Is it time to upgrade your operating system? Are you planning to switch from Windows to Linux? You may want to try dual booting. Follow this guide to install a new operating system from any manufacturer on your computer.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Determine Which Operating System to Install
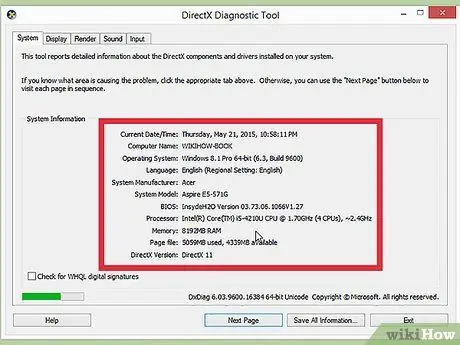
Step 1. Check the system requirements
If you have decided to install a new operating system, you will first need to decide which one to use. Operating systems have varying system requirements, so if you have an older computer, you need to make sure you can use a newer operating system.
- Most Windows installations require at least 1 GB of RAM and at least 15-20 GB of hard disk space. Make sure your computer meets these requirements. If it doesn't, you can try installing an older operating system, such as Windows XP.
- Linux operating systems typically do not require the space and power required of Windows operating systems. The requirements depend differently on the distribution you choose (Ubuntu, Fedora, Mint, etc.).
Step 2. Decide whether to buy or download
Windows licenses must be purchased. Each license is combined with a code valid for a single installation. Most Linux distributions are free to download and install, although some corporate versions are not free and require purchase (Red Hat, SUSE, etc.).
Step 3. Research the compatibility of your software
Make sure the operating system you want to install supports the programs you want to use. If you use Microsoft Office for work, you will not be able to install it on a Linux machine. There are replacement programs available, but functionality may be limited.
Many games that run on Windows will not run on Linux. The number of supported titles is growing, but you have to be careful, if you are an avid gamer, that your library is transferred without problems
Step 4. Get your new operating system
If you bought a pair of Windows in the store, you should have received an installation disc along with the product code. If you don't have the disc, never have a valid code, you can always download a copy of the disc online. If you are installing Linux, it can install an ISO of the distribution from the developer's site.
An ISO file is a disk image that must be sterilized on disk or copied to a bootable USB drive
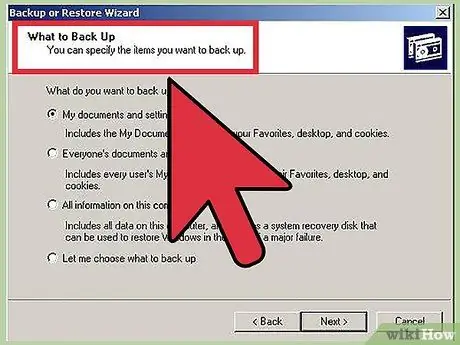
Step 5. Backup your data
When you are installing a new operating system, you will probably want to wipe the hard drive data. This means that you will lose all files on your computer, unless you back them up. Always make sure that any important files are copied to a suitable location for backup before starting the installation process. Use an external hard drive or burn data to DVD.
- If you are installing an operating system alongside the existing one, you probably won't need to delete any data. However, it is wise to back up your important files.
- You cannot copy programs with the backup process; they will need to be reinstalled once you have finished installing your new operating system.
Method 2 of 3: Install a New Operating System

Step 1. Determine the order of your installation
If you are installing a Linux distribution that you want to run alongside Windows, you will need to install Windows first and then Linux. This is because Windows has a load mode that needs to be placed before Linux is installed, otherwise Windows will not load.
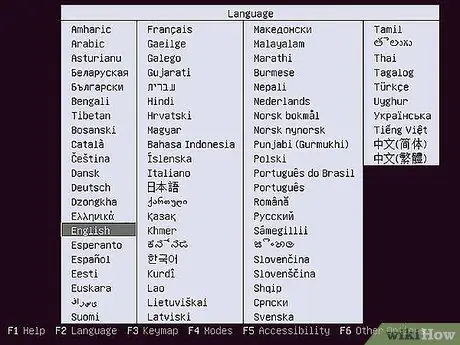
Step 2. Boot from your installation disc
Insert the installation disc into your drive; restart your computer. Normally the computer boots from the hard drive first, so I would need to change some settings in your BIOS to boot to the disc in the drive. You can enter the BIOS by pressing the designated Setup key during the boot process. The key will be marked on the same screen as the manufacturer's logo.
