A histogram is a graph that shows the frequency, or number of times, that a given item appears over a specific range. A histogram is similar to a bar chart, but its area is normally used to graphically represent how often a certain item appears. Histograms are used to represent a set of continuous data, such as time, a measurement, or a temperature. The main problem with a histogram chart is the difficulty of comparing two data series and the impossibility of obtaining an accurate reading of the values assumed by the data. If you are a student or a professional, knowing how to draw a histogram chart will be useful for you to graphically represent the statistical data of a particular project or activity.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Draw by Hand

Step 1. Draw the axes of the Cartesian plane using a ruler
These are the vertical and horizontal axes, which represent the basic drawing of a histogram. If you find it difficult to trace the two axes perfectly perpendicular to each other, help yourself by using the corner of a sheet of paper.

Step 2. Calculate the distribution of the data series
In a histogram, data is represented in groups or ranges. These groups must be evenly distributed, so as to divide the abscissa axis (X axis) into identical intervals.
For example: 0-4 apples, 5-9 apples, 10-14 apples, etc., placing them on the abscissa axis so that they are equidistant from each other (for example at 2 cm distance)
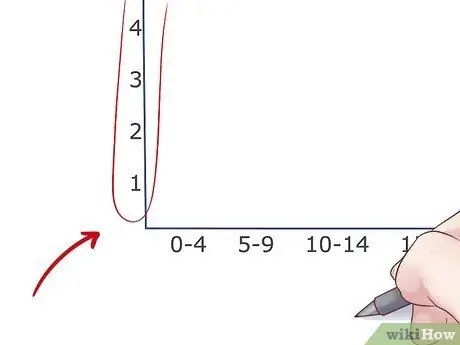
Step 3. Subdivide the vertical axis (ordinate axis)
Frequency is always reported on the vertical axis of a histogram. On the basis of the data to be represented, it is necessary to bring the reference scale back to the Y axis and divide it into equidistant intervals. Make sure you leave enough space at the top of the chart to make it easy to read.
- For example, if the maximum frequency of the dataset to be plotted was 54, the highest number on the Y-axis reference scale would be 60.
- If the frequency does not develop progressively, but is constantly at very high values, you can shorten the scale on the Y axis by eliminating most of the unused lower numbers. For example, if the first frequency is 32, you can use a measurement scale that starts at 25 or 30.
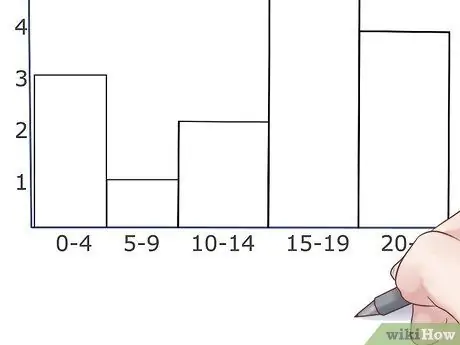
Step 4. Draw the bars
Draw a horizontal line at the frequency value for each range or group of data. Now draw the two side lines of the bar so that it is centered with respect to the data range it represents. Make sure the bars are all the same width. Normally in a histogram the bars are contiguous since they represent a continuous series of data, but it can still happen that a specific range has no elements to represent.
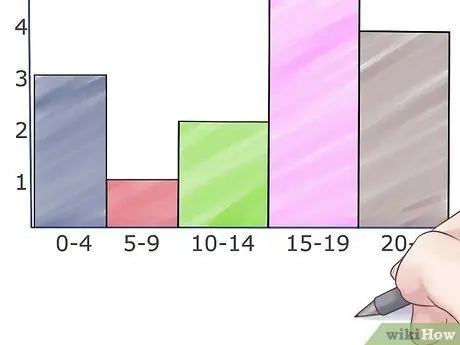
Step 5. Color the graph
Color the bars in the column chart using colored pencils, markers, or highlighters. This will make it easier to distinguish the ranges into which the data has been split.
Method 2 of 3: Use Excel
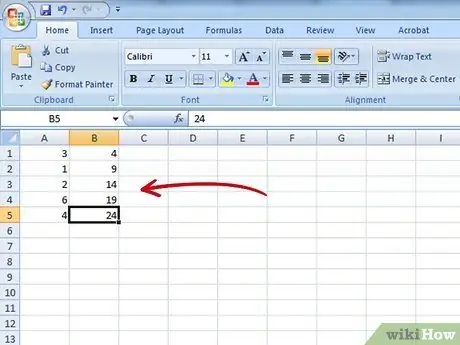
Step 1. Set the data
Start Excel and create a new document. Fill in column "B" with the ranges or groups into which you have divided the data series in question (for example 20/30/40, 0/5/10/15, etc.). Each range must occupy a single cell. Now fill in column "A" with the frequency of each single data range; in other words it is the level or height that will be reached by the bar that graphically represents the data range in question.
