This article explains how to create a histogram on Microsoft Excel. This is a column chart that shows how often data is presented; for example, the number of people who scored a certain score on a test.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Enter Data

Step 1. Open Microsoft Excel
This program's icon looks like a white "X" on a green background. Press it and the Excel Workbooks page should open.
On Mac, following this step should open a new Excel sheet. In this case, skip the next step
Step 2. Create a new document
Click New workbook in the upper left corner (Windows), or click File then New workbook (Mac).
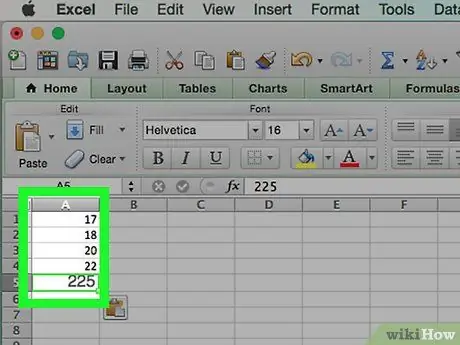
Step 3. Determine the maximum and minimum of the data source
This is important in deciding which classes will be and how many to use.
For example, if your data ranges from 17 to 225, the minimum is 17 and the maximum is 225
Step 4. Determine how many classes to use
These numbers divide the histogram data into groups. The simplest way to determine them is to divide the maximum data (for example 225) by the number of points in your graph (for example 10), then round to the nearest integer; only in rare cases will you use more than 20 numbers or less than 10. If you don't know how to proceed, you can use one of the following formulas:
- Sturges Rule: The formula for this rule is C = 1 + 3, 322 * log (N) where C. is the number of frequency classes e No. the number of observations; once you find C, round it to the nearest integer. This rule is best suited to linear or "clean" datasets.
- Rice's rule: the formula for this rule is cube root (number of observations) * 2 (for a data series with 200 observations, you need to calculate the cube root of 200, then multiply by 2. This formula is best suited to chaotic data or inconsistent.
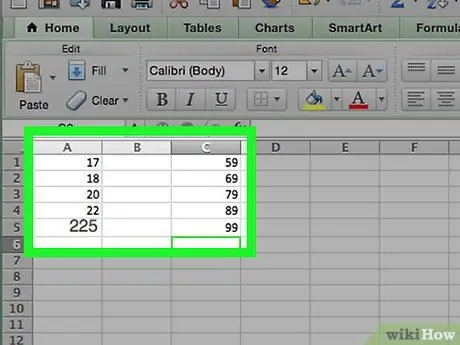
Step 5. Decide on the classes
Now that you know how many to use, it's up to you to determine the most even distribution. They should increase linearly, including the minimum and maximum data.
- For example, if you want to create a histogram to represent the results of a test, you should choose classes in increments of 10 that indicate the various grading thresholds (e.g. 59, 69, 79, 89, 99).
- It is quite common to increase classes in increments of 10, 20, or even 100.
- If you have data that is very different from others, you can exclude it from the class range or expand it enough to include it.
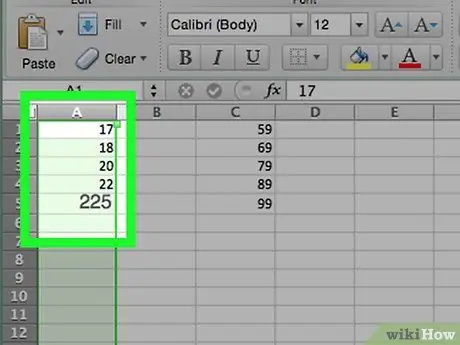
Step 6. Add the data in column A
Write each observation in the respective cell of the column.
For example, if you have 40 observations, add each item in the cells ranging from A1 to A40.
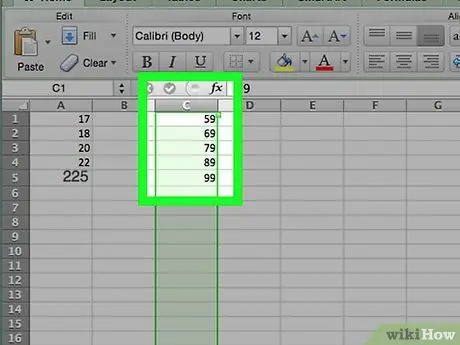
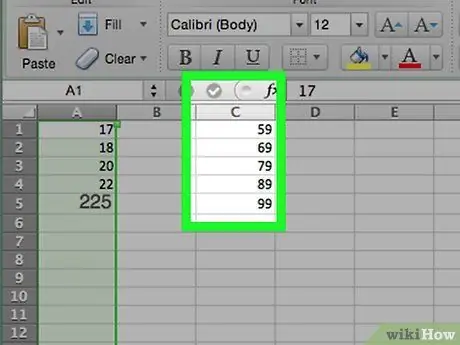
Step 7. If you are using a Mac, add the classes in column C
Start from the cell C1 and proceed down, typing each number. Once this step is complete, you can proceed with creating the histogram.
