If you've accidentally just overwritten a file or folder with a new version, don't despair and don't act on impulse, you may still be able to recover the previous content. The programs you can use to scan your hard drive and attempt to restore deleted files are many and available for all operating systems. If you have configured an automatic backup to run through the operating system features, it is very likely that your file still exists in one of the backups.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: PhotoRec (Windows, Mac, and Linux)
Step 1. Stop working on the storage drive where the overwritten file resides
As soon as you realize that you have accidentally deleted or overwritten a file, do not save any more content on the affected memory drive. Likewise, don't run any programs anymore. Stop using your computer completely. As new data is written to disk, the chances of the old file being physically overwritten and erased forever increase. If you immediately stop using the disk or memory unit in question, you will increase the chances of being able to restore the old file.
Step 2. Download the free PhotoRec program, but do so using a computer (recommended) or a different hard drive than the one where the file to be recovered resides
It is a very powerful program for restoring deleted data. It does not have a graphical interface, but it performs most of the same functions implemented by professional and very expensive programs. You can download PhotoRec for free from the following URL www.cgsecurity.org, as part of the TestDisk suite of programs.
- PhotoRec is available for Windows, OS X and Linux systems.
- Make sure you download the program to another computer to make sure you don't overwrite the information you want to recover. You can also download PhotoRec to a separate hard drive, but using a second computer is considerably safer.
Step 3. Connect a blank USB memory drive to your computer
In the ideal situation, you need to use a USB storage drive that is large enough to hold both the PhotoRec program and any files or folders you wish to restore. You must take this precautionary measure to avoid that, using the original hard drive, the restored data overwrites the information to be recovered, thus defeating the entire process.
PhotoRec is only 5MB in size, so any USB storage drive should be suitable for your purpose
Step 4. Extract the contents of the compressed file you downloaded
TestDisk is downloaded as a ZIP archive (on Windows systems) or BZ2 (on Mac). At the end of the download extract the contents of the file.
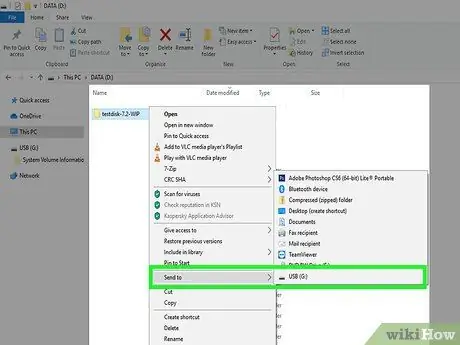
Step 5. Copy the "TestDisk" folder inside the USB drive
This way you can run PhotoRec directly from the USB drive.
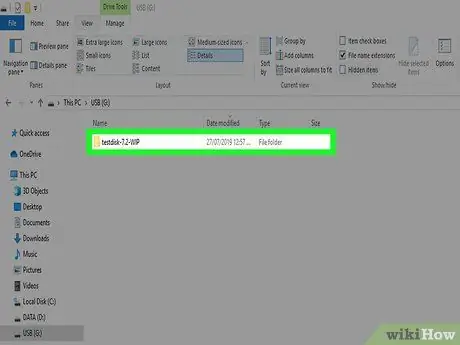
Step 6. Insert the USB drive into the computer where the information to be recovered resides
Navigate to the "TestDisk" folder on the USB drive.
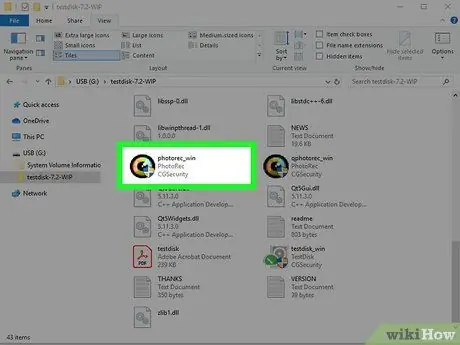
Step 7. Start the "photorec" program
A Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac, Linux) window will open.
To navigate between the menu items, you can use the arrow keys on the keyboard, while to confirm or make your choices you can use the Enter key
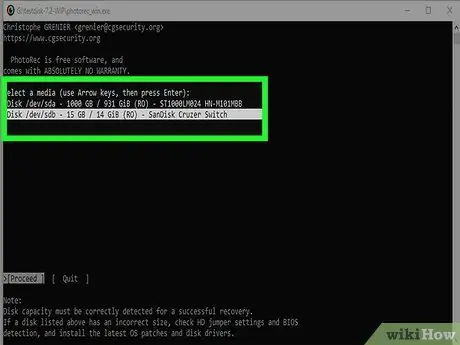
Step 8. Select the hard drive to retrieve information from
The disks will be simply numbered, to identify the one to be processed you will therefore have to rely on the size.