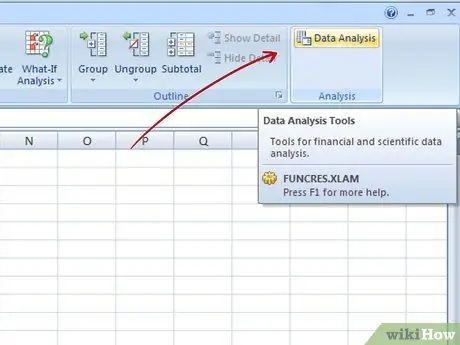
Step 2. Run your data analysis
To do this, go to the "Tools" menu and choose the "Data Analysis" option. As this is not a standard Excel feature, it is very likely that you will need to install it first via the "Add-ons" function.
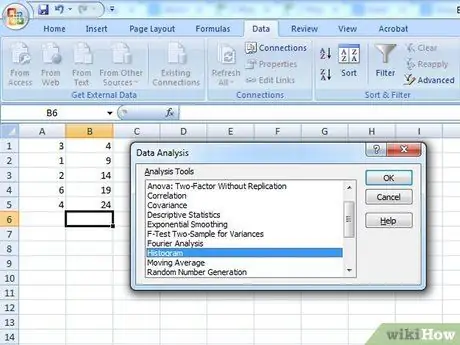
Step 3. Create the histogram
Go to the "Data Analysis" menu and choose the histogram item, then press the "OK" button.
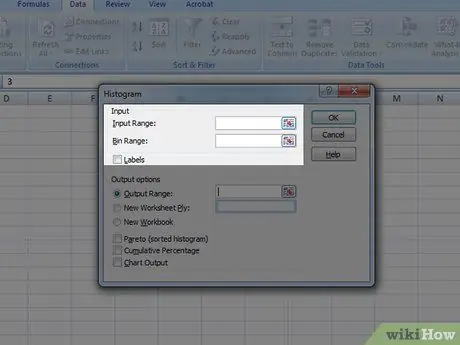
Step 4. Set the data series values and ranges to graph
To do this, you will need to use the appropriate menu and select the relevant data column created in the previous steps.
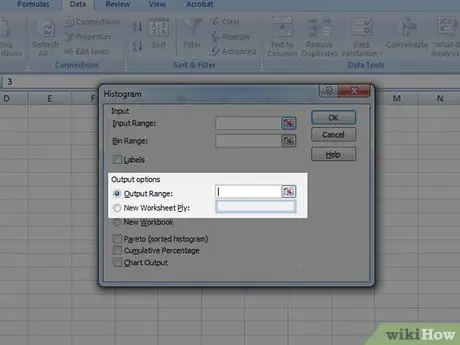
Step 5. Choose the output mode
Select the "Output Graph" checkbox, then press the "OK" button.
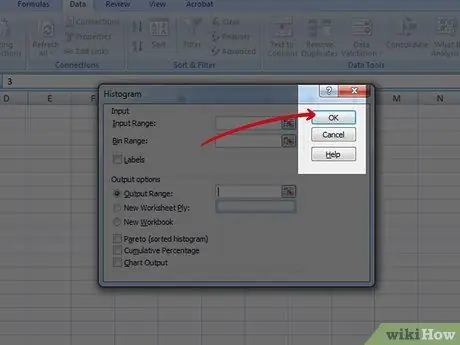
Step 6. Finished
Have fun analyzing your chart and don't forget to save the project.
Method 3 of 3: Using an Online Program
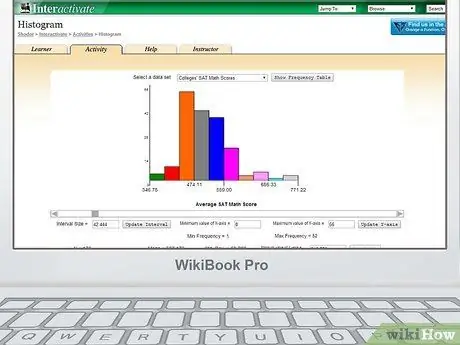
Step 1. Log in to the site with which to create your histogram
This article uses the following website.
