Using a Windows computer it may be useful to know how to check the status of the current active network connection. You can do this in several ways: in Windows 10 you can access the "Network and Sharing Center", while, in all other versions of the Microsoft operating system, you can use the "netstat" command. This is a feature that can be used via the command line, which allows you to detect any problems in the network connection or measure the traffic present. Fortunately, using this tool only takes a few simple steps.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Access the Network and Sharing Center menu in Windows 7/8 / 8.1 / 10
Step 1. Access the "Start" menu
Step 2. Select the "Settings" item
Step 3. Choose the "Network" item
Step 4. Access the "Network and Sharing Center"
This is a feature of Windows 10 that allows you to check the status of network connectivity, the type of active connection, data sharing with other computers and the status of the connection to the web.
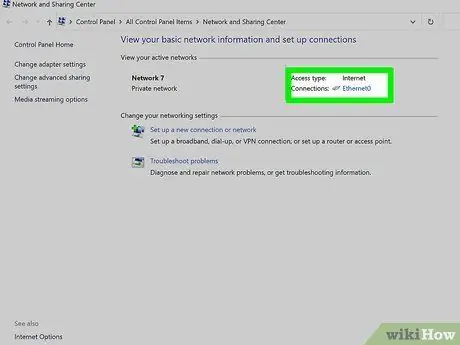
Step 5. Select the icon next to "Connections"
It should match the type of network connection that is currently active. For example, using a wired connection (ie made via a network cable), you will find the "Ethernet" link, instead, using a Wi-Fi connection you will see an icon characterized by five increasing bars, accompanied by the words "Wi-fi (wireless_net_name) ".
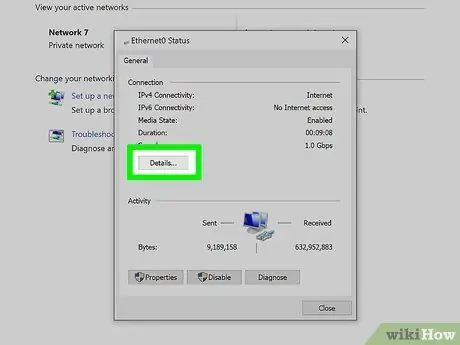
Step 6. Press the "Details" button
A new window will appear where you can find all the details related to your network connection.
Method 2 of 4: Use the Windows 7 Network Connections Folder
Step 1. Access the "Start" menu
Step 2. Search using the keyword "ncpa.cpl" (without quotes)
Step 3. Wait for the Network Connections folder icon to appear
This operating system feature shows all network connections configured on the system.
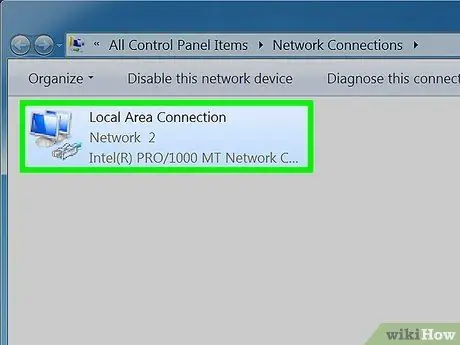
Step 4. Select the desired network connection using the right mouse button
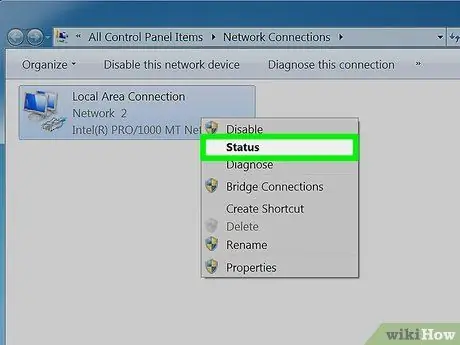
Step 5. Select the item "Status" from the context menu that appeared
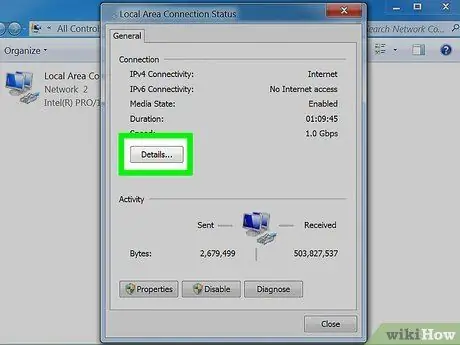
Step 6. Wait for the selected network connection status window to appear on the screen
This is the window from which you can consult the status and details of the network connection. For more information on this, you can press the "Details" button.