In the case of a partitioned hard drive, the list of logical drives that reside on it (for example C:, D:, E: etc.) will only be displayed after you have selected it
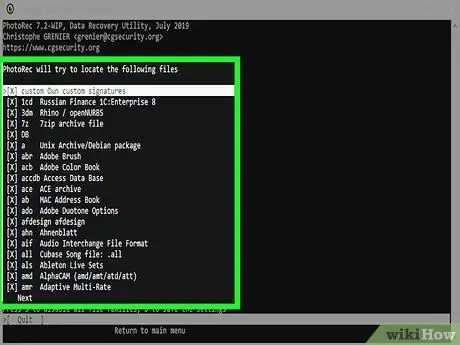
Step 9. Choose the type of scan to perform
By default PhotoRec restores any supported file. If you want to speed up the process, specify directly which type of file you want to recover.
- You can change the type of file to search for using the File Opt menu.
- After logging into File Opt, you can deselect all the options there by pressing the "S" key. At this point, scroll through the list of items to choose only the one related to the type of file you are looking for.
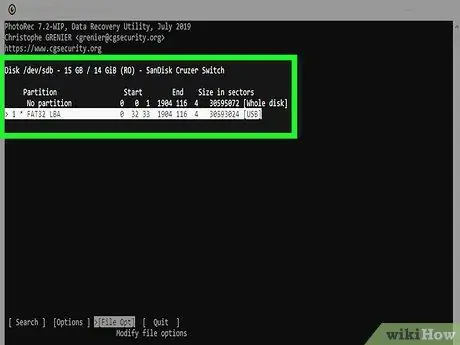
Step 10. Choose the partition
You will need to do this based solely on size, although some partitions may be labeled as assigned by the operating system.
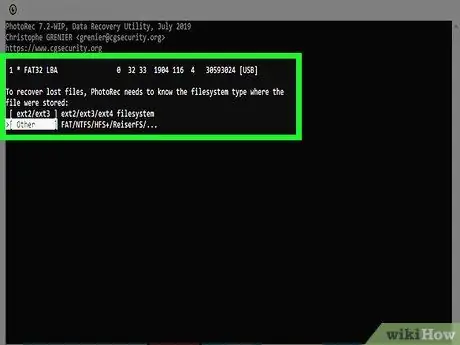
Step 11. Choose the filesystem type
If you are using a Linux system, choose the ext2 / ext3 option. If you are using a Windows or OS X system, choose the Other item.
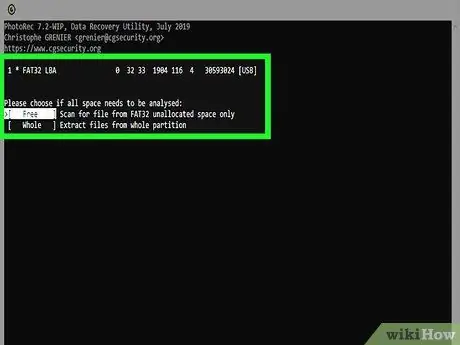
Step 12. Choose the type of search
The choice depends on why the file was deleted:
- Free: Choose this option if you have deleted or overwritten the information in question.
- Whole: Choose this option instead if your data has been lost due to a hard drive malfunction.
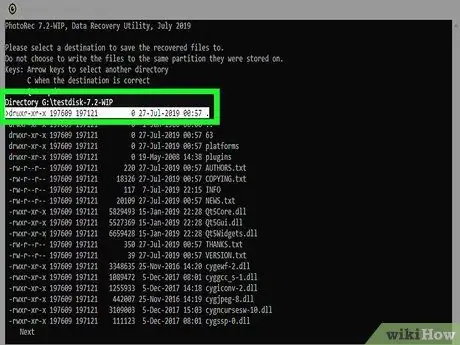
Step 13. Choose the folder to save the recovered data
Make sure the destination folder does not reside on the same disk being restored.
- To access the complete list of drives installed on your computer, use the.. option at the top of the directory listing. This will allow you to select a destination folder on another partition or USB drive.
- After choosing the directory to save the recovered data, press the "C" key.
