This article explains how to use common keyboard shortcuts on a Windows or Mac computer. Keyboard shortcuts allow you to perform actions that require multiple steps by simply pressing two or more keys at the same time.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Windows
Step 1. Understand how keyboard shortcuts work
To use a keyboard shortcut you will need to press one or more modifier keys along with a letter key (or another modifier key). Modifier keys include the following:
- Ctrl - Usually found on the left and right side of the keyboard. The Ctrl key on the right is positioned to the left of the arrows.
- Alt: Located on the left and right side of the keyboard, more towards the center than Ctrl.
- ⇧ Shift: Symbolized by an arrow pointing up, this key is located on the left and right side of the keyboard.
- Fn: The "function" key allows you to use the secondary functions of other keys. Commands that use "function" keys (such as F8) may require the use of the Fn key.
- ⊞ Win: This key features the Windows logo and is usually found at the bottom left of the keyboard.
- Arrows: Although not technically modifier keys, arrows can be used to select various elements.
- Enter: This key opens a selected item. This is basically the same as clicking with the left mouse button.
Step 2. Use general keyboard shortcuts to access Windows features
These combinations allow you to perform the main Windows operations:
- F1: opens the "Help" page. To use it you need to be connected to the internet. If your computer has the Fn key, you may need to hold it down along with F1.
- ⇧ Shift + F10: opens the context menu of a selected item. This function is usually performed by clicking with the right mouse button.
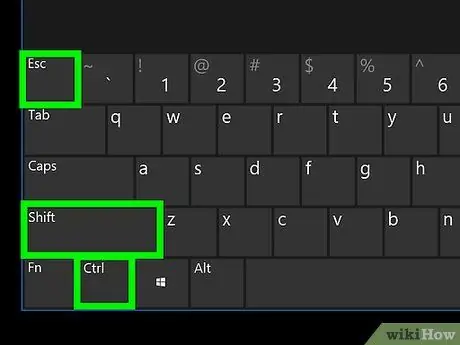
- Ctrl + ⇧ Shift + Esc: Opens the "Task Manager" window.
- Ctrl + Alt + Del: opens a menu that allows you to perform various operations, such as logout, computer lock and so on (works for Windows versions between XP and 10).
- Alt + Space: Opens the "System" menu of the current window, from which you can resize, minimize, maximize or move the currently open window.
- Ctrl + Tab ↹: allows you to move between the tabs of the currently open window (for example in a browser).
- Ctrl + Esc: Opens the "Start" menu.
- Alt + Tab ↹: allows you to move between open windows, excluding the desktop.
- Alt + F4: close an open window or program.
- ⇧ Shift + Del: permanently delete a selected item. With this action the item will be permanently deleted, so it will not be moved to the trash, even if you need to click "Ok" to confirm it.
- ⊞ Win: opens "Start".
- ⊞ Win + L: locks the computer. If it is not password protected, the user selection screen will open.
- ⊞ Win + R: opens the "Run" window.
- ⊞ Win + M: Minimize all open windows and show desktop.
- ⇧ Shift + ⊞ Win + M: restore all minimized windows.
- ⊞ Win + E: Opens the "File Explorer" window.
- ⊞ Win + Ctrl + F: Search for another computer in your network (only applies to computers that have been added to the network).
- ⊞ Win + Tab ↹: displays all currently open windows.
- ⊞ Win + Pause: opens the "System" properties window.
- ⊞ Win + Stamp R Sist: allows you to make a screenshot.
- Ctrl + F: Opens a search bar that allows you to search for specific words or phrases on the page.
Step 3. Use keyboard shortcuts to help you type, copy and paste
On Windows there are several specific shortcuts for editing texts. They can be exploited for most of the actions associated with the typing, copying and pasting process:
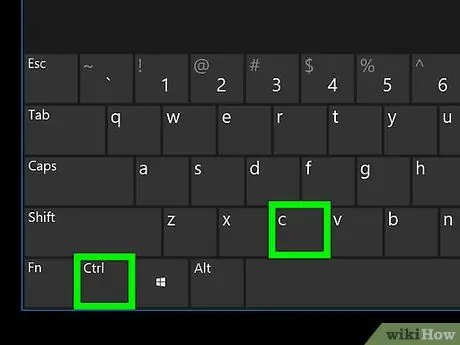
- Ctrl + C: Copy selected text. You can also use this key combination to copy selected files or folders.
- Ctrl + X: Copy and delete selected text (this feature is called "cut").
