Rubies have always been appreciated for their incredible hardness and brilliance of color. Unlike what happens with other precious stones, there is no precise universal classification, but most jewelers rely on different characteristics to evaluate their quality. This article will teach you to recognize its quality, select the right setting for a jewel and understand the methods of extraction or creation of this precious stone. Some ruby mines are compromised in human rights violations or environmental disasters, but there are alternative sources that do not pose moral problems.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Evaluating a Ruby

Step 1. Choose the karats according to your budget and your tastes
The carat (ct.) Is the unit of measurement of the mass of a gem. In general, the larger the gem, the more expensive it is. However, there are significant price differences between a 1, 3, and 5 carat stone and a 0, 9, 2, 9 or 4, 9 carat stone. Remember that the choice of the number of carats often depends on aesthetic and practical issues, as well as on the value. In fact, those with thin fingers or less flashy tastes may prefer a smaller piece of jewelry.
- Generally speaking, a natural 1-carat ruby costing less than € 220 is considered to be of "commercial quality" rather than "high value". From € 600 upwards, it is considered to be of a high standard, while from € 9,000 per carat upwards it is exceptional and rare.
- Typically, a lab-created ruby sells for around 85-90% of the price of a natural one of the same quality.
- Since large rubies are rare, the price increases dramatically compared to the size. A commercial-grade 5-carat ruby can be worth 10 times more than a similar 1-carat ruby, while a higher-quality 5-carat ruby (which is quite rare) can be worth 25 times more than a similar 1-carat one..

Step 2. Choose the cut
The cut of a gem corresponds to the shape that the cutter gives to a precious stone. In general, this is a matter of personal taste, although most rubies are cut in an oval, round or cushion shape (a rounded square). Heart and emerald cuts (a rectangle with sharp corners) are also very common, but because demand is low, they can be a bit cheaper than a similar quality gemstone cut differently.

Step 3. Choose the color
In jewelry catalogs or websites you can choose a ruby by color or hue. Even if the most precious rubies are the red ones and tending to purple, even those red-orange or tending to pink are of high quality. The choice of color is a matter of taste.
- If you are interested in pink rubies, look for pink sapphires as well. Sapphire and ruby come from corundum, and therefore are classified as colored varieties of this same mineral. Therefore, pink stones can be classified in both one and the other variety.
- Pink rubies are in demand more in Asia than in Western countries and, therefore, are worth more in this continent.
- Some companies describe the color of the stones according to the areas of the world they come from, but it is not an accurate system.

Step 4. If you shop on the Internet, find a company that provides buyer returns
Even if, by shopping online, you can select a ruby based on the characteristics previously reported, it is extremely difficult to evaluate it in detail based on a photo. Anyone who sells gemstones on the net may include some information, using the valuation methods below, but even if they are telling the truth, there is a risk of disappointment once delivered. If you need to buy a ruby online, always make sure it is returned and look for reviews on the company to avoid any scams. When it is delivered to you, judge it by the criteria you will find below, and send it back for a refund or replacement if it doesn't match what you want.

Step 5. Look at the ruby under a light source
Inside you will be able to spot one or more black or gray spots, called extinctions, where light has no difficulty in penetrating. The more it has, the lower the value of the stone will be. Turn it under the light source to see what extinctions look like from different angles. If the presence of these characteristics negatively affects your choice, be aware that light colored and shallow cut stones tend to have fewer extinctions, although they can present other problems, such as windows (chromatic voids that give a transparent aspect, as if you were looking through a window), and a lesser brilliance.
The precise effect of extinctions on the price of the ruby is a rather subjective matter

Step 6. Check the saturation of the stone
This characteristic is also called purity of color or intensity, and should be included in the description of the ruby. Vivid colored rubies have richer hues and are the most valuable, followed by those that have strong saturation. A medium, light or weak saturation has a color masked by significant shades of brown or gray, which give a less defined hue.
The evaluation of saturation essentially depends on the judgment of the jeweler, not on a scientific classification method

Step 7. Observe the tone of the ruby
The tone indicates the amount of color present in the stone and ranges from very dark to very light. Rubies that have a medium tone tend to be the most precious, but even in this case it is a matter of personal taste.

Step 8. Evaluate the purity of the stone
Many rubies contain inclusions, which are materials that are visibly trapped within the gem. In general, the more transparent the stone, the more precious it is. However, some collectors appreciate the unique look that rubies acquire when they contain some inclusion. The "silky" filaments of rutile can be very appreciated, because they are able to give shine to the gem. If they are arranged in a star, the ruby takes the name of star ruby and can be very rare and precious.
- There is no precise classification system for the purity of the ruby. A commonly used method is to rate the stone from 1 (perfectly clear) to 4 (with many inclusions).
- Another rather widespread system classifies gems from IF (internally flawless; internally pure), VVS (very very small inclusions; very very small inclusions, difficult to detect with the magnifying glass), VS (very small; very small, visible inclusions with the magnifying glass), SI (small inclusions; small inclusions, barely visible to the naked eye) and I (inclusions; inclusions easily visible to the naked eye).

