Formatting a disk erases all data on it and creates a new file system. You need to do this if you want to install Windows on a disk, or if you want to start using it after inserting it into your computer. It is also a quick way to delete all the data there. If you want, you can even reduce the size of existing drives and format the freed space to create a second partition for your computer. If you have decided to give away or throw away a computer, you can use special tools to erase all your data securely.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Format the Primary Drive
Step 1. Backup all important data
Formatting a disk deletes all data on it and removes the operating system. Make sure you have a copy of the files you need elsewhere, such as on an external drive or saved in the cloud.
If you are looking to securely delete data on a drive before throwing it away, read the Safely Format a Drive section of the article

Step 2. Insert the Windows installation disc
You will use it to format the drive. This is the easiest way to format the primary drive, as you don't have the option to do it directly from within the operating system. It is not necessary to use the disk that contains your copy of Windows, because you will not enter a product key (if you do not intend to install Windows again). If you can't find an installation disc, you have other options based on your version of Windows:
- Windows 7: You can download an ISO file for Windows 7 by entering your product key here. You will then need to copy the ISO file to a blank DVD or USB drive using the Windows 7 USB / DVD Download Tool which you can find here.
- Windows 8: you can download the Windows 8 Media Creation program from the Microsoft website at this address. This application downloads and creates a Windows installer on a blank DVD or USB drive (4GB or larger). Run the program and follow the prompts to create the installation files.
- Windows 10: You can download the Windows 10 Media Creation program from Microsoft's website at this address. Run the application to create Windows 10 installation files on a blank USB drive or DVD. Most users should download the 64-bit version of the program. If you are unsure, check if your version of Windows is 32-bit or 64-bit.

Step 3. Configure your computer to boot from the drive that contains the installation files
To run the program and format the disk, you need to set the computer to start on the drive of choice (DVD or USB) instead of the hard drive. To do this, the procedure differs depending on your operating system, particularly if you are using Windows 7 (or earlier) or Windows 8 (and later).
- Windows 7 (and earlier): restart your computer and press the BIOS, SETUP or BOOT key that is indicated at the bottom of the first screen that appears on the monitor. The most common keys are F2, F11, F12, and Del. In the boot menu, set the drive that contains the installation files as the primary boot drive.
- Windows 8 (and later): Click the Power button in the Start menu. Hold Shift and click Restart to open the "Advanced Startup" menu when Windows opens. Click the "Troubleshoot" option, then "Advanced Options". Click "UEFI Firmware Settings", then open the BOOT menu. Sets the drive that contains the installation files as the primary boot drive.
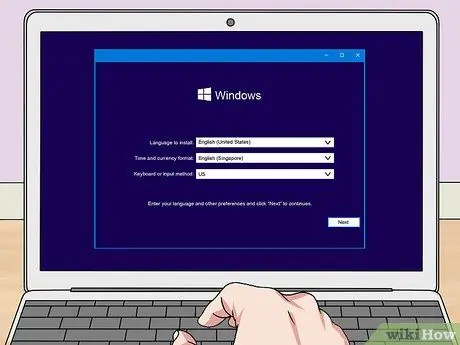
Step 4. Start the installation
Windows will load the configuration files and start the installation. You will be asked to choose a language and agree to the terms before continuing.
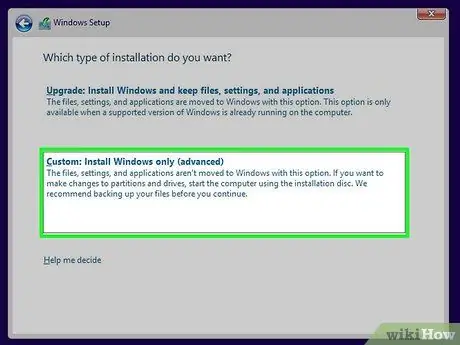
Step 5. Select the "Custom" installation
This allows you to format the hard drive in the process.
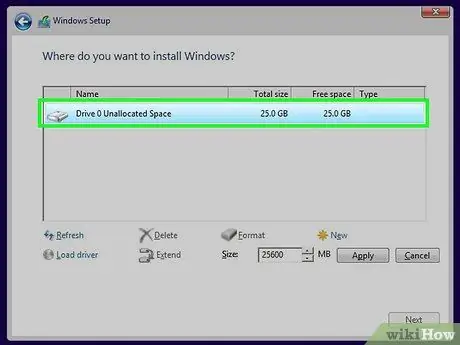
Step 6. Choose the partition you want to format
Once you get through the first few installation screens, you will be shown all hard drives and partitions. Usually you will see several partitions, one for the operating system, one for recovery and the ones you have created or disks you have added.
- You can delete partitions on the same disk to merge them all into one unallocated partition. This operation deletes all data in the partitions. Click the "Drive Options" button to view the "Delete" entry.
- If you delete all partitions, you need to create a new one before you can format it. Select the unallocated space and click "New" to create a new partition. You will be able to choose the size according to the available space. Note that it is usually not possible to create more than four partitions on a single disk.
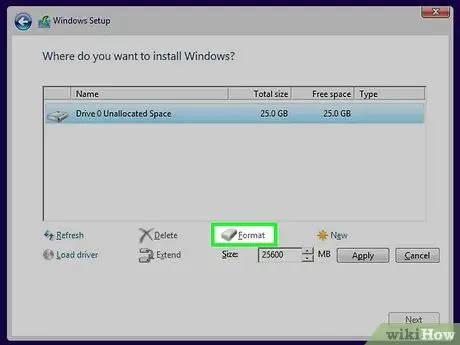
Step 7. Format the selected partition
Click the "Format" button after selecting the partition or drive you want. If you don't see the button, click "Drive Options" and it should appear. You will be notified that the operation will delete all data present. Confirm and the operation will start automatically. It will take a few minutes to complete.

