The Windows Registry is a registry that stores configuration information about many important parts of that operating system. By modifying it you can shape Windows the way you like.
Steps
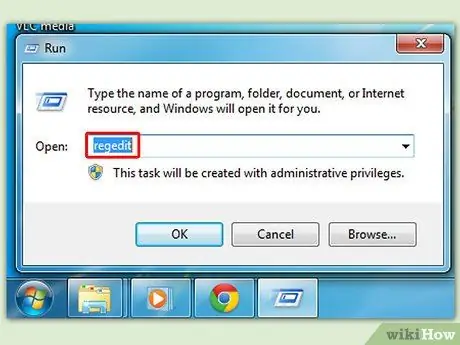
Step 1. Go to the Start menu to open the Run window and then type regedit and press Enter to open the registry editing program
General informations
Method of Archiving the Register
- On Windows 95, 98 and Me, the Registry is contained in two hidden files in the Windows folder, called USER. DAT and SYSTEM. DAT.
-
On Windows 2000 and Windows XP, the Registry is stored in several Hives, which are located in the / windows / system32 / config and / Documents {username} folders
Registry structure
- The registry has a hierarchical structure, like the folders on your hard drive. Each branch (identified by the folder icon in the Registry Editor, see below) is called a Key. Each key can contain other keys and Values. Each value contains the true information stored in the registry. There are three types of values; String, Binary, and DWORD - the use of these values depends on the context.
-
There are six main branches (5 on Windows 2000 and Windows XP), and each of them contains a specific portion of the information stored in the Registry. Are the following:
- HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT - this branch contains all file types plus OLE information for the applications that use them.
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER - this branch contains the HKEY_USERS part information for the current user.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE - this branch contains information about all hardware and software installed on your computer. Since you can specify multiple hardware configurations, the current configuration is specified in HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG.
- HKEY_USERS - this branch contains some preferences (such as color and control panel settings) for all users of the computer. On Windows 95 / 98 / Me, the default branch contains the currently logged in user. On Windows 2000 / XP, the default branch contains a template that will be used by newer users.
- HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG - this branch leads to the part of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE appropriate to the current hardware configuration.
- HKEY_DYN_DATA (Windows 95 / 98 / Me only) - this branch leads to part of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE for use with Windows Plug & Play subsystems.
Use the Registry Editor
-
The Registry Editor (regedit.exe) is included with Windows to allow you to view and edit the contents of the registry. When you open the editor, you will see a window divided into two panes. On the left side you will find a tree with folders (see Registry Structure above), and on the right side the contents (values) of the folder you have selected (key).
- To expand a certain branch, click on the small + sign to the left of any folder, or double-click on it.
- To view the contents of a key (folder), click on the desired one, and observe the values listed on the right side. You can add a new key or value by selecting New from the Edit menu. You can rename any value and almost any key with the same method used to rename files; right click on an object and click on rename, or click on an object you have already selected, or press F2 on the keyboard. Finally, you can delete a key or value by clicking on it and pressing Delete on the keyboard, or by right-clicking on it and selecting Del.
Possible changes
Uninstall Programs Manually
- Just because Windows XP offers the Add / Remove Programs feature doesn't mean all applications will appear in the list. Furthermore, even if an application is present, there is no guarantee that the uninstallation will be successful. When you find yourself in a similar situation, with this method you will be able to get rid of the application. Be careful, as these steps may not remove all data associated with the application and may have an effect on other programs. Create a restore point.
- Find the application folder and delete all files in the folder. Also delete the folder.
- Open regedit and find HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SOFTWARE, then look for the application folder. Delete the folder.
- Open regedit and find HKEY_CURRENT_USER / SOFTWARE, then look for the application folder. Delete the folder.
-
To remove the application entry from Add / Remove Programs (if any), open regedit and navigate to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SOFTWARE / Microsoft / Windows / CurrentVersion / Uninstall key and find the application folder. Delete the folder.
Some applications have Services attached to them. If this is the case, open HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / System / CurrentControlSet / Services and find and delete the service
-
On Windows Explorer, open the individual user settings and delete the program references. The most common places to look are:
- C: / Documents / All Users / Start Menu / Programs and delete the relevant entries.
- C: / Documents / All Users / Start Menu / Programs / Start and delete the relevant entries.
- C: / Documents \% YourUsername% / Start Menu / Programs and delete the relevant entries. Repeat for each user.
- C: / Documents \% YourUsername% / Start Menu / Programs / Start and delete the relevant entries. Repeat for each user.