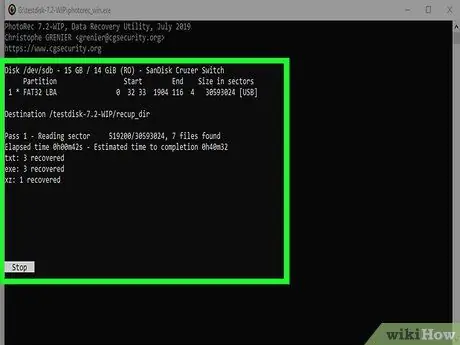
Step 14. Wait for PhotoRec to complete the recovery process
The program will try to recover all the deleted files present on the chosen partition. The time required to complete the procedure will be shown on the screen, together with the number of files recovered.
This recovery process takes a long time, especially in the case of very large partitions and multiple file types to locate
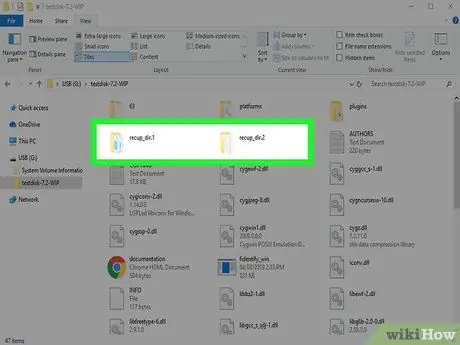
Step 15. Check the recovered data
After the scan is complete, go to the destination directory to check the data that has been recovered. The original filename will most likely be lost, so you'll need to physically access each restored item to see if that's what you're looking for.
Method 2 of 3: Recuva (Windows)
Step 1. Stop working on the storage drive where the overwritten file resides
As soon as you realize that you have accidentally deleted or overwritten a file, do not save any more content on the affected memory drive. Likewise, don't run any programs anymore. Stop using your computer completely. As new data is written to disk, the chances of the old file being physically overwritten and erased forever increase. If you immediately stop using the disk or memory unit in question, you will increase the chances of being able to restore the old file.
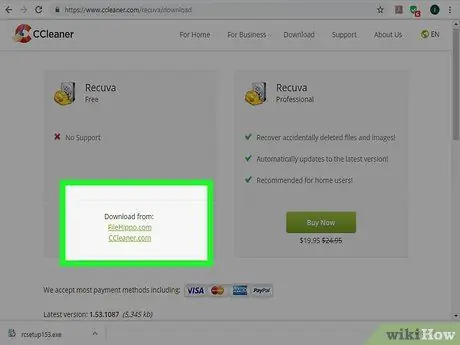
Step 2. Download the Recuva installation file to a second hard drive
You can also use a different computer than the one where the data to be recovered resides. Recuva is available free for download at this URL www.piriform.com.
Step 3. Connect a blank USB memory drive to your computer
This is the drive on which you will need to install Recuva. This way you can run the program safely, without the possibility of overwriting the data you want to recover.
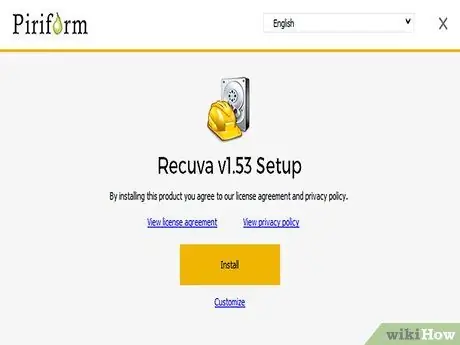
Step 4. Launch the Recuva installation wizard
To proceed, press the Next button.
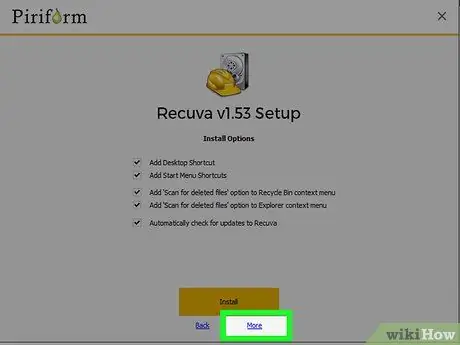
Step 5. Press the button
Advanced to be able to change the folder where the program will be installed.
Select an option to proceed.
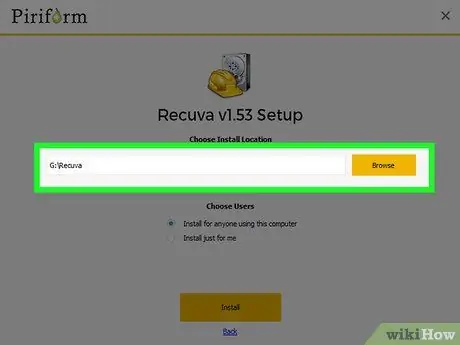
Step 6. Choose the USB storage device as the installation drive
You will have the additional need to create a "Recuva" folder inside it.