Method 3 of 4: Use the Netstat Command in Windows Vista or Later Versions
Step 1. Access the "Start" menu
Step 2. Perform a search using the keyword "cmd"
To do this, type the string "cmd" (without quotes) in the search field of the "Start" menu of Windows Vista (or a later version). This will give you access to the command prompt.
Step 3. Wait for the Command Prompt window to appear on the screen
This is the command line where you can run the "netstat" command. The "netstat" command allows you to use additional parameters; some of the most used are listed and explained below.
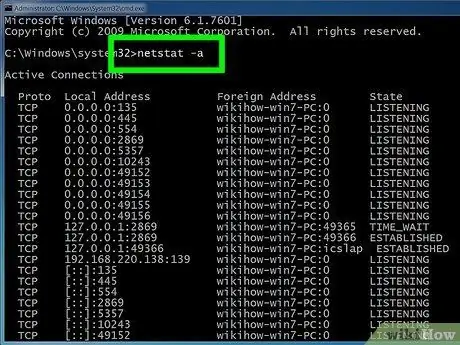
Step 4. Use the "netstat -a" command to view the currently active connections
This command displays a list of all currently active TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connections, including the port number. The local address and the external address of active connections are also reported, together with their current status ("waiting", "established", "listening", etc.).
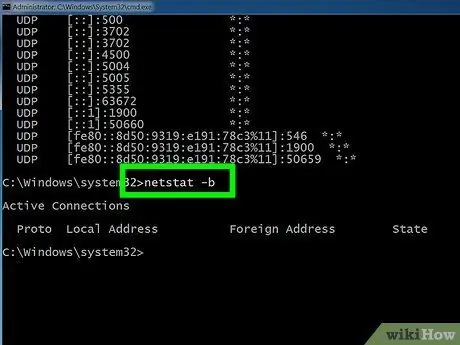
Step 5. Use the "netstat -b" command to view which programs are using the network connections
This parameter allows you to view the same information as the previous command ("netstat -a"), but with the addition of the name of the program used by the connection.
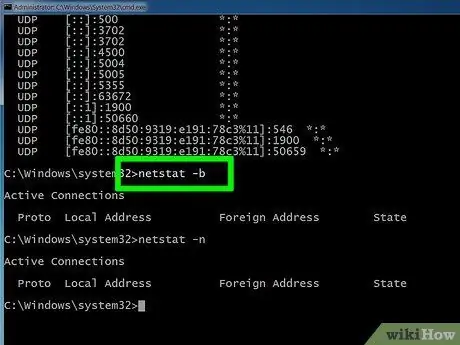
Step 6. Use the "netstat -n" command to view the IP addresses
This command displays the list of active network connections, but displays the IP address in the "Local Address" and "External Address" columns, instead of the computer or service name.
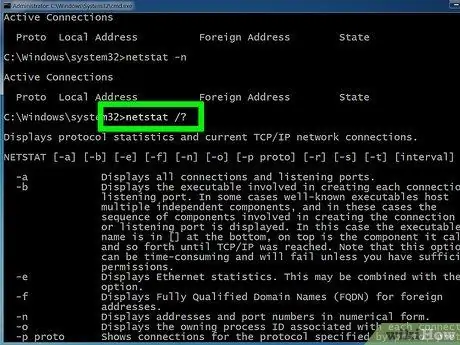
Step 7. To view the list of parameters available to the netstat command, you can use the command "netstat /?
A list of all parameters that can be used with the version of the netstat command present in the computer's operating system will be displayed.
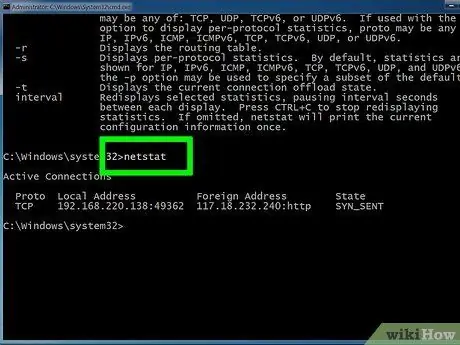
Step 8. Check for active network connections
After typing the desired "netstat" command, you will see a list of all active TCP / UDP connections, with their IP addresses involved.
Method 4 of 4: Use the Netstat Command in Windows XP

Step 1. Access the "Start" menu
Step 2. Select the "Run" item
The "Run" window will appear.
