Vaginismus is a female sexual dysfunction. It occurs when the muscles in the vagina involuntarily contract in an attempt to have intercourse, causing discomfort and pain. In addition to interfering with a healthy sex life, this disorder can prevent sufferers from inserting tampons or undergoing pelvic exams. The causes vary, and it is good to analyze them to find the right treatment. Although vaginismus is annoying, embarrassing and stressful, it is absolutely treatable.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Identifying Vaginismus

Step 1. Take the pain you feel when having sex seriously
The first symptom of vaginismus, and also the most annoying one, is a painful sensation that appears the moment you try to have intercourse. Every woman experiences this pain differently: it can give a burning sensation, tingling, constriction, tearing, or as if the partner is "hitting a wall". In many cases, the pain and involuntary muscle contractions are severe enough to prevent satisfying intercourse entirely.
- Many women find they have this problem the first time they try to have sex. This disorder is called "primary vaginismus".
- Others develop it later, in this case we therefore speak of "secondary vaginismus". Consequently, it is important not to underestimate this key symptom just because you have been sexually active in the past without feeling any discomfort.

Step 2. See if you have any other problems with vaginal penetration
In addition to pain experienced during sexual intercourse, women with vaginismus may have difficulty with other types of penetration, including pelvic exams and inserting tampons. Here are other symptoms:
- Unconsummated marriage;
- Constant sexual discomfort or pain following childbirth, candida / urinary tract infections, sexually transmitted diseases, interstitial cystitis, hysterectomy, cancer, surgery, sexual assault, or menopause;
- Constant sexual pain of unknown origin;
- Breathing blocked when trying to have sex.
Step 3. Pay attention to other muscle spasms
Vaginal muscle contractions and spasms are typical symptoms of vaginismus, but some women can also experience them in the legs or lower back. They occur more frequently when trying to have sex.

Step 4. Don't ignore your sexual abstinence
Many women with vaginismus begin to carefully avoid situations of an intimate nature. Staying away from sexual activities or romantic relationships for pain or embarrassment due to symptoms is clearly a sign that should not be overlooked: seek medical attention.
Remember that withdrawal is not your fault and is caused by an involuntary association that the body makes, which is that "sex equals pain"

Step 5. Make an appointment with your gynecologist
Go to this specialist to talk to him about your concerns. Clearly explain the extent and severity of the symptoms.
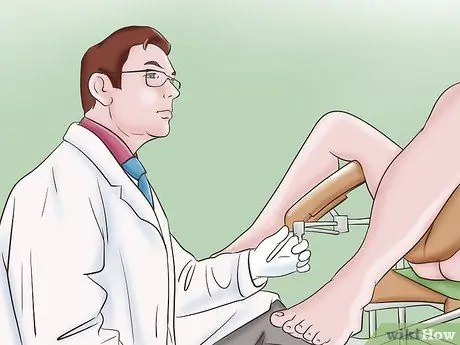
Step 6. Discard other disturbances
Doctors should perform a pelvic exam and watch for any vaginal discomfort or contractions. In addition, he will likely recommend further tests to rule out other possible causes of these symptoms.
Vaginismus could have an obvious physical cause, such as an infection, injury, or hypersensitivity of the nerves when the vagina opens (induced vulvodynia)
Step 7. Request a diagnosis
If all other possible causes of your symptoms are ruled out, your gynecologist may diagnose you with primary or secondary vaginismus. In addition, it can tell you whether the disorder is global (i.e. it happens in all situations involving vaginal penetration) or situational (i.e. it occurs only in some cases, for example when you try to have sex).
- Unfortunately, female sexuality and related dysfunctions are not fully understood. It can happen that you run into doctors who neglect the symptoms or are unable to help. In this case, one must insist on obtaining a diagnosis and following treatment. If your gynecologist doesn't support you, look for one who has experience with vaginismus and other types of female sexual dysfunction.
- There are other possible diagnoses, such as apareunia, a general term referring to the inability to have sexual intercourse (vaginismus is a form of it), and dyspareunia, which generically refers to the pain felt during sexual intercourse.
- These diagnoses allow for more accurate treatment. In fact, when you know the cause of the disorder, you can turn to several experts on the subject.
Part 2 of 3: Understanding the Causes of Vaginismus

Step 1. Consider the role that anxiety plays
Many women with vaginismus can link these symptoms to feelings of anxiety, fear, and stress. These moods can have deeper roots or be related to factors that come into play at a certain time, such as lack of sleep or excessive work stress.