Step 8. Install the operating system
Formatting the primary drive removes the operating system, so you won't be able to use your PC until you install another one. You can continue with the Windows installation once the disk is formatted, or you can install a different system such as Linux. To install Windows, follow the rest of the directions in the setup program. If you prefer Linux, you need that operating system's installer. Read How to Install Linux for more instructions on obtaining the various versions of Linux.
Method 2 of 4: Format a Secondary Drive

Step 1. Open the Disk Management utility
When you connect a new external drive or install a new internal hard drive, you need to format it before it appears in Windows Explorer. You can do this thanks to the Disk Management program.
- Press ⊞ Win + R and type diskmgmt.msc to open Disk Management. In Windows 8 and 10, you can right-click the Start button and select "Disk Management".
- It may take a few seconds for all the disks you have installed to appear.
- If you are looking to securely delete data on a drive before throwing it away, read the Safely Format a Drive section of this article.
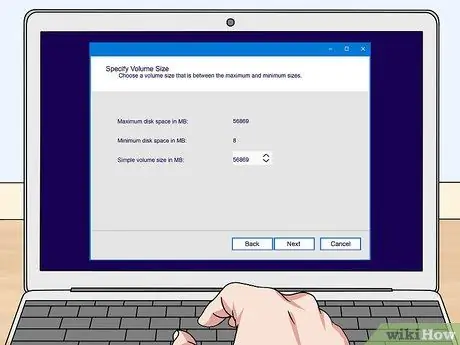
Step 2. Create a partition on the new drive (if asked)
If you open Disk Management for the first time after installing a new drive, you will likely be prompted to initialize the disk. Don't worry if the window doesn't appear.
Select "GPT" if the new disk is 2TB or larger. Select "MBR" if the new disk is smaller than 2TB
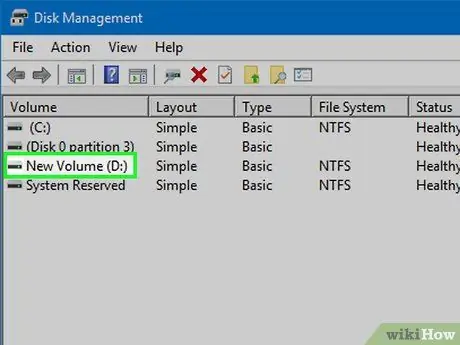
Step 3. Select the drive you want to format
In Disk Management you will see all disks and partitions listed. If you have just mounted a new drive, you will probably find it on a line dedicated to it, labeled "Unassigned". Expand the "Status" column to see more details about each partition.
- You cannot format the Windows "Boot" partition, because it is the one on which the operating system is installed.
- Formatting a drive erases all data on it, so make sure beyond doubt that you choose the right one.
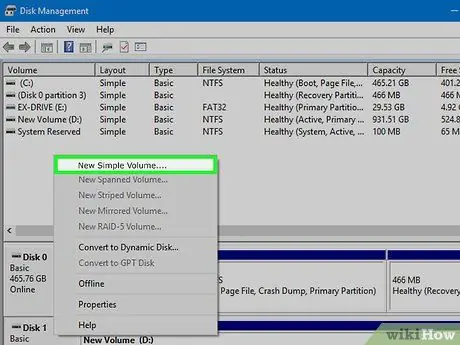
Step 4. Create a partition (if needed)
If the drive is Unassigned, you need to right click on it and select "New Simple Volume". Follow the prompts to create a partition from unallocated space.
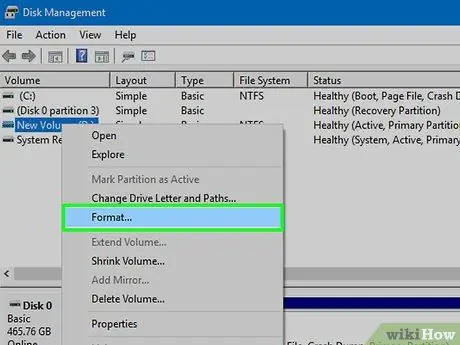
Step 5. Right click on the drive or partition and select "Format"
The Format window will open.
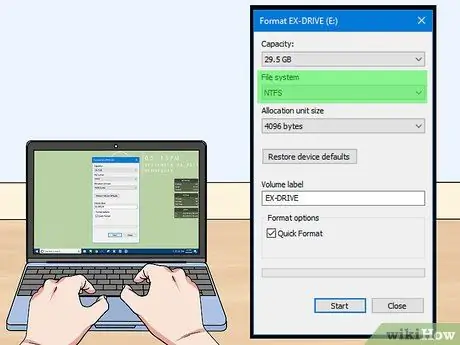
Step 6. Set the formatting options
You can name the drive (Volume Label), as well as choose the file system. For Windows, select "NTFS" for maximum compatibility. You can also choose whether to perform a quick format. Uncheck this box only if you suspect the disk is damaged.
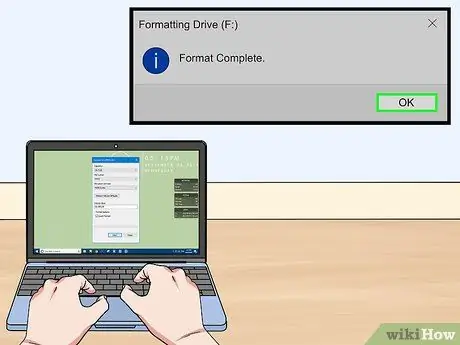
Step 7. Wait for the operation to finish
Click the Format button when you have chosen the desired options. This process can take a few minutes. Once finished, you can use the disk to save files and install programs.
Method 3 of 4: Restrict an Existing Unity