Skip this step on Windows
Part 2 of 3: Creating the Histogram on Windows
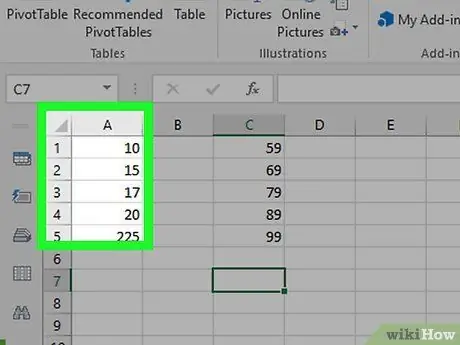
Step 1. Select the data
Click the first cell of the column TO, then hold down Shift as you click the last cell in the same column that contains data.
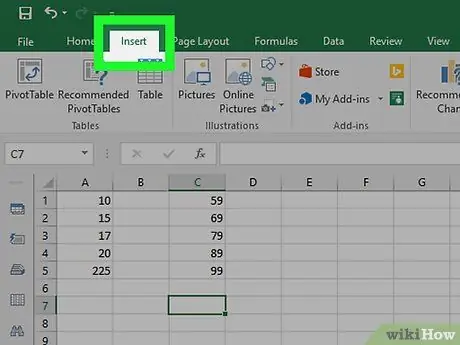
Step 2. Click the Insert tab
It is located on the green ribbon at the top of the Excel window. Press it and the toolbar at the top will change, showing the menu insert.
Step 3. Click Recommended Charts
You will find this option in the "Charts" section of the bar insert. Press it and a window will open.
Step 4. Click the All Charts tab
It is located at the top of the window that has just opened.
Step 5. Click Histogram
You will see this entry on the left side of the window.
Step 6. Select the Histogram template
Click the leftmost icon to select the traditional model (instead of the sorted data one), then click OK. This will create a simple histogram with the selected data.
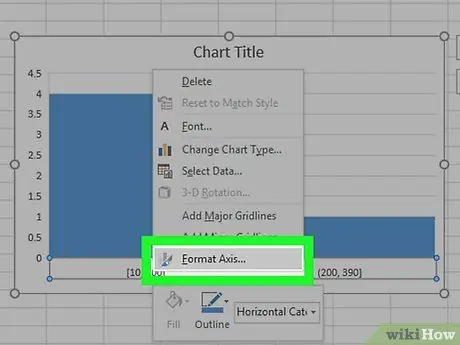
Step 7. Open the horizontal axis menu
Right-click on the horizontal axis (i.e. the one with numbers in brackets), click Axis format … in the pop-up menu that opens, then click the bar chart icon in the "Format Axis" menu that appears on the right side of the window.
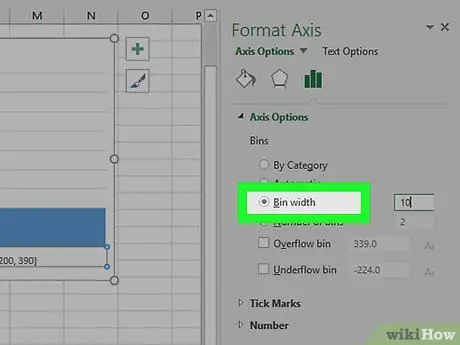
Step 8. Check the "Class range" box
You will find it in the center of the menu.
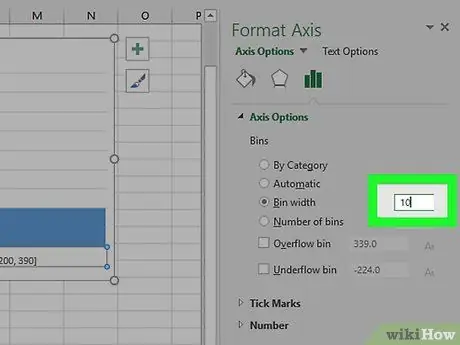
Step 9. Enter the range of classes
Type the value of a single class in the "Class range" field, then press Enter. Excel will automatically format the histogram to display the correct number of columns based on classes.