- Ctrl + V: Paste the copied text where the mouse cursor is positioned. This method also works with files and folders.
- Ctrl + Z: Undo the last change. Depending on the program, this command can be used multiple times to clear multiple errors.
- Ctrl + Y: redo the last undone change. Depending on the program, this command can be used multiple times to revert multiple undone changes.
- Ctrl + P: Print the document.
- Ctrl + S: save the document.
- Ctrl + B: Bold selected text. This method works with Microsoft Office products and most e-mail services.
- Ctrl + U: Underlines the selected text. This method works with Microsoft Office products and most e-mail services.
- Ctrl + I: Italicize selected text. This method works with Microsoft Office products and most e-mail services.
Step 4. Use keyboard shortcuts in the File Explorer window
You can use several keyboard shortcuts to navigate in this window:
- F2: change the name of a selected item.
- F4: Place the mouse cursor in the address bar.
- F5: Reload a folder.
- F6: Select a different panel in the "File Explorer" window.
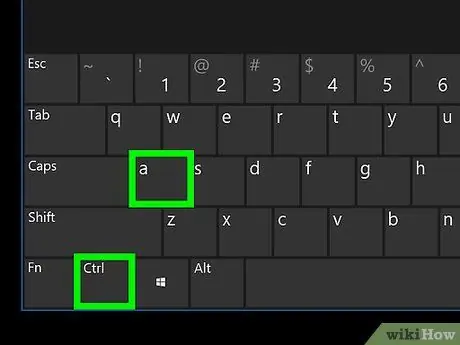
- Ctrl + A: Select each item in the current window.
- Alt + Enter: Open the "Properties" menu of the selected element.
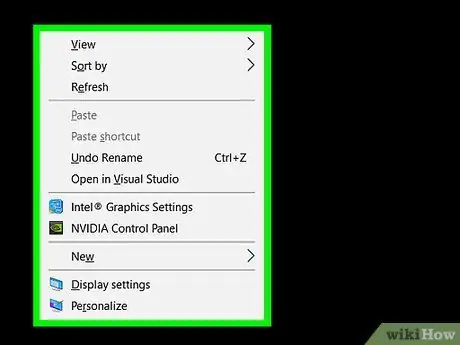
Step 5. Use the keyboard shortcuts that go in conjunction with the use of the mouse
Most programs have an advanced menu that can be accessed by pressing a key and using the mouse at the same time:
- ⇧ Shift + right mouse button: shows a drop-down menu with various options depending on the item you clicked on.
- ⇧ Shift + double click- Runs the alternate double-click command, which is the second option in the right-click drop-down menu.
- Alt + double click: opens the "Properties" window of an element.
Method 2 of 2: Mac

Step 1. Understand how keyboard shortcuts work
To use one, you'll need to press one or more modifier keys along with a letter key (or another modifier key). Modifier keys include the following:
- Command: Located to the left and right of the spacebar.
- Option: Located next to the Command keys.
- Control: located on the left side of the keyboard.
- Fn: located at the bottom left of the keyboard. This key activates the alternative uses of the "Function" keys (such as F8).
- ⇧ Shift: Located on the left and right side of the keyboard.
- Arrows: Although they are not technically modifier keys, they can be used to select various elements.
- Enter: Located on the right side of the keyboard. Opens a selected item.

Step 2. Use keyboard shortcuts to perform common actions
Instead of using the mouse or program buttons, you can use the Mac keyboard to perform actions such as copying files or text and opening certain software:
- Command + X: Copy a selected text or file, then delete it from its current location (this action is also called "cut").
- Command + C: Copy a selected text or file without deleting it.
- Command + V: Paste a copied item.
- Command + Z: Undo the last command.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + Z: Re-execute the canceled command.
- Command + A: Select all items in the currently open folder.
- Command + F: Open the search bar in a specific window, browser, or program.
- Command + G: Find the next occurrence of the item (such as a word) you searched for earlier.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + G: Find the previous occurrence of the item you searched for.
- Command + H: Hide the foreground application or program window.
- Command + Option + H: Hide all windows except the foreground application or program.
- Command + M: Minimizes the foreground window.
- Command + Option + M: Minimizes all windows of the foreground application.
- Command + N: opens a new document, window or tab depending on the program used.
- Command + O: Open a selected item (such as a file or folder).
- Command + P: Print the currently open document.
- Command + S: Save the currently open document.
- Command + Q: Close the foreground application.
- Command + Esc: Opens the menu to force quit an application.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + Option + Esc: Press and hold these keys for three seconds to force quit the foreground application.