Step 2. Consider the ideas you've always had about sex and sexuality
Women with vaginismus usually exhibit more deeply ingrained negativity regarding their sexual sphere. These emotions can date back to childhood or be linked to a particularly traumatic event.
When negative views about sex arise at a young age, another possible cause of vaginismus comes into play - the lack of proper sex education

Step 3. Try to understand the role of past experiences
According to some estimates, the likelihood that women with vaginismus were victims of sexual interference during their childhood is two times higher than those who do not suffer from this problem. Events that appear to contribute to the disorder range from mild trauma to severe damage. Here are some of them:
- Sexual abuse by a known person.
- Sexual violence.
- Pelvic trauma.
- Domestic violence.
- Highly negative first sexual experiences with a consenting partner.

Step 4. Remember that problems in your relationship can also contribute
If you suffer from secondary and situational vaginismus, the disorder may be due to difficulties you have with a sexual or permanent partner. The issues can be varied, including lack of trust, fear of making a romantic commitment, fear of becoming too vulnerable or opening up to pain and disappointment.
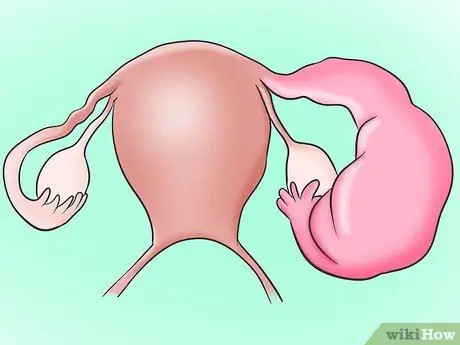
Step 5. Remember that certain medications and conditions can also affect you
Several disorders can cause or exacerbate the symptoms of vaginismus. If it occurs after a period in which your sex life has been normal, this is likely the situation. Here are some medical problems that can contribute to vaginismus:
- Urinary tract infections and other problems affecting this system.
- Sexually transmitted infections.
- Cancer of the sexual or reproductive organs.
- Endometriosis.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease.
-
Vulvodynia or vestibulodynia.
Surgical procedures that affect the female reproductive organs, such as a hysterectomy, can also cause vaginismus
Step 6. Recognize the role that certain stages of reproduction can play
For many women, secondary vaginismus is caused by childbirth. If it was very difficult or damaged the sexual organs, this is more likely to be the cause. Other women suffer from this disorder due to the hormonal changes and dryness that usually accompany menopause.
Secondary vaginismus can also be caused by fear of having children or going through childbirth

Step 7. If there is apparently no cause, accept it
Some women fail to find out why they have vaginismus. In fact, in certain cases it is impossible to identify with certainty a physical or psychological cause.
According to some research, the symptoms of vaginismus are attributable to general defense mechanisms, triggered by situations that seem to pose a threat. It is therefore clear that this disorder should not always be considered as a sexual dysfunction
Part 3 of 3: Treating Vaginismus