Step 1. Open the Disk Management utility
You can shrink one of the existing drives to allocate the free space created in this way to a new partition. This can be useful if you have a lot of free space on a drive and want to create a separate drive for some specific files, such as photos.
Press ⊞ Win + R and type diskmgmt.msc to open Disk Management right away. In Windows 8 and 10 you can also right-click the Start button and select Disk Management from the menu
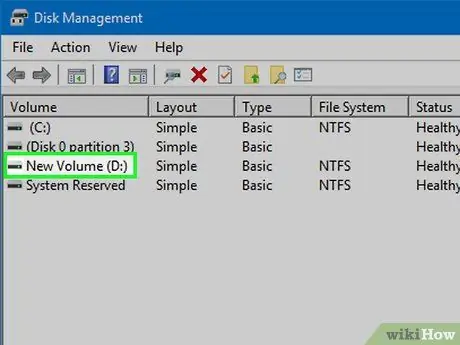
Step 2. Select the partition you want to shrink
You can do this on all partitions that contain free space. Usually you will choose one with at least several GB of free space, so that the new partition is useful. Make sure you leave enough space for the existing partition, especially if it is the boot partition. Windows works best if the disk on which it is installed is at least 20% free.
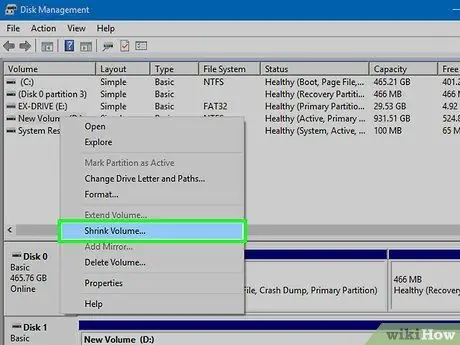
Step 3. Right click on the partition and select "Shrink Volume"
A new window will open after Disk Management has determined how much space is available to create a new partition.
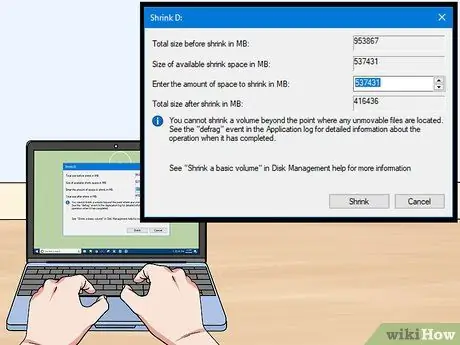
Step 4. Enter the size of the new partition
The window will show how much space can be removed from the existing drive in megabytes (MB). 1024MB equals one gigabyte (GB). Enter the number of MB you want to shrink the drive by (creating a new partition of that size).