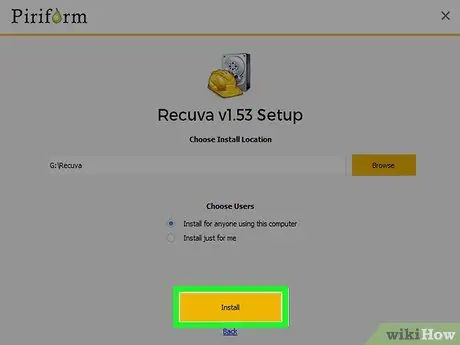
Step 7. Uncheck all additional installation options, then press the button
Install.
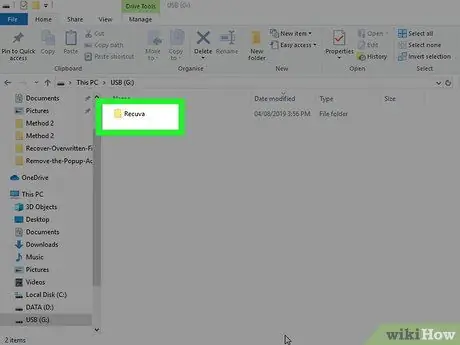
Step 8. Navigate to the Recuva folder on the USB drive
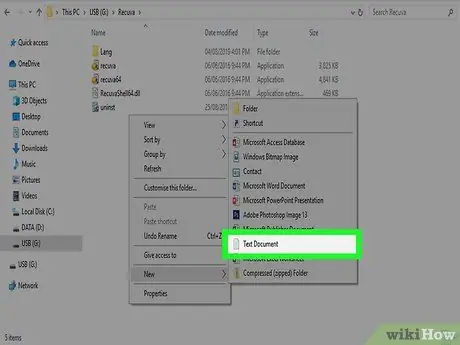
Step 9. Select an empty spot inside the folder with the right mouse button, then choose the "New" option from the context menu that appeared and then select the "Text document" item
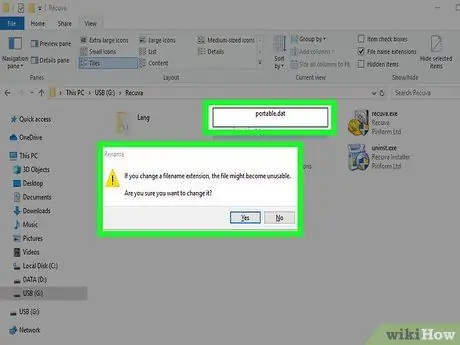
Step 10. Change the file name to
portable.dat.
Confirm your willingness to change the extension of the file in question.
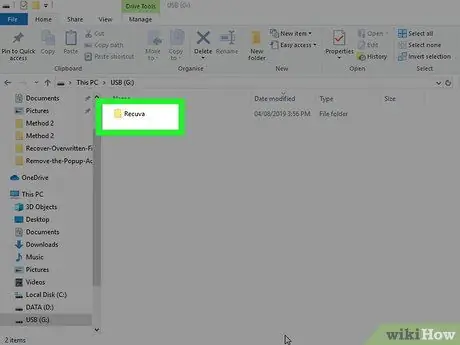
Step 11. Now insert the USB drive into the computer where the data to be restored resides
Access the Recuva folder on the USB drive.
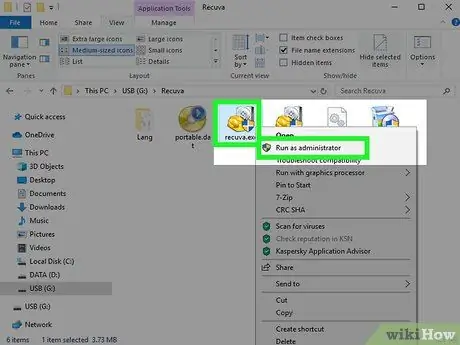
Step 12. Run the "recuva.exe" file
The data recovery wizard will appear.
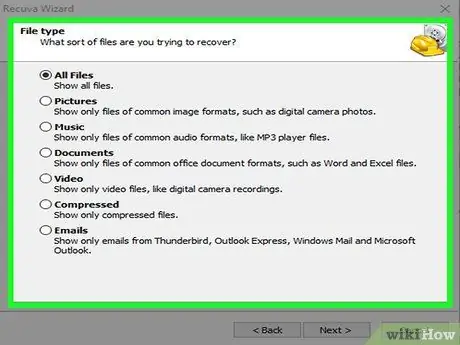
Step 13. Select the type of file to search for
You can search for all file types supported by the program, or focus on a specific set.
