The MAC address, or Media Access Control, is a unique tool used to identify the computer on the network. Changing the address can help you diagnose any network errors, or you can just change it to use a name you like. Read this guide to find out how.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Using Device Manager
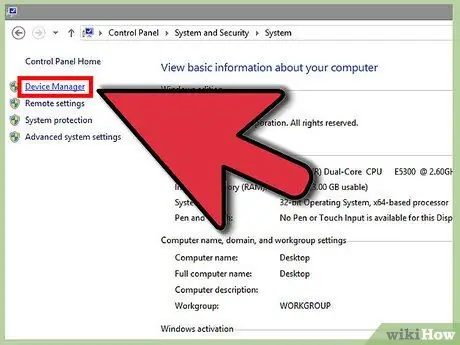
Step 1. Open Device Manager
You can access it from the Control Panel. If you use the categorical arrangement, it will be in the System and Security section.
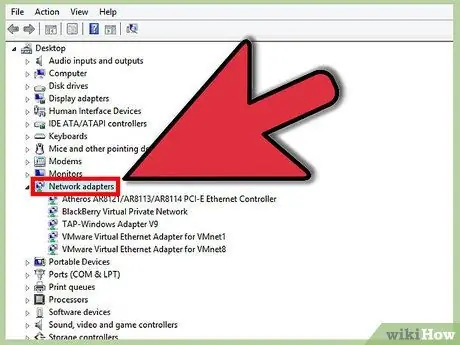
Step 2. Expand the Network Adapters section
In the Device Manager you will see a list of all the hardware installed on your computer. These components are divided into categories. Expand the Network Adapters section to get a list of all network adapters present on your computer.
If you are unsure which network adapter you are using, see Step 1 for device information
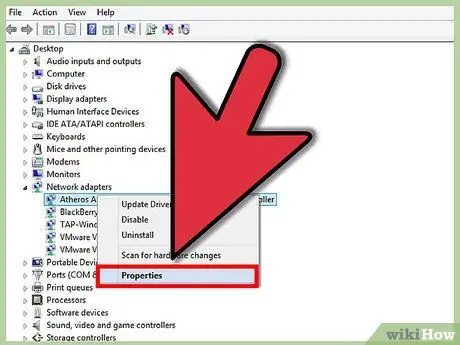
Step 3. Right click on the adapter
Select Properties from the menu to open the network adapter properties window.
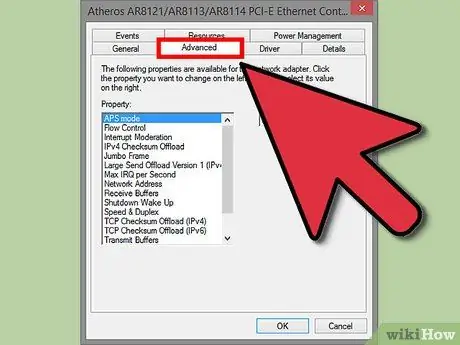
Step 4. Click on the "Advanced" tab
Look for the "Network Address" or "Locally Administered Addresses" options. Selecting it, you will see a "Value" field on the right. Click on the radio button to activate it.
Changing the address in this way is not possible for all adapters. If you can't find any of these, you'll need to use one of the other methods described in this article
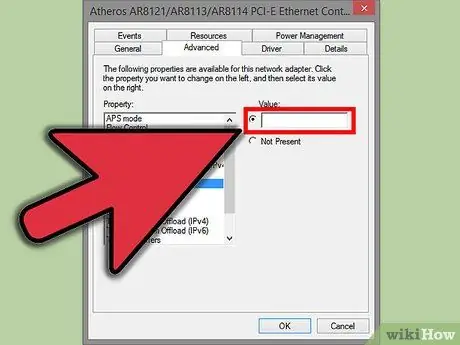
Step 5. Enter the new MAC address
This is a 12-digit value, and must be entered without hyphens or colons. For example, if you wanted the MAC address to be "2A: 1B: 4C: 3D: 6E: 5F", you would type "2A1B4C3D6E5F".
Step 6. Restart your computer for the changes to take effect
You can also enable or disable the adapter directly from Windows, without having to reboot. Simply using the Wi-Fi On / Off button found on ThinkPads and Vaio's will not restart the card properly.

Step 7. Make sure the changes have actually been applied
Once your computer has restarted, open the command prompt and type
ipconfig / all
write down the physical address of your adapter. That should be the new MAC address.
Method 2 of 3: Using Registry Editor
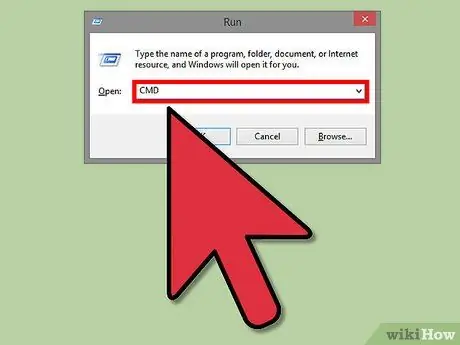
Step 1. Find your network adapter ID
To identify it in the registry, you will need to get some information via the command line. Open the command prompt by typing "cmd" in the "Run" box (Windows key + R).