- Command + Space: Opens the "Spotlight" search bar.
- Command + Tab ↹: Go to the next most recently used application among the open apps.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + ~: Move to the next window of the foreground application.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + 3: Take a full screen screenshot.
- Command +,: Opens the preferences associated with the foreground application.
Step 3. Put your computer to sleep, log out or shut it down
There are several abbreviations you can use to quickly lock your computer:
- Control + power button- displays a dialog box asking if you want to put your computer to sleep, restart or shut down.
- Control + Command + power button: force restart the Mac.
- Control + ⇧ Shift + power button: Turn off the Mac screen.
- Control + Command + media eject button: close all applications, then restart your computer.
- Control + Option + Command + power button: closes all applications, then turns off the computer.
- ⇧ Shift + Command + Q: Log out of the user account. You will be asked to confirm.
- Option + ⇧ Shift + Command + Q: Log out of the user account without asking for confirmation.
Step 4. Use abbreviations to navigate the Finder
You can use keyboard shortcuts to perform various actions within the Finder:
- Command + D: Duplicate selected items.
- Command + E: Eject the selected drive (like a USB key).
- Command + F: Open Spotlight in the Finder.
- Command + I: Show the "Get Info" window for a selected item.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + C: Open the "Computer" folder.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + D: Open the "Desktop" folder.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + F: Open the "All my files" folder.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + G: Opens the "Go to Folder" window.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + H: Open the "Home" folder.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + I: Open iCloud Drive.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + K: Opens the "Network" window.
- Option + Command + L: Open the "Downloads" folder.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + O: Open the "Documents" folder.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + R: Opens the "AirDrop" window.
- Control + Command + ⇧ Shift + T: Add the item selected in the Finder to the Dock.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + U: Open the "Utilities" folder.
- Command + Option + D: Hide the Dock (or show it if it was hidden).
- Control + Command + T: Add the selected item to the Finder sidebar.
- Option + Command + P: Hide the address bar (or show it if it is hidden).
- Option + Command + S: Hide the sidebar (or show it, if hidden).
- Command + J: Show "View Options" folder.
- Command + N: Opens a new window in the Finder.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + N: Create a new folder in the Finder location you are currently in.
- Command + Option + N: Create a smart folder in the Finder location you are currently in.
- Command + Option + V: Move copied files from their original location to where you are currently.
- Command + 1, 2, 3 or 4: Change the appearance of the icons in the current folder. # * Command + [: Show the last viewed folder.
- Command +]: Open the next folder in the path.
- Command + reduce brightness: Enable or disable screen mirroring when your Mac is connected to another display (such as a TV).
- Command + Delete: Send a selected file to the "Trash".
- Command + ⇧ Shift + Delete: Empty the trash by asking for confirmation.
- Command + Option + ⇧ Shift + Delete: Empty the trash without confirmation.
- Option + increase brightness: opens the monitor settings.
- Option + Mission Control: Opens the "Mission Control" preferences.
- Option + Volume Up: Opens the Mac's "Sound" preferences.
- Command + Mission Control: Show "Desktop".

Step 5. Use shortcuts to edit text in a document
Instead of clicking on the various buttons in the word processor, you can use abbreviations to edit the text:
- Command + B: Bold selected text.
- Command + I: Italicize the selected text.
- Command + U: Underlines the selected text.
- Command + T: Hide the "Font" window or show it if it has been hidden.
- Command + D: Select the "Desktop" folder within an "Open" or "Save" dialog box.
- Command + Control + D: Show the definition of a selected word.
- Command + ⇧ Shift +:: show the "Spelling and Grammar" window.
- Command +;: looks for spelling errors in the document.
- Control + L: Places the cursor in the center of the screen.
- Command + Option + F: Opens the search field.
- Command + Option + C: Copy the formatting settings of the selected text.
- Command + Option + V: Apply copied style to selected text.
- Command + Option + ⇧ Shift + V: Apply the surrounding content style to the pasted element within that content.
- Command + Option + I: Opens the "Inspector" window.
- Command + P + ⇧ Shift: Opens the document settings to determine the print format.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + S: Opens the "Save As" window.
- Command + ⇧ Shift + -: Reduces the font size of a selected item (or the size of an image).
- Command + ⇧ Shift ++: Increase the font size of a selected item (or the size of an image).
- Command + ⇧ Shift + ?: Opens the "Help" window.






