Partitioning a hard disk means dividing it into two or more logical memory units that are totally independent of each other. The larger the hard drive, the longer it will take to recover the data. Partitioning a large hard drive can be helpful in reducing the time it takes to access the information it contains. Partitioning a computer's main hard drive offers the advantage of being able to separate the operating system from other data, making it easier and faster to back up your most important files. By creating multiple partitions, you will also have the option to install several operating systems on a single computer. Before partitioning a hard drive, it is best to determine how much free space is still available. You should have a specific reason for wanting to partition your computer's main hard drive, as it will help you determine the size of the partition.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Calculating the Partition Size
Step 1. Open the Windows search bar
Press the Windows key combination to access the search bar.
Step 2. Type the keyword partitions into the search bar that appears, then press the Enter key
Step 3. Click on "Create and format hard drive partitions"
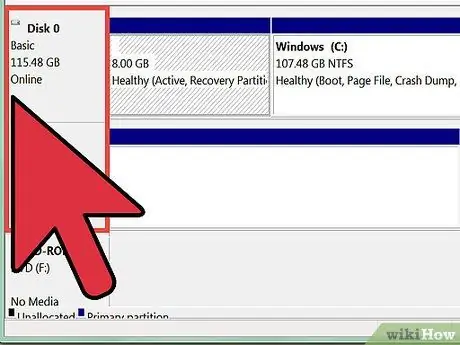
Step 4. Review the list of hard drives installed on your computer
Within the "Disk Management" system window, in the "Volume" column, all the hard drives installed on the computer are listed. The drive indicated by the letter (C:) is normally the main hard disk of the PC, on which the Windows installation is located. The "Capacity" column shows the total size of each memory unit, while the "Available space" column shows the amount of free space still available for each volume.
If more than 90% of a hard drive's capacity is already occupied by data, it is best not to use it to create the new partition you need, as the amount of free space remaining will be too limited
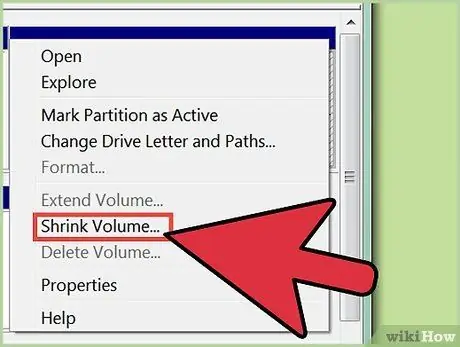
Step 5. Resize the existing volume
Before you can create a new partition, you need to resize the existing storage unit. In this way, you will create the free space that you will then go to assign to the new partition. Select the hard disk to be partitioned with the right mouse button, then click on "Shrink volume".
- The operating system will calculate the amount of space that can be subtracted from the selected volume in order to create the new partition.
- The information in question will be displayed in the "Minimize" dialog box.
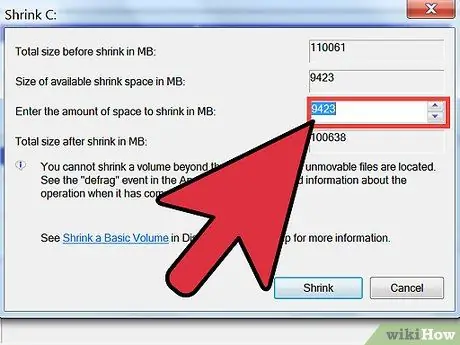
Step 6. Choose by how much you want to reduce the current size of the selected volume
This is the space you are going to reserve, in MB, for the new partition. In the text field "Specify the amount of free space to shrink", type the number of MB that will be subtracted from the volume you have selected.
- If you want to use all the free space available on the hard disk for the new partition, copy the value in the "Reduce space available in MB" field and paste it into the "Specify the amount of free space to reduce in MB".
- All numbers shown in the "Shrink" dialog box are expressed in MB. Remember that 1000 MB equals 1 GB.
- The size of the new partition should be larger than the free space you really need. This is because it is always better to have enough free space inside a hard drive or volume.
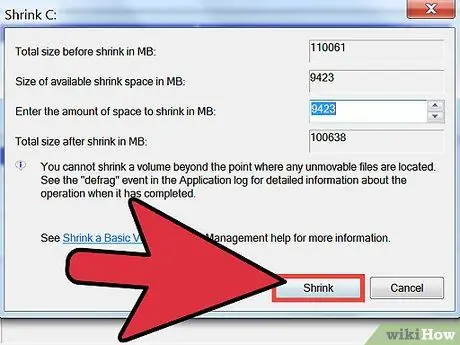
Step 7. Click the Shrink button
The space that will be subtracted from the selected volume will be indicated as "unallocated space" in the "Disk Management" window.