Step 1. Try seeing a therapist
A professional can help you regardless of the cause of vaginismus (which can be psychological, emotional, or physical). In fact, it is often enough to know that you have this disorder to experience feelings such as fear and anxiety before having sex. This creates a vicious cycle that exacerbates the symptoms. Moods like depression, isolation, and low self-esteem are other common side effects brought on by this sexual dysfunction.
- The results of treatment are much more positive when the woman and her partner are motivated, willing to cooperate and willing to resolve relationship conflicts. Hence, a couple psychological assessment is a great starting point for treating vaginismus.
- If vaginismus is linked to anxiety disorders or past sexual trauma, a therapist can help you deal with these issues so you can move on.
- A particular type of therapy, called cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy (TCC), can be quite helpful for some women. This treatment focuses on the relationship between mental processes and actions, so a trained psychotherapist can help you change the thoughts and behaviors related to your sexual problems.
Step 2. Learn about exposure therapy, or flooding
It is a technique used to combat vaginismus which involves a gradual desensitization to penetration. With the help of a specialist it can be effective, even for those women who have always suffered from this disorder. To implement it, vaginal penetration exercises are usually performed with the use of dilators.
This same method is also used for self-treatment, to which a guide is added that can help you continue on your own in a safe and satisfying way

Step 3. See a physical therapist
Ask your primary care physician for a referral to a physical therapist who has experience with treating vaginismus and other female sexual dysfunctions. Since the pelvic floor muscles play a vital role in vaginismus, physiotherapy is one of the best treatments. Here's what this specialist might do:
- Teach you breathing and relaxation techniques.
- Teach yourself to contract your pelvic floor muscles to control them.
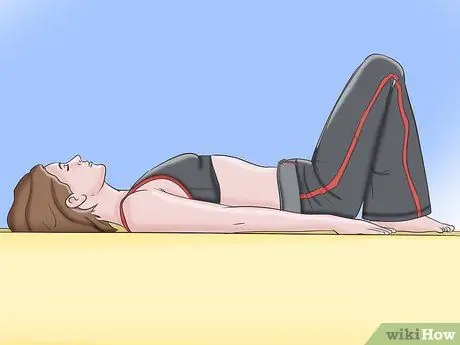
Step 4. Do the Kegel exercises
They were designed to help control the pelvic floor muscles. To perform them, you simply need to contract the muscles that you would use to stop the flow of urine, hold this position for a few seconds and relax them. Aim to do about 20 contractions at a time, repeating as many times as you can throughout the day.
Some doctors recommend doing Kegel exercises with one finger inserted into the vagina (you can insert up to three fingers). Using your finger allows you to feel the muscle contraction, so you can better control vaginal movements

Step 5. Consider vaginal dilators you can use at home
Your gynecologist can recommend this cone-shaped instrument that fits into the vagina. It gets progressively larger, allowing the vaginal muscles to stretch and get used to penetration.
- To start, apply the same pressure as you would when you have to pass stool. This helps you enlarge the vaginal opening. Then, insert your fingers into the vagina (not the dilators for now), continuing to push or apply pressure.
- When you start using the dilators, leave them in the vagina for 10-15 minutes. The vaginal muscles will get used to the pressure.
- If you have a partner, you can ask him to help you insert the dilators.

Step 6. When having sex, relax and don't rush
Women with vaginismus need to be patient and try different treatments before moving on to actual sexual intercourse. If you try to become sexually active right away, you risk experiencing unpleasant or uncomfortable sensations, which triggers a vicious cycle of pain and anxiety that makes vaginismus worse. It is essential to have a patient and understanding partner.
- When trying to have sex, go slowly, use a lot of lube, and experiment to find the most comfortable positions.
- Doctors generally suggest grasping the penetrative object and placing it partially or completely in the vagina, just as was done with vaginal dilators. This applies equally to penises and vibrators.
Advice
- Some women feel embarrassed or ashamed of vaginismus, so they don't ask for help to fight it. If this is the case, remember that you are not suffering from it and that it is a treatable condition. Seek out a sympathetic doctor and a good psychotherapist, and work hard to start having a healthy sex life.
- Some doctors and websites may recommend medicines, including local anesthetics, to treat vaginismus. In general, however, this is not a good idea: local anesthetics numb the external pain, but they do nothing to solve the problem itself, so it becomes more difficult to defeat the ailment.






