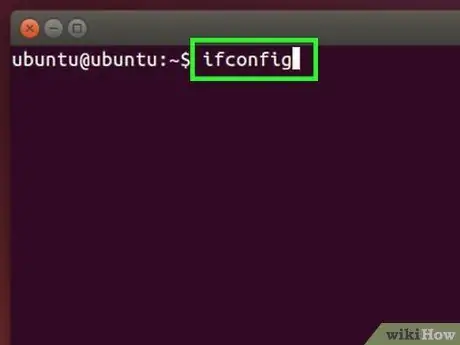
Step 2. View the computer's network configuration settings
Type the command ifconfig inside the Linux "Terminal" window and press the Enter key.
If a notification message appears stating that you need to use a system administrator account to be able to execute the indicated command, follow these instructions and repeat the procedure
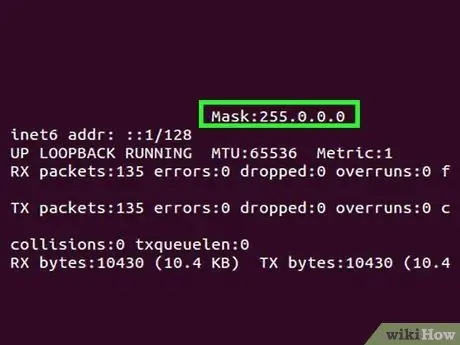
Step 3. Find the address of the subnet mask
It should be listed under "Mask" or "Subnet Mask". The address begins with the number "255".
Method 4 of 4: Configure a TV or other Device
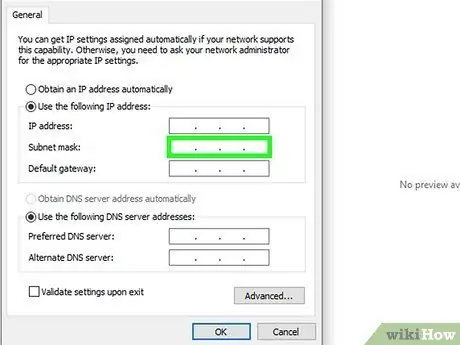
Step 1. Use the same subnet mask used by the computer or any other device connected to the local network
When setting up the network connection of a Smart TV or other type of device, you will be asked to provide the subnet mask address as well. This is a parameter of the network connection that is related to the local configuration of the network. For best results and to avoid making mistakes, follow the steps described in the previous methods of the article to find the address of the subnet mask in use on your home LAN. The same address used by the computer or any other device currently connected to the network will also be fine for the TV or other equipment you need to connect.
- If the device you are trying to set up still does not have access to the network, view the network information used by the computer and refer to this data to change the network connection settings of the device you are working on.
- If you can't find your computer's network configuration, try entering the address "255.255.255.0". In most cases it is the value that is used as the subnet mask to configure a home LAN.
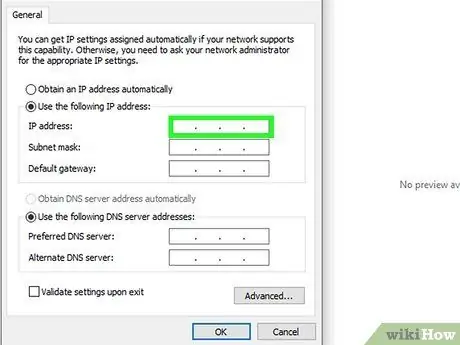
Step 2. Change the IP address
If your device still can't connect to the network or the web, try checking its IP address. It is located in the same window where you entered the subnet mask value. Compare the IP address of the device in use with the one assigned to the computer (also visible in the same place where you found the subnet mask). Copy the IP address of the computer, taking care to change the last group of numbers. Choose a value larger than that used by the computer, but less than 254. To avoid that the address you are going to choose is already used by other devices on the network, increase that of the computer by at least 10 units.
- For example, if the address assigned to the computer is "192.168.1.10", for the new device use the value "192.168.1.50" or "192.168.1.100".
- If you can't find your computer's network address, try checking the label on the bottom of the router or modem or search online using the make and model of these network devices along with the keywords " IP address". Remember to keep the first three groups of numbers unchanged and change the last.
- If you can't find any useful data, try the following network addresses: "192.168.1.100", "192.168.0.100", "192.168.10.100" or "192.168.2.100".
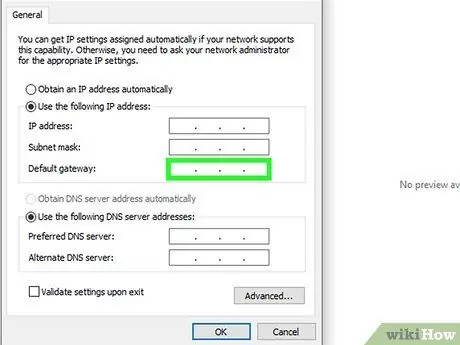
Step 3. Set the network gateway address
Also in this case it is necessary to use the same value used by your computer or any other device already connected to the network. This address is normally the one used by the router / modem that manages the local LAN you wish to access. In most cases this value corresponds to a normal network IP address except that it ends with the number "1".
- For example, if the IP address of one of the devices currently connected to the network is "192.168.1.3", the gateway address will almost certainly be "192.168.1.1".
- Start the internet browser of your choice and type in the prefix http: followed by the gateway IP address in the address bar. If the value entered is correct, you will be redirected to the administration page of the modem / router that manages your home network.
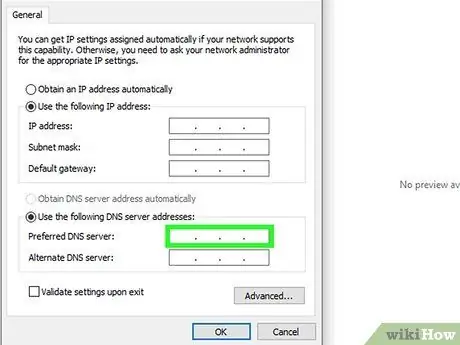
Step 4. Set up DNS servers
Use the same DNS addresses that your computer uses. Alternatively you can enter the network gateway address. If you prefer, you can search online using the keywords "public DNS server".
Step 5. Contact the technical support of the device manufacturer
If the latter continues to have problems connecting to the network with the indicated settings, seek help by contacting the customer service or technical support of the company that manufactured the device.
Advice
- If the subnet mask is set to "0.0.0.0", it may mean that your device is not currently connected to the internet.
- The "subnet mask" address is displayed only for currently active network adapters, ie those that are actually connected to a network. For example, if you are using a wireless connection, the netmask address will only be visible within the configuration of the Wi-Fi network card. If your device has multiple network interfaces, for example a wireless card and a regular Ethernet card, you will need to refer to the configuration of the active card to find the netmask.
- Networks that exclusively use the new IPv6 protocol do not use the netmask. This information is included directly within the IP address. The fourth group of digits (which in this case is distinguished by a colon and not by a period as happens in IP addresses that use the IPv4 protocol) represents the netmask. If binary notation is used, bits 49 to 64 are those that store the "subnet mask".