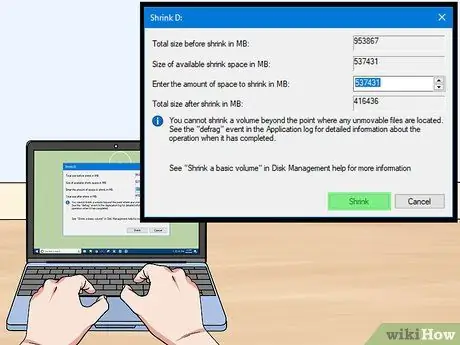
Step 5. Start the reduction operation
Click "Shrink" to remove the specified space from the existing drive. You'll see it appear in Disk Management on the same drive hosting the old partition.
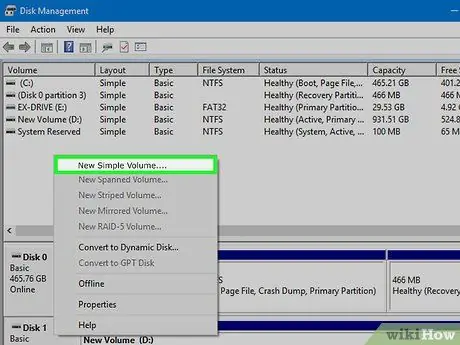
Step 6. Create a partition
Right click on the unallocated space and select "New Simple Volume". The new volume creation wizard will open.
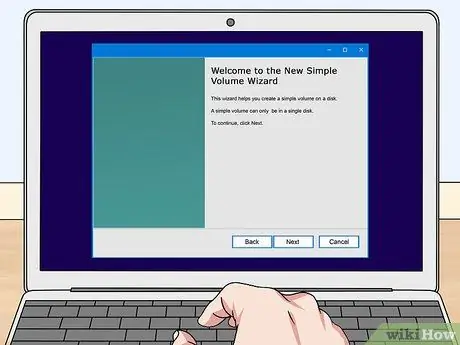
Step 7. Follow the prompts to create the partition
You will be able to choose how much of the unallocated space to use for the new partition. You will also need to assign a letter to the volume.
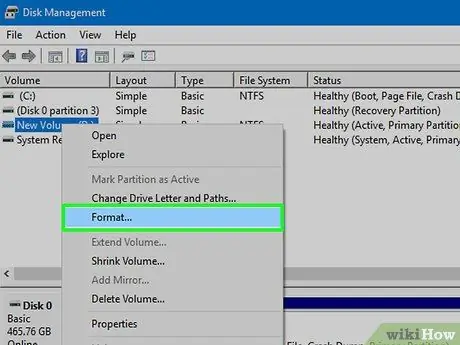
Step 8. Format the new partition
During the wizard, you will be asked to format the partition. You can do it right away by choosing a file system, otherwise you can do it later with the steps described in the previous method.
Method 4 of 4: Format a Drive Safely
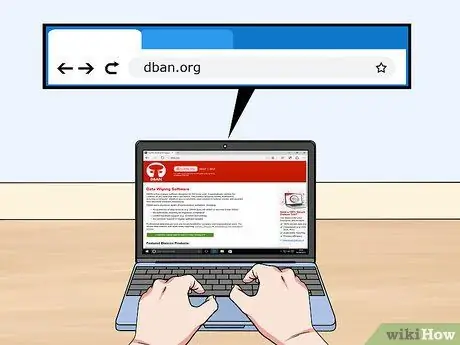
Step 1. Download DBAN
DBAN is a free program that can format hard drives and overwrite data securely so that it cannot be recovered. Follow these steps if you plan to give away, sell, or throw away your computer or drive to prevent identity theft.
- You can download DBAN from dban.org. The free version is suitable for the needs of most users.
- You cannot use DBAN to securely wipe solid state drives (SSDs). You have to use a paid program like Blancco.