-
Type
ipconfig / all
- and press "Enter". Note the Description and Physical Address for the active device. Ignore those that are not active (Media Disconnected).
-
Type
net config rdr
- and press Enter. Note the GUID, which is displayed in braces "{}" next to the Physical Address.
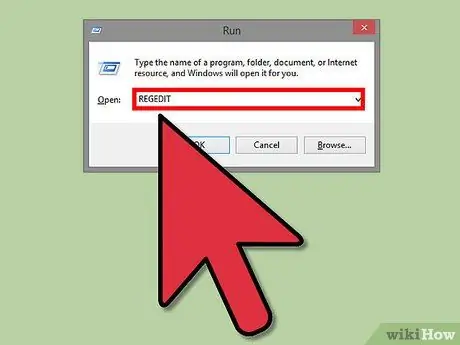
Step 2. Open the Registry
You can start it by typing “regedit” in the run box (Windows key + R). The registry will allow you to change the settings of your network card.
Applying incorrect changes could cause the system to malfunction
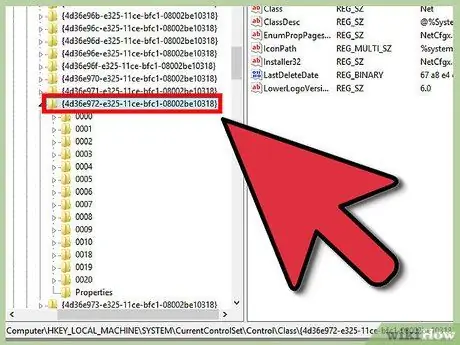
Step 3. Go to the right registry key
Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SYSTEM / CurrentControlSet / Control / Class {4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}. Expand it by clicking on the arrow.
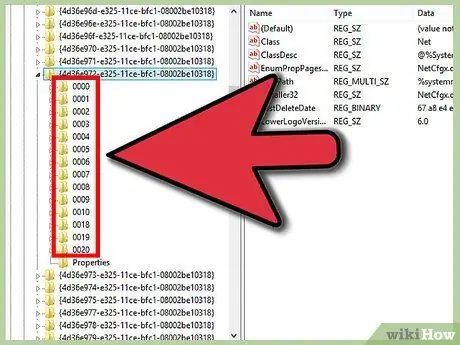
Step 4. Find your adapter
You will see several folders called "0000", "0001" and so on. Open each of these folders and compare the DriverDesc field to the values you have that you wrote down in the first step. To be sure, compare the NetCfgInstanceID field with the GUID obtained in the first step.
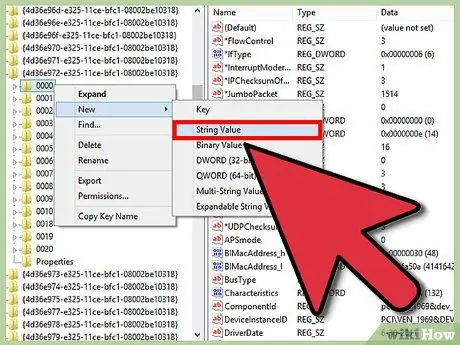
Step 5. Right-click on the folder corresponding to your device
For example, if the right folder is 0001, right click on that folder and select New -> String Value. As the value name enter "NetworkAddress".
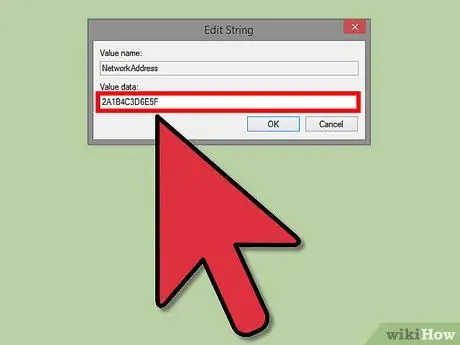
Step 6. Double click with the right mouse button on the NetworkAddress data
Enter the new MAC address in the “Value data” field. A MAC address is a 12-digit value, and must be entered without hyphens or colons. For example, if you want the MAC address to be "2A: 1B: 4C: 3D: 6E: 5F", you will need to enter "2A1B4C3D6E5F".