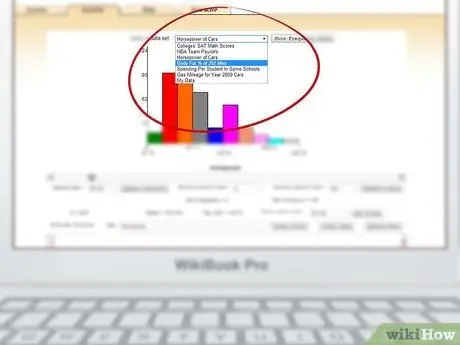
Step 2. Choose a predefined format
At the top of the page there is a drop-down menu with which you can select sample data series, which you can later modify with your own data. Alternatively, you can create a new chart completely from scratch.
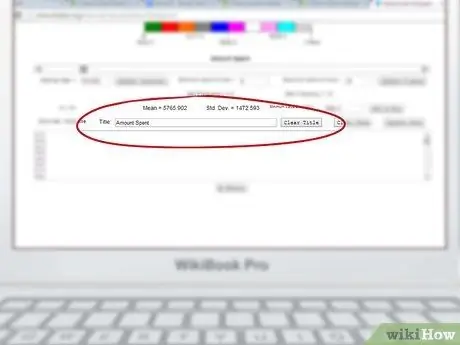
Step 3. Name the chart
In the central part of the page there is a field called "Title" where you can enter the title to be assigned to your chart.
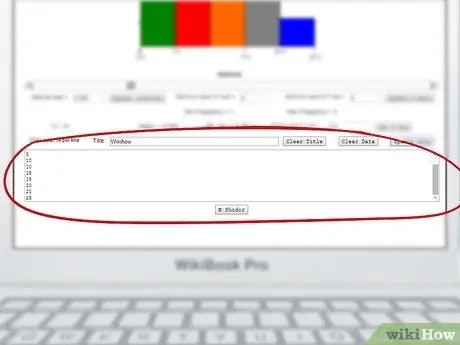
Step 4. You can enter your details in the box at the end of the page
Below the text field for the title, there is a large box in which to enter the data series to be graphed. Enter only one item per row (e.g. 5, 5, 5, 10, 10, 15, 15, 20, 20, 25, etc.).
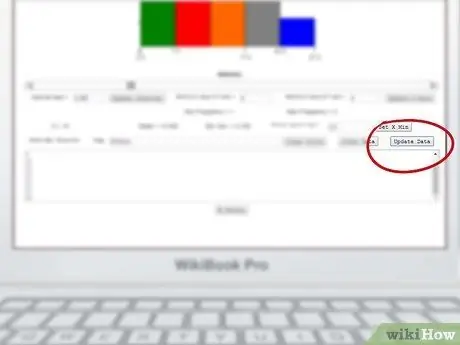
Step 5. Refresh the data
To do this, press the "Update Data" button located in the upper right part of the data set box.
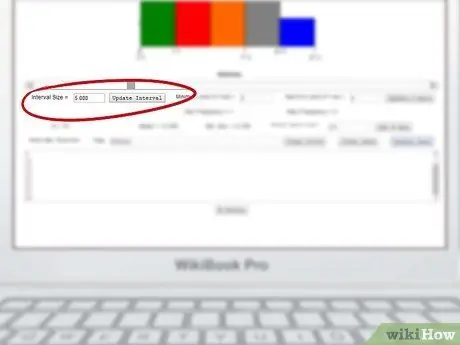
Step 6. Change the frequency
The graph should adapt the data automatically, but you can always intervene manually by changing the size of the interval and the maximum and minimum values of the measurement scales shown on the axes.
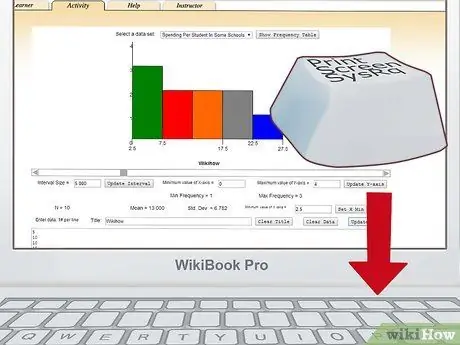
Step 7. Print or save your job
To save an image of your chart, you can use the "Print Screen" function of the keyboard. Then proceed to paste and crop the image obtained using Microsoft Paint or the image editor of your choice. At the end of the changes save the work and, if you need to have it in paper version, proceed to print it.
Advice
- Do not forget to report the quantities represented on the X and Y axes, so that the graph is correct and legible.
- When counting items within datasets, it can be helpful to unmark them to avoid counting them multiple times.
- When drawing a histogram, use the ruler so that you can draw precise, straight lines.






