This article shows you how to change your workbook (also called "directory" in more technical jargon) when using the Windows "Command Prompt". In order to fully utilize the potential offered by the "Command Prompt", a system administrator account must be used.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Open the Command Prompt

Step 1. Access the "Start" menu
To do this, you can click the Windows logo button located in the lower left corner of the desktop or you can simply press the ⊞ Win key on your keyboard.
If you're using Windows 8, place your mouse cursor in the upper right corner of your desktop, then select the magnifying glass icon that appears
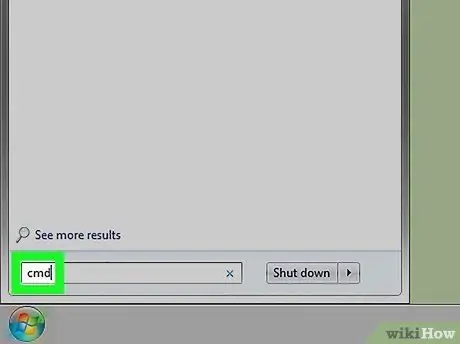
Step 2. Type the keyword command prompt
The relevant application icon should appear in the search results list.
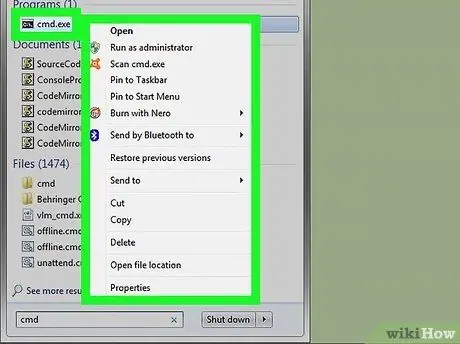
Step 3. Select the "Command Prompt" icon with the right mouse button
It features a small Windows window with a completely black background. This will bring up a context menu.
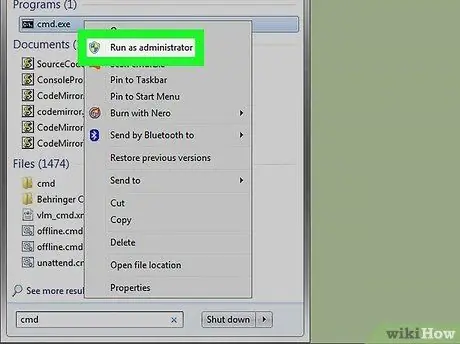
Step 4. Choose the Run as administrator option
It is located at the top of the context menu that appeared. This will open the command prompt with the privileges of the computer administrator account.
- Confirm your choice by pressing the button Yup when required.
- If the user account you are using is not the administrator of the computer or if the computer is restricted in use or is part of a network (for example, of a school, library or company), you will not be unable to open a "Command Prompt" window.
Part 2 of 2: Changing Directories
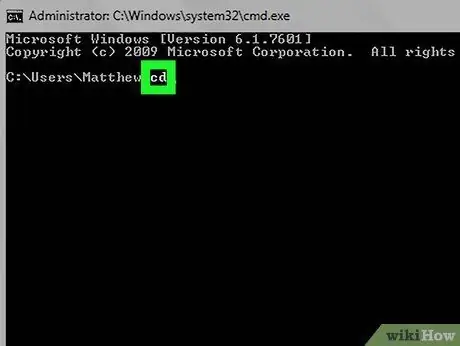
Step 1. Type the command cd
Make sure you also include the space after the "cd" command. This is the acronym for the English wording "change directory", which indicates the action of modifying the current working folder (or directory).
Do not press the Enter key
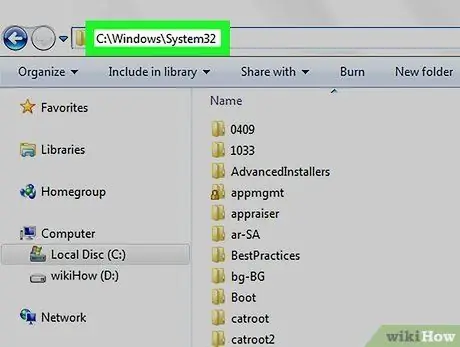
Step 2. Determine the full "path" of the new directory you wish to set up
The path of a directory or folder represents the path to follow in order to access it. For example, assuming we want to set the "System32" directory, which is located inside the "WINDOWS" folder, as the working folder, we will have to use the complete path "C: / WINDOWS / System32 \".
To find the full path of any folder, open a "File Explorer" or "Explorer" window, select the drive icon where it is stored and access the desired item. The path is represented by the string that is displayed in the address bar of the window
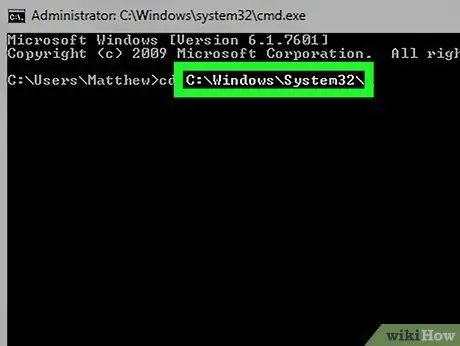
Step 3. Type the full path of the directory you want to set into the command prompt window
The string you copied must be inserted after the "cd" command. Make sure you also include a blank space, which separates the "cd" command from the path of the folder under consideration.
- For example, the complete command to access the Windows "System32" folder will be the following cd Windows / System32. The command to access drive "D:" of the machine in use will instead be cd D:.
- Since the default location where directories are stored is the hard drive (for example "C:" or "D:"), you do not need to also specify the drive letter in the command.
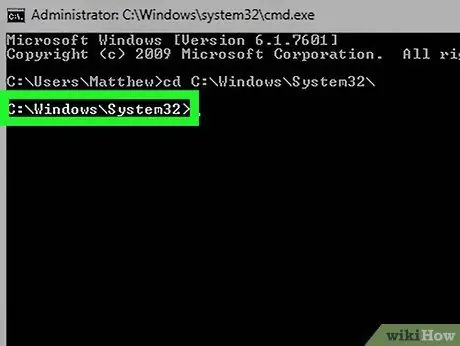
Step 4. Press the Enter key
This will set the current "Command Prompt" working directory to the one indicated in the command.
Advice
- It is very useful to move between directories, using the "Command Prompt", when you need to delete files stored in specific folders.
-
Here are some of the most commonly used commands to change the "Command Prompt" working directory:
- D: or F: - change the working path pointing to another memory unit identified by the letter indicated (for example a partition, an external hard disk or a USB key);
- .. - allows you to move to the directory directly above the one currently in use (for example to quickly go from the path "C: / Windows / System32" to the folder "C: / Windows");
- / d - change memory drives and directories at the same time. For example, if the "Command Prompt" currently points to the "D:" drive, using the "cd / d C: / Windows" command will go directly to the "Windows" directory inside the "C:" drive;
- - the root folder of the storage drive currently in use is set directly (for example "C:" or "D:").