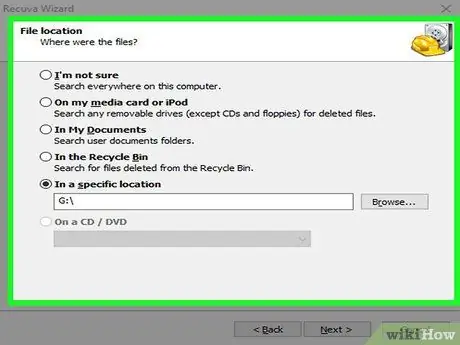
Step 14. Select the folder to scan
You can choose to scan your computer's entire hard drive, or focus your searches on a single specific folder.
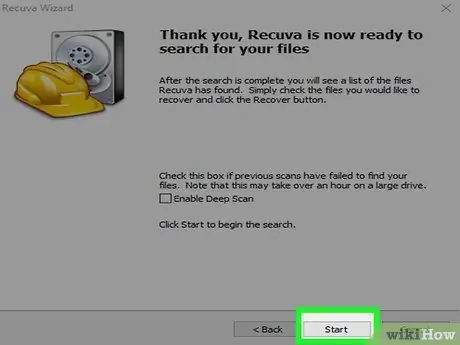
Step 15. Start the scan
Recuva will begin scanning the contents of the indicated location for deleted files that match the specified specifications.
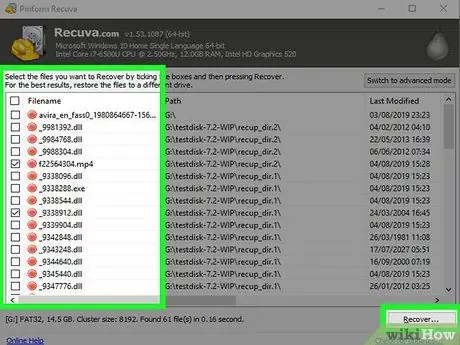
Step 16. Check the restored items to find which ones to keep
When the scan is complete, a complete list of all files found will be displayed. Select the check button for the files you want to restore, then press Recover….
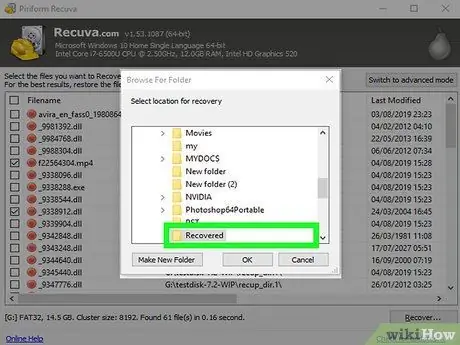
Step 17. Choose the folder to save the recovered data
Make sure the destination folder does not reside on the same disk being restored, otherwise an error will be generated when attempting to recover.
Method 3 of 3: Restore a Previous Version of a File
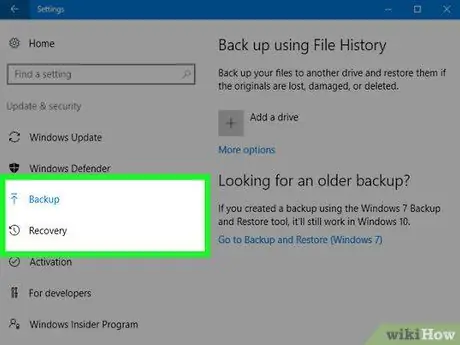
Step 1. To recover a previous version of a file, use the Windows File History feature
Both Windows 7 and Windows 8 implement this feature. In order to be exploited, this functionality of the Microsoft operating system must first be activated.
Check out this guide for more information on how to use File History in Windows 8
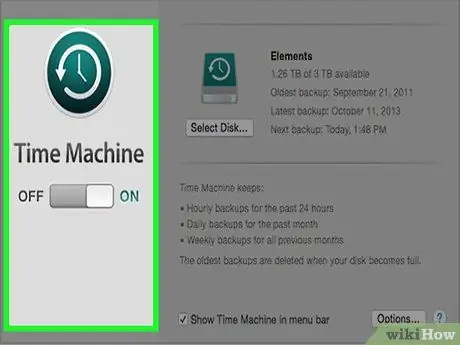
Step 2. To recover a previous version of a file on OS X systems you can use the Time Machine function
In order to use this program you will first have to configure it, so that data backups are saved on an external drive, after which you will be able to access all versions of a file at any time.