- Common keys used for setup include F2, F10, F12 and Del / Delete.
- Once you are in the setup menu, move to the Boot section. Set your DVD / CD player as the first boot device. If you are installing from a USB drive, make sure it is inserted and then select it as the first boot device.
- Once you have selected the correct drive, save your changes and exit Setup. Your computer will restart.
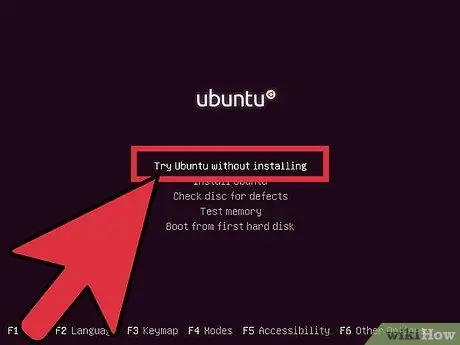
Step 3. Test your Linux distribution before installation
Most Linux distributions can be loaded directly from the installation disk. This will allow you to try the new operating system before starting the installation process. Once I'm ready for installation, click the relevant program on the desktop.
This is only possible with Linux distributions. Windows does not allow you to test the operating system before installing it
Step 4. Wait for the program to finish loading
It doesn't matter which operating system you have chosen: the setup program will need to copy files to your computer before it can continue. This can take a few minutes; it depends on the speed of your computer hardware.
You will likely have to choose some basic options, such as language and keyboard layout
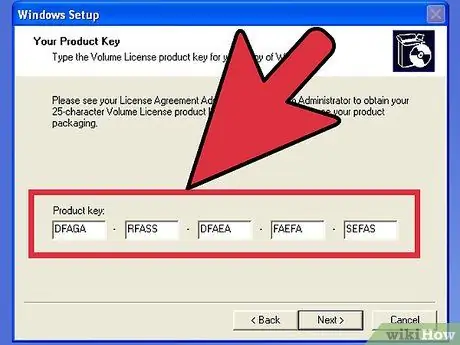
Step 5. Enter the installation code
If you are installing Windows 8, you will need to type the code before you can start the installation. Older versions of Windows, on the other hand, will ask you for this code after completing the installation. Linux users don't need code unless it's a paid version like Red Hat.
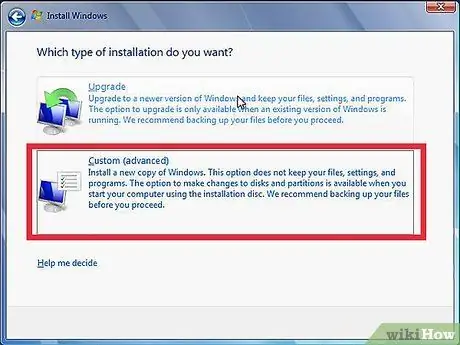
Step 6. Choose your installation type
Windows which will offer Upgrading or Custom Installation options. Even if you are upgrading an older version of Windows, it is highly recommended that you choose custom installation, starting from scratch. This procedure minimizes the problems that may arise later from combining old and new settings.
If you are installing Linux, you will have the opportunity to install it alongside your existing operating system (Windows) or to wipe the disk and install Linux on your own. Choose the option that best meets your needs. If you choose to install it with Windows, you can choose how much hard disk space to dedicate to Linux
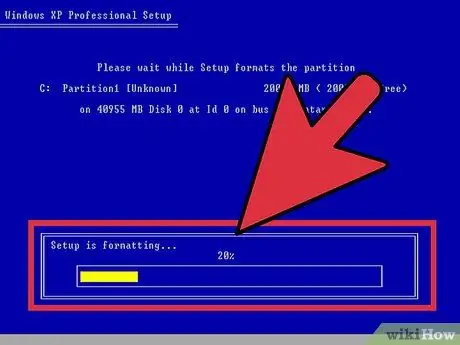
Step 7. Format your partitions
If you are installing Windows, you will have to choose which hard disk partition to install it on. Deleting partitions will also delete the data on the partition and the space will be considered unallocated. Select the unallocated space and create a new partition.
