Some people find it useful to enable Task Manager on their computers, as it provides information on computer usage. This system utility and Windows management program provides information on various aspects of computer performance, including physical memory, handles, allocated memory, Central Processing Unit (CPU) usage, kernel memory, and threads. It also provides information on applications in use, network statistics and activities, system services, processes and users with access. There are those who also find Task Manager useful for prioritizing processes, forcing process shutdowns, setting processor affinity, or for shutting down, restarting, hibernating or disconnecting Windows.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Enable Task Manager in Windows NT (Windows 2000)
Step 1. Click the "Start" option on the desktop page
This is the same "start" that you use to shut down your computer.
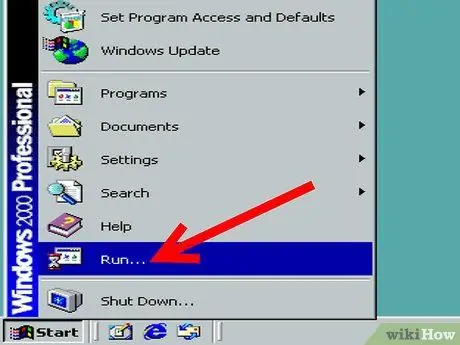
Step 2. Select the "Run" option and look for the box where you can type a command
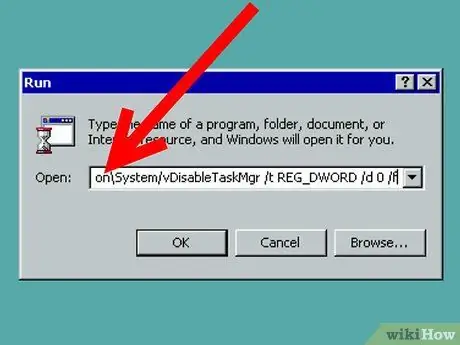
Step 3. Cut and paste the following command into the box where you add information:
REG add HKCU / Software / Microsoft / Windows / CurrentVersion / Policies / System / v DisableTaskMgr / t REG_DWORD / d 0 / f.
Method 2 of 4: Open and enable Task Manager in Windows XP
Step 1. Choose the "Start" option on the main desktop page and click it to open the options
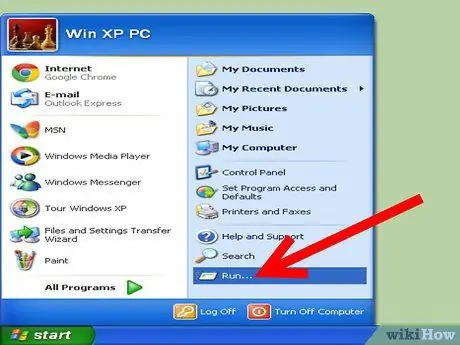
Step 2. Select the "Run" option
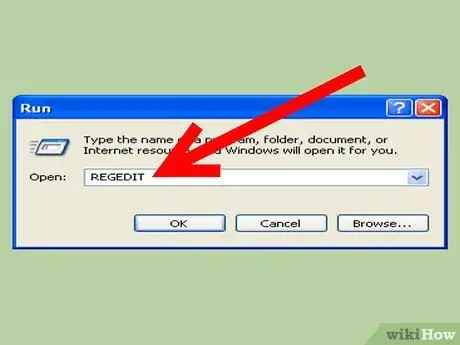
Step 3. Type "Regedit.exe" in the rectangle where information is entered
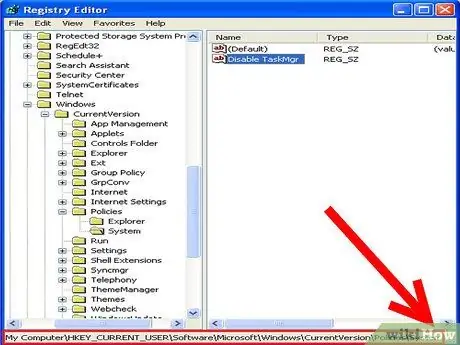
Step 4. Find your way on the branch:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER / Software / Microsoft / Windows / CurrentVersion / Policies / System.
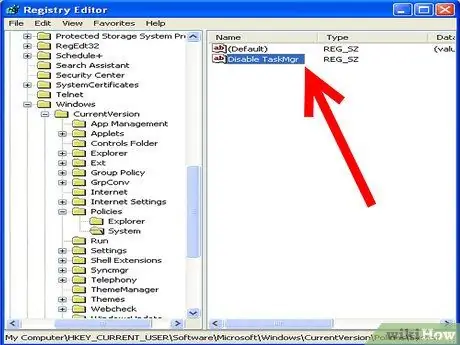
Step 5. In the right pane, find the "DisableTaskMgr" value and click it
While it may seem odd to use a disable tool when you want to enable something, this is the correct way to change the settings.
Step 6. Close the Regedit.exe section
Method 3 of 4: Set up Task Manager in Windows XP Professional