-
If you didn't find any entries in the previous steps and the application starts automatically, open
HKEY_CURRENT_USER / Software / Microsoft / Windows NT / CurrentVersion / Windows and delete the entry.
Move the Location of the History Folder
By default, the History files (the URLs of the sites you have visited, sorted by day) are stored in the% USERPROFILE% / Local Settings / History folder. You can move these files to any folder with the following Registry changes:
- Hive: HKEY_CURRENT_USER
- Key: Software / Microsoft / Windows / CurrentVersion / Explorer / UserShellFolders
- Name: History
- Data Type: REG_SZ
- Value: path to the new folder
Delete the Pagefile when you shut down your computer
When Windows is shut down, it leaves the pagefile intact on the hard drive. Some programs may store sensitive information in plain text format in memory (which will then be written to disk). You may want to delete this file for security reasons, or to speed up system defragmentation.
Delete Shared Documents
New in Windows XP is the "Shared Documents" folder that appears in Computer. This is a simple link to another area of the disk. You can prevent this folder from appearing by deleting the following Registry Subkey:
- Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- Key: SOFTWARE / Microsoft / Windows / CurrentVersion / Explorer / My
- Computer / NameSpace / DelegateFolders
- Subkey: {59031a47-3f72- 44a7-89c5-5595fe6b30ee}
- Delete the entire Subkey and everything in it.
You could right click on the subkey and export it before deleting it, just to be safe. This method will also prevent the current user's "Documents" from appearing in the same Computer area. Be careful and make backup copies often when editing the Registry.
Change the Explorer Toolbars
This method will help you add an image to the background of the Explorer toolbar.
- To do this go to HKEY_CURRENT_USER / Software / Microsoft / Internet Explorer / toolbar and add a new string value called BackBitmapShell and set its value to the image path.
- To add a bitmap background to the Internet Explorer toolbar, go to HKEY_CURRENT_USER / Software / Microsoft / Internet Explorer / toolbar and create a new string value called BackBitmapIE5 (for Internet Explorer 5), then set the path of the bitmap file as the value.
Show the Recycle Bin on Computer
- Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
-
Key: SOFTWARE / Microsoft / Windows / CurrentVersion / Explorer / Computer / NameSpace
In NameSpace create a new key called {645FF040-5081-101B-9F08-00AA002F954E}
Now create a Default "Trash" value in the right panel without quotes.
Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Attributes
- 70 01 00 20? Add rename and delete to menu
- 50 01 00 20? It just adds the rename item to the menu
- 60 01 00 20? It just adds the delete item to the menu
- 47 01 00 20? Add cut, copy and paste to the menu
- 40 01 00 20? Return the menu to default settings
Turn off XP Faster
When a user shuts down Windows XP, the system must first stop all running services. Occasionally the services will not stop immediately and Windows will wait for the program to shut down before stopping them. The Windows wait time can be changed in the registry. If you change this setting, the system will stop services faster. To change the setting, follow these directions:
- Open Regedit.
- Open HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SYSTEM / CurrentControlSet / Control.
- Click on the "Control" folder.
- Select "WaitToKillServiceTimeout"
- Right click on the entry and select Edit.
- Set it to a value less than 2000.
View Messages when XP starts
If you want to see a legal message or any other message in a window when Windows starts, you will find the instructions below:
- Open Regedit.
- Open HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SOFTWARE / Microsoft / Windows
- NT / CurrentVersion / Winlogon.
- Change the key "legalnoticecaption" with the name you want to give the window.
- Change the key "legalnoticetext" with the message you want to appear in the window.
- Restart your computer.
Change the Internet Explorer Title
- Hive: HKEY_CURRENT_USER
- Key: Software / Microsoft / Internet Explorer / Main
- Name: Window Title
- Data Type: REG_SZ
- Value: Text
- The text you enter as a value will appear as the title of the Internet Explorer window.
- Note: This method only tested on IE versions 5 and 6.
Warnings
- Some information on deleting the pagefile at shutdown. This setting offers no performance enhancements. The file will not be deleted, but simply overwritten with zeroes. You won't be able to speed up a defragmentation with this method. Deleting the pagefile serves primarily as a security measure. Note that the shutdown will take longer.
- Write down the changes and initial values. You may need to restore the registry to its initial settings.
- It may not be possible to edit the registry in some versions of Windows.
- Editing the registry can be very dangerous, and can cause permanent damage to your system!