If you are installing Linux, the partition must be formatted in the Ext4 format
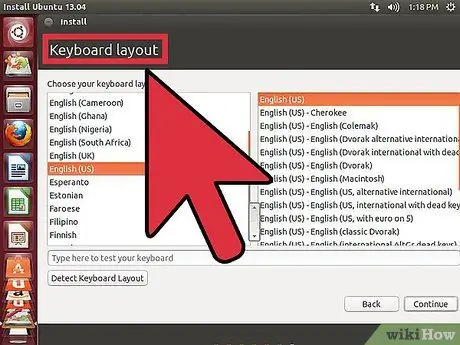
Step 8. Set the options for Linux
Before installation begins, the program will ask you for the time zone and you will need to create a username and password. You will use them to log into your Linux distribution and to authorize changes to the operating system.
Windows users must enter personal information after the installation is complete
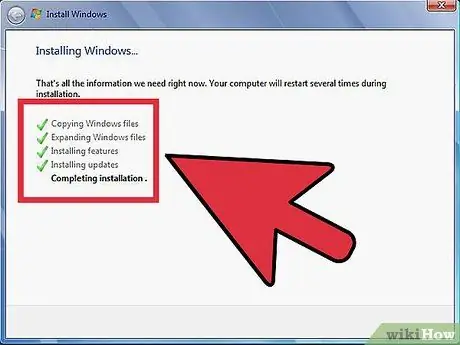
Step 9. Wait for the installation to complete
Depending on the speed of your computer, it can take up to an hour to complete the process. Most installations end there. Your computer may need to restart several times during the installation process.
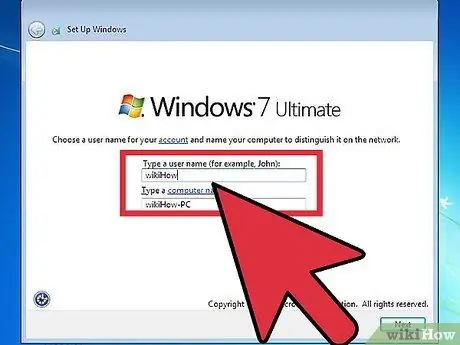
Step 10. Create your Windows login
Once the Windows installation is complete, you will need to create a username. I could also choose a password, although it is not necessary. After creating your login information, you will be asked for the code.
In Windows 8, you will be asked to customize the colors. Later, you can choose to sign in with a Microsoft account or use a more traditional Windows username
Step 11. Install drivers and programs
Once the installation is complete, you will find yourself on your new desktop. From here you can install your programs and check that the installed drivers are up to date. Also install an antivirus if you plan to connect to the internet.
Method 3 of 3: Install Specific Operating Systems
Step 1. Windows 7
Windows 7 is Microsoft's most popular operating system. Follow the specific guide for detailed instructions.
Step 2. Windows 8
Windows 8 is Microsoft's latest operating system. There is a detailed guide on its installation process.
Step 3. Ubuntu
Ubuntu is one of the most common Linux distributions. Click for instructions on how to install the Ubuntu distribution.

Step 4. Mac OS X
If you want to upgrade your copy of the Mac OS X operating system, try this guide.
Step 5. Linux Mint
Linux Mint is the newest Linux distribution that is becoming more and more popular. Follow this guide to learn how to install it.
Step 6. Fedora
Fedora is a very stable old Linux distribution. This guide will show you how to install it.

Step 7. Mac OS X on an Intel or AMD (Hackintosh) computer
If you are very patient and want Mac OS X on your PC, check out these guides.
Advice
- You can speed up the installation process by moving your data during the backup (cut and paste), rather than making a copy. After the backup is complete, defragment your hard drive. This way the installation of the new operating system will perform the formatting much faster. You will notice the difference especially when using an IDE hard drive larger than 40GB or a Serial ATA (SATA) drive larger than 500GB.
- Some operating systems, including Linux, have an installation wizard for newbies and a customizable one for advanced users. If you don't know what it means to create a hard drive partition, choose an installation wizard - it will automatically create the necessary hard drive partitions.
Warnings
- Make a backup copy of all your data before performing an installation, unless you are updating your operating system to a newer version. In any case, it is always convenient to have a backup copy of all your data.
- If you're moving from the Windows world to a Linux operating system and don't know what you'll need in the new operating system, a full installation isn't the right choice. If your computer is recent enough to support an installation on a USB device, install Linux on a stick. Alternatively, you can boot Linux directly from CD.
- Windows cannot read hard drive partitions used by Linux.
- If you are installing Windows and plan to access the Internet, install good antivirus software before doing so.