Step 1. Select the "Start" option on the main desktop page
Step 2. Choose the "Run" option and then look for the rectangle where you can enter the information
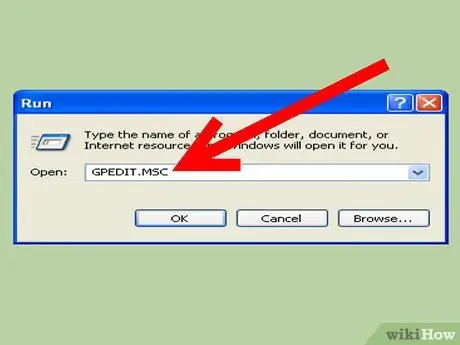
Step 3. Type:
gpedit.msc.
Step 4. Select and click “OK”
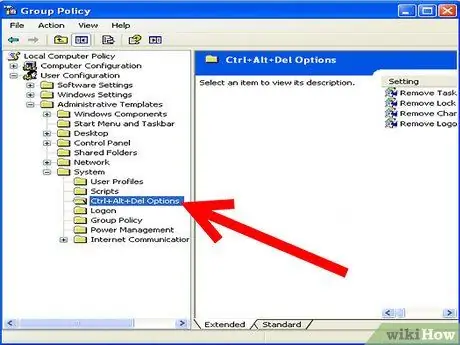
Step 5. Navigate to the following branch:
User Configuration / Administrative Templates / System / Ctrl + Alt + Delete Options / Remove Task Manager.
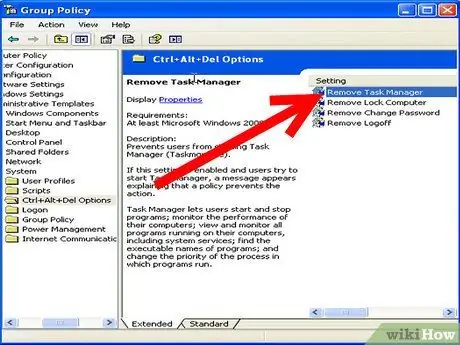
Step 6. Locate the "Remove Task Manager" option and double click it
Again, this is the correct way to enable Task Manager in Windows.
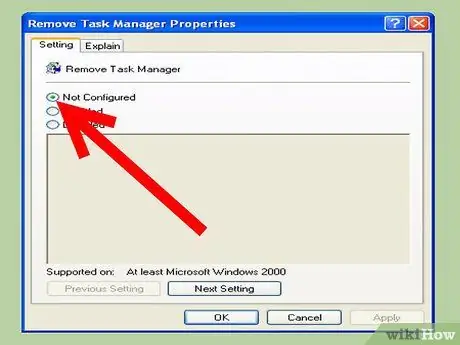
Step 7. Set the policy on your computer to "Not Configured"
Method 4 of 4: Set up and enable Task Manager in Windows Vista
Step 1. Determine what version of Windows Vista you have
You may have Home Basic, Home Premium, or other editions. In the case of Home Basic and Home Premium, go to the search box in the "Start" menu.
- You can right click or type "Crtl + Shift + Enter" with the keyboard and select "Run as administrator". This option appears in a pop-up and runs the Registry Editor in an advanced state.
-
Navigate to: HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPolicies.

Enable Task Manager in Windows Step 17Bullet2 -
Open "System".

Enable Task Manager in Windows Step 17Bullet3 - Select "DisableTaskMgr". While it may seem odd to use a disable tool when you want to enable something, this is the correct way to change the settings.
-
Change the Value data to 0.

Enable Task Manager in Windows Step 17Bullet5
Step 2. Review other settings for versions of Vista other than Home Basic and Home Premium
-
Go to the "Start" menu on the desktop screen and click it.

Enable Task Manager in Windows Step 18Bullet1 -
Select "Search" and type "gpedit.msc." This launches a pop-up tool that takes you to the advanced options.

Enable Task Manager in Windows Step 18Bullet2 - Go to "User Configuration" and select the "Administrative Template" option.
- Identify "System" and go to "Options Ctrl + Alt + Del".
- Select "Remove Task Manager" and choose the option to "Enable".