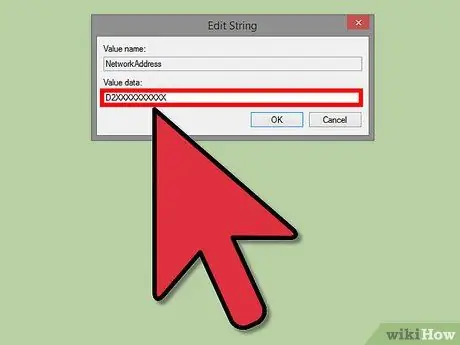
Step 7. Make sure the MAC address is formatted correctly
Some adapters (especially Wi-Fi cards) do not accept MAC addresses if the second half of the first 8-number series is not 2, 6, A, E. This has been a requirement since the days of Windows XP and the address should have the following format:
- D2XXXXXXXXXX
- D6XXXXXXXXXX
- DAXXXXXXXXXX
- DEXXXXXXXXXX
Step 8. Restart your computer for the changes to take effect
You can also activate or deactivate the adapter directly from Windows, without having to reboot. Simply using the Wi-Fi On / Off button found on ThinkPads and Vaio's will not restart the card properly.

Step 9. Make sure the changes have actually been applied
Once your computer has restarted, open the command prompt and type
ipconfig / all
write down the physical address of your adapter. That should be the new MAC address.
Method 3 of 3: Using SMAC
Step 1. Download the SMAC program
It is a paid tool (with free demo) that allows you to quickly change the MAC address, it is compatible with Windows XP, Vista and 7. Make sure you download the file only from a trusted site.
Once the download is complete, install the program. The default installation settings should be fine
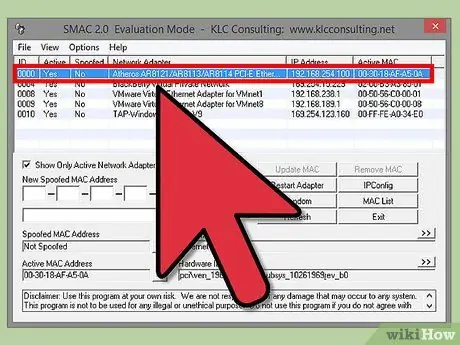
Step 2. Select your adapter
Once SMAC is open, you will see a list of installed network devices. Select the adapter whose address you want to change.
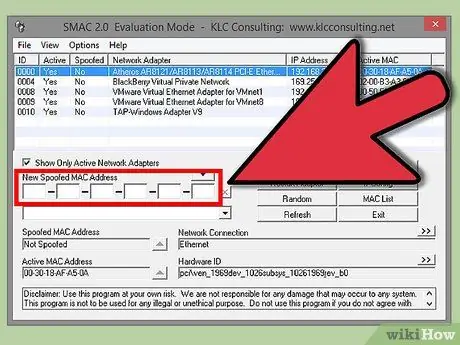
Step 3. Enter your new address
In the fields under “New Spoofed MAC Address”.
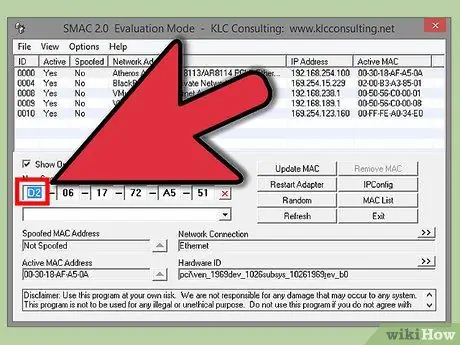
Step 4. Make sure the MAC address is formatted correctly
Some adapters (especially Wi-Fi cards) do not accept MAC addresses if the second half of the first 8-number series is not 2, 6, A, E. This has been a requirement since the days of Windows XP and the address should have the following format:
- D2XXXXXXXXXX
- D6XXXXXXXXXX
- DAXXXXXXXXXX
- DEXXXXXXXXXX
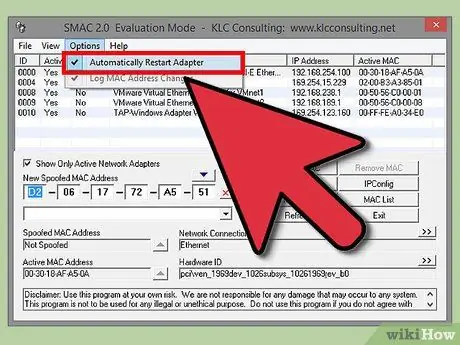
Step 5. Click Options
Select “Automatically Restart Adapter” from the menu by placing the check mark in the relevant box.
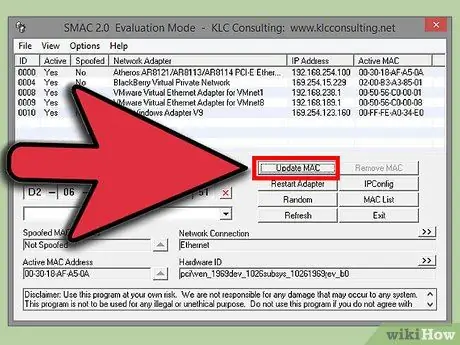
Step 6. Click on the “Update MAC” button
The network connection will be temporarily disabled and the MAC address will be updated. Check that the address has actually been updated on the program's list of network devices.