Step 9. Find out about the treatments the ruby has undergone
Natural and untreated rubies are rare and expensive. Almost all of them undergo heat treatments by jewelers to intensify the color. This manipulation is widely accepted, since it does not affect the durability of the stone and improves its appearance. However, if the gem has undergone a surface diffusion treatment or remediation, it means that additional material has been added to correct the gem's defects. Usually, the value of rubies manipulated with these methods is less high, because these treatments have a limited effect over time.
Part 2 of 3: Choosing the Frame

Step 1. Choose the metal according to your tastes and how much you can spend
Mostly rubies are set in white gold, but the choice of metal depends on personal tastes. If you buy a ruby to give it to someone, try to find out what metal the other jewelry they own is made from. The lower the carat, the lower the price, but it can be less shiny or tends to oxidize.

Step 2. Choose the claw setting if the ruby is large
In this type of setting, the prongs are small metal claws that grab the gem at the edges and keep it in place. It is quite common for larger stones.

Step 3. Choose the bezel frame
In this setting, the metal perfectly wraps the sides of the gem to stop it. Also this kind of setting is rather used for large stones, such as the half-bezel setting that captures the gem only partially.

Step 4. Find other solutions for arranging the smaller stones
If the jewel contains a greater number of small stones, you cannot use the models described above. For example, you can choose a pavé setting (tiny balls made from metal), a rail (setting similar to a long channel that contains the stones) or invisible (setting where the stones are next to each other so that the setting remain totally invisible).
Part 3 of 3: Find out about the sources from which the rubies come

Step 1. Consider buying a lab-created ruby for its great value for money
Rubies created in the laboratory are chemically identical to natural ones and, therefore, are just as beautiful and resistant. Generally speaking, they are less expensive than natural rubies which have the same qualities, since it is cheaper to produce them synthetically than to locate and extract them. They are an excellent choice if you are hesitant to buy natural stones that may come from sources where respect for human rights and the environmental impact of the mines are in question.
- They are often called synthetic rubies. Do not confuse them with imitations or artificial rubies, which are not real rubies and are much less resistant and bright.
- The starry ones are considered to be the most beautiful rubies, but in nature they are extremely rare and expensive compared to those created in the laboratory.

Step 2. Look for "recycled" gems
About 98% of the rubies sold have been on the market for decades, as they are extremely resistant. Claiming that they do not cause any kind of environmental impact, some companies specifically promote some of their gemstones as "recycled" stones, as they come from publicly owned jewelry and retail sales.
Objections point out that by purchasing new rubies, there is a danger of supporting mining companies that exploit local populations and damage the environment
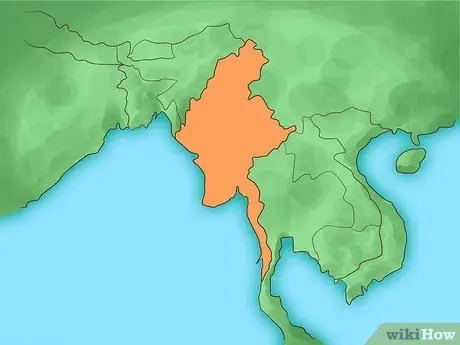
Step 3. Learn about Myanmar rubies
Most of the world's rubies come from Myanmar, a country formerly known as Burma. Although the oldest rubies may have come from the famous Mogok Valley, they are currently mainly mined in the Mong Hsu region. Thanks to the long tradition of this country and the huge quantities of stones found, Burmese rubies have gained a very special prestige. However, due to human rights violations by the Myanmar government, the import of new gems from the region is banned in the United States and Canada, and has more recently been banned in the European Union.
The purple-red rubies, known as "pigeon blood", come from this area and are extremely valuable
Step 4. Consider buying rubies from other countries
Sri Lanka (Ceylon), Thailand and several African nations export rubies, or have done so in the past, but the market is very irregular, because each new mine discovered corresponds to one that has just been emptied. None of these sources are as famous as Myanmar, but at least some are not implicated in environmental or human rights issues. The governments of Tanzania, Ghana and Zimbabwe are trying to regulate the environmental impact of the mines. However, the results are uncertain, as individuals or small groups involved in these activities do not have the money to comply with environmental regulations. The extraction of rubies in the United States is subject to very strict environmental regulations, but it constitutes only a small fraction of the entire world extraction.