For example, if you have decided to use classes in increments of 10, write 10 in the field
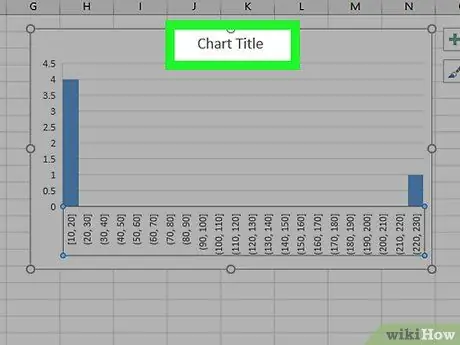
Step 10. Label your chart
This step is only necessary if you want to add titles to the chart axes or to the figure itself:
- Aces titles - click the + green on the right of the graph, check the box "Axes titles", click Axes titles on the left or at the bottom of the chart, then enter the title of your choice.
- Graphic title - click the text field Graphic title at the top of the histogram, then enter the title you want.
Step 11. Save the histogram
Press Ctrl + S, select a save path, choose the name and click Save.
Part 3 of 3: Creating the Histogram on Mac
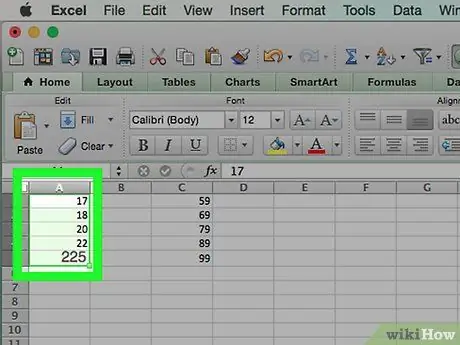
Step 1. Select the data and classes
Click the first value in the column TO to select it, then hold down Shift as you click the column cell C. which is on the same row as the last cell TO which contains a value. This will select all the data and its classes.
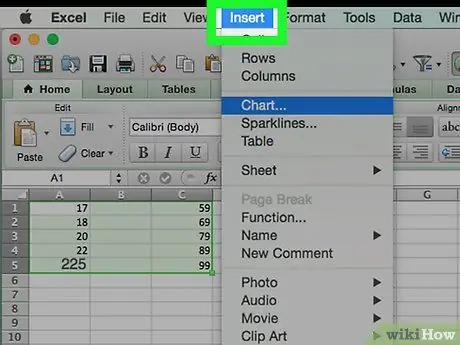
Step 2. Click Insert
This is a green ribbon tab at the top of the Excel window.
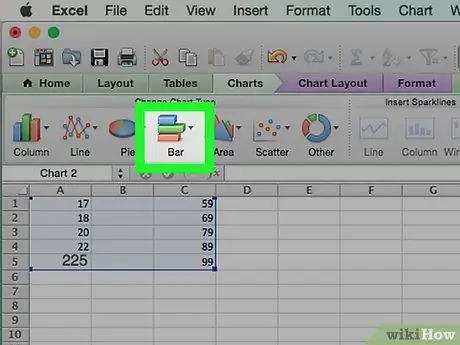
Step 3. Click the bar graph icon
You will find it in the "Charts" section of the bar insert. Press it and a drop-down menu will appear.
Step 4. Click the "Histogram" icon
This is the series of blue columns under the "Histogram" heading. This will create a histogram with your data and classes.
Make sure you don't click on the "Pareto (sorted histogram)" icon, which is represented by blue columns with an orange line
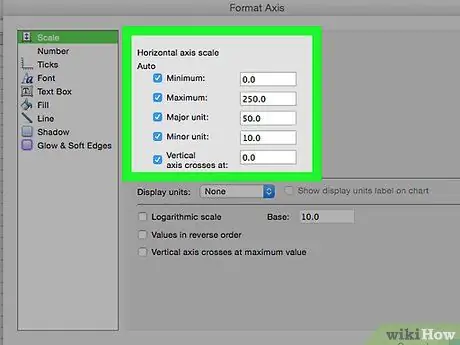
Step 5. Check the histogram
Before saving, make sure the graph is accurate; if not, edit the classes and create another chart.
Step 6. Save your work
Press ⌘ Command + S, choose a name and save location if needed, then click Save.