Part 2 of 2: Create a New Partition
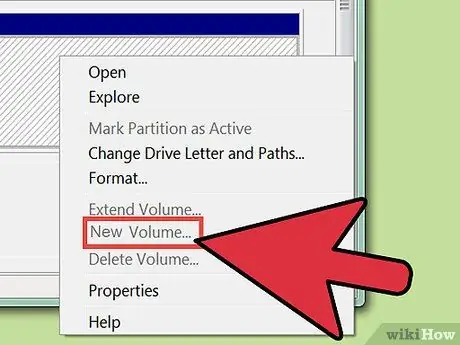
Step 1. Create a new partition using the unallocated space
Select the bar marked "Unallocated" using the right mouse button, then click on "New Simple Volume" from the context menu that will appear.
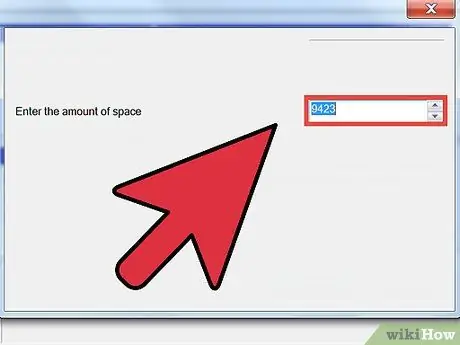
Step 2. Choose the size that the new partition will have
Enter the number of MB to use to create the new partition in the "Simple Volume Size in MB" text field of the "New Simple Volume Wizard" window. At this point, click on the Next button.
If you want to use all the free space available, use the value listed under "Maximum disk space size in MB"
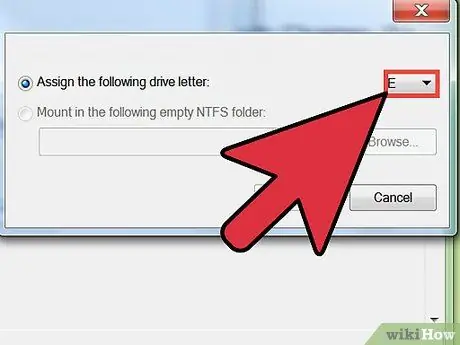
Step 3. Assign a drive letter to the new logical partition
Click on the "Assign this drive letter" button. Click on the appropriate drop-down menu, select the drive letter you want to assign to the new partition, then click the Next button.
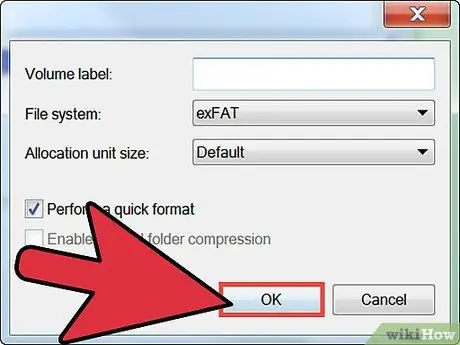
Step 4. Choose the configuration settings with which to format the partition
Click the "Format this volume with the following settings" button and click the Next button.
- In this case, you can use the default settings without any risk.
- The file system is logical structure that will be used to store information within the hard drive. The "NTFS" format (from English "New Technology File System") is the file system used by all modern computers with a Windows operating system. Unless you have a very good reason not to, you should choose this type of file system. The other options available to you are "FAT32" and "FAT". Use these file system formats if you want to install operating systems such as Windows 95, Windows 98 or Windows ME.
- The "Allocation Unit Size" text field indicates the size of the individual memory blocks that will be used to store information on the hard disk. Using smaller allocation units is a great way to make more efficient use of the free space available. Unless you have a very good reason not to, choose to use the default allocation unit size. If you are planning to use partition to store large media files, it may be better to use larger allocation units.
- Inside the "Volume Label" text field, there is the name that will be assigned to the new partition. You can choose to use whatever name you prefer.
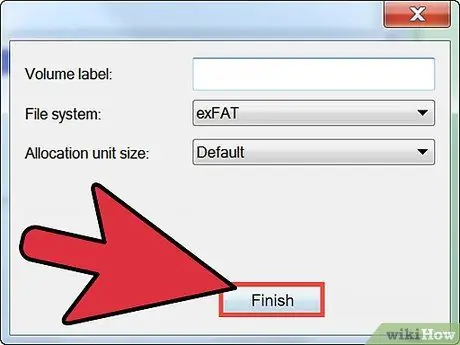
Step 5. Click the Finish button
Within the final screen, you will find a summary of the settings you have selected. When you click on the Finish button, the formatting procedure of the new partition will start.
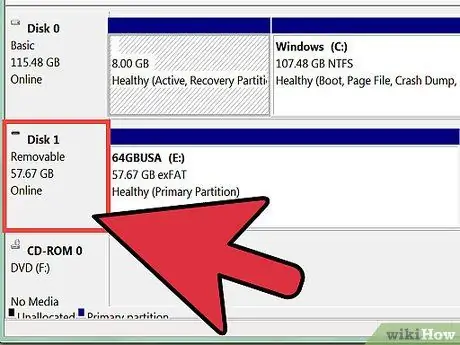
Step 6. Examine the new partition
Make sure that in the "Disk Management" window the unallocated space bar has been replaced by the one corresponding to the new partition you created.