Step 2. Make a copy of DBAN on a blank DVD or CD
DBAN is small in size, so you can write it on plain blank CD. If you are using Windows 7 or later, you can right-click on the downloaded ISO file and select "Write to disc" to write the program to a blank disc inserted in the burner.

Step 3. Configure the computer to boot from the DBAN disk
To start DBAN when Windows opens, you must configure the computer to start from the optical drive.
- Windows 7 (and earlier): restart your computer and press the BIOS, SETUP or BOOT key that is indicated at the bottom of the first screen that appears on the monitor. The most common keys are F2, F11, F12 and Del. In the boot menu, set the optical drive as the primary boot drive.
- Windows 8 (and later): Click the Power button in the Start menu. Hold Shift and click Restart to open the "Advanced Startup" menu when Windows opens. Click the "Troubleshoot" option, then "Advanced Options". Click "UEFI Firmware Settings", then open the BOOT menu. Set the optical drive as the primary boot drive.

Step 4. Start DBAN
Once the boot order is set, restart your computer to start DBAN. Press Enter on the main program screen to get started.

Step 5. Select the drive to be erased
Use the directional arrows to choose the hard drive to erase, then press the Spacebar to confirm. Be careful not to choose any disks you want to keep, as there is no way to go back once the operation has started. If you don't pay attention, it's really easy to delete the Windows installation by mistake.

Step 6. Press
F10 to start the deletion procedure.
This way you will use the default DBAN settings that provide for secure data deletion. It will be nearly impossible to retrieve the information after the operation, which usually takes several hours.