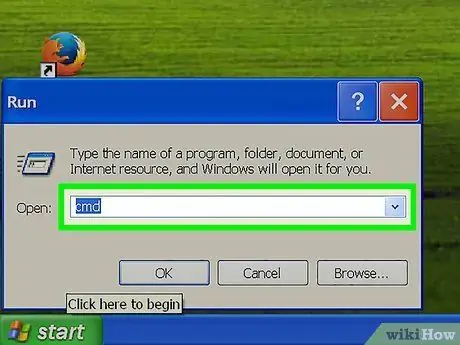
Step 3. In the "Open" field type the keyword "cmd" (without quotes)
Step 4. Wait for the Command Prompt window to appear on the screen
This is the command line where you can run the "netstat" command. The "netstat" command allows you to use additional parameters; some of the most used are listed and explained below.
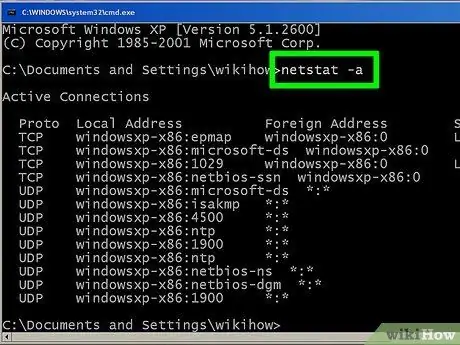
Step 5. Use the "netstat -a" command to view the currently active connections
This command displays a list of all currently active TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connections, including the port number. The local address and the external address of the active connections are also reported, together with their current status ("waiting", "established", "listening", etc.).
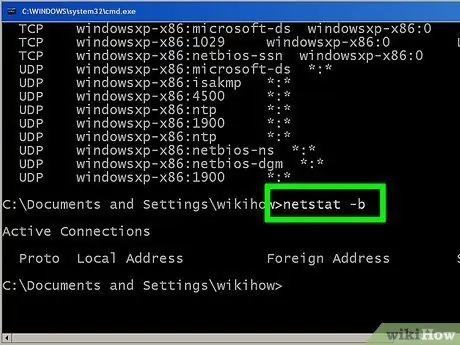
Step 6. Use the "netstat -b" command to view which programs are using the network connections
This parameter displays the same information as the previous command ("netstat -a"), but with the addition of the program name used by the connection.
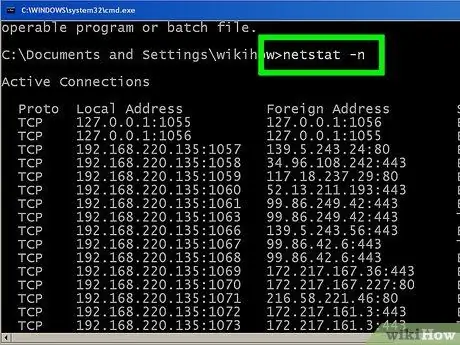
Step 7. Use the "netstat -n" command to view the IP addresses
This command displays the list of active network connections, but displays the IP address in the "Local Address" and "External Address" columns, instead of the computer or service name.
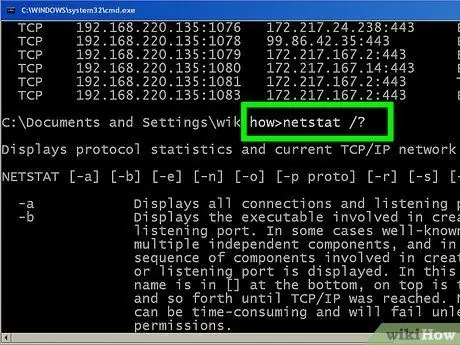
Step 8. To view the list of parameters available to the netstat command, you can use the command "netstat /?
A list of all parameters that can be used with the version of the netstat command present in the computer's operating system will be displayed.
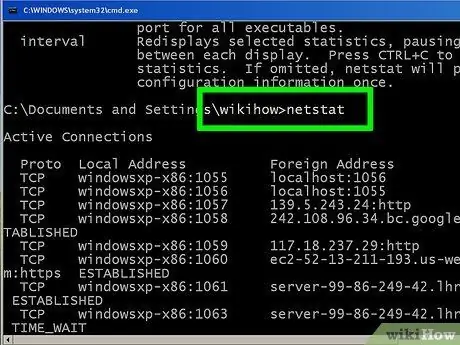
Step 9. Check for active network connections
After typing the desired "netstat" command, a list of all active TCP / UDP connections will be displayed, with their IP addresses involved.
Advice
- On Linux systems it may indicate that the "netstat" command is outdated or deprecated. In this case you can replace it with the commands "ip -s", "ss" or "ip route".
- A valid alternative is to use the "TCPView" tool, which can be downloaded from this link
- Experiment. There are many UNIX commands available for diagnostics (such as the "netstat" command seen above). For a complete list of these commands, you can simply search the web using the search engine of your choice.






