You don't have to feel intimidated by multiplying two-digit numbers, as once you have mastered the underlying mechanism it will be very easy to do the calculations correctly. If you know how to multiply single-digit integers, you're ready to move on to two-digit multiplication. Start by multiplying the first number by the digit corresponding to the units of the second, then repeat the previous operation using the digit of the second number corresponding to the tens. When finished, add the two numbers to find out the final result of the multiplication.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Do Column Multiplication
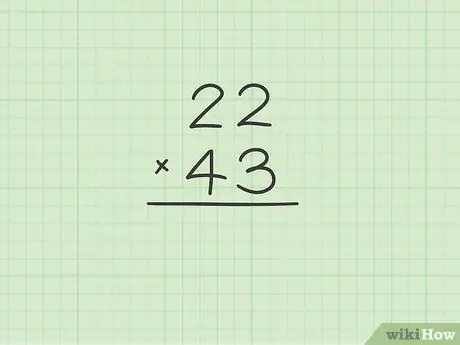
Step 1. Arrange the two numbers to multiply in a column
Start by writing the first factor of the multiplication, then bring the second exactly below the first. Even if there is no predetermined order in which to choose which number to place above and which below, if one of the two factors ends with the number 0, for example 40, it is preferable to set it as a multiplier, i.e. reporting it as the second factor. In this way, the calculations will be simpler and faster.
For example, if you need to multiply the numbers 22 and 43, start by arranging them in a column
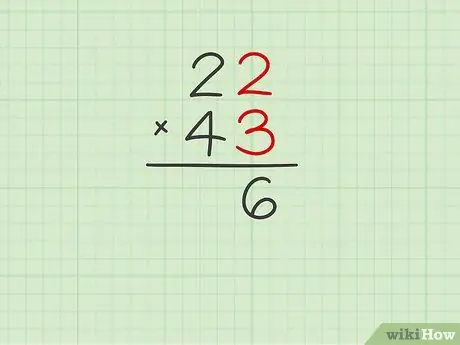
Step 2. Start by multiplying the number corresponding to the units of the multiplier (the multiplication factor shown in the lower part of the column) by the same value as the multiplicand (the multiplication factor shown in the upper part of the column)
For the moment do not take into account the figure corresponding to the tens of the multiplier. Simply perform the indicated calculation and report the result directly below the two numbers you multiplied.
Continuing with the previous example, 22 x 43, you will have to multiply 3 by 2 to get the result 6

Step 3. Now multiply the figure corresponding to the units of the multiplier by that corresponding to the tens of the multiplying
In this case, use the same multiplier number used in the previous step and multiply it by the other digit that makes up the multiplying. After performing the calculations, report the result under the column corresponding to the tens.
Continuing with the previous example, 22 x 43, you have to multiply 3 by 2 (in this case the one related to the tens) obtaining 6. At this point, under the two factors of the multiplication you should have the number 66
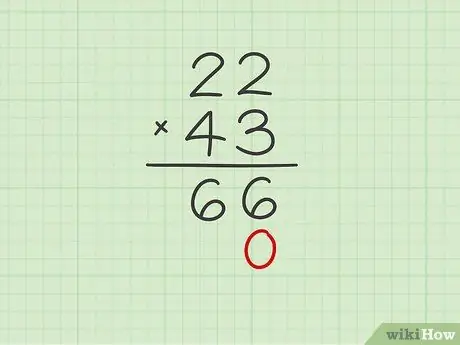
Step 4. Write the number 0 under the units column
Before doing the second part of the multiplication, you need to place a zero below the units column. In this way, you will be forced to write the new result starting from the column corresponding to the tens.
Continuing with the previous example, put a 0 directly below the number 6 in the units column

Step 5. Now multiply the number corresponding to the tens of the multiplier with that corresponding to the units of the multiplying
At this point, you have already done the calculations related to the units, so you need to do the ones for the tens of the multiplying. Write the result to the left of the zero you added in the previous step.
Continuing with the initial example, you will get 4 x 2 = 8. Put the number 8 to the left of the number 0

Step 6. At this point, multiply the number corresponding to the tens of the multiplier with that corresponding to the tens of the multiplying
Write the result on the left of the number you entered in the previous step.
Again you will need to multiply 4 x 2, so bring another 8 to the left of the number 80 you got in the previous step

Step 7. To get the final result, add the two partial products
Being a multiplication between two-digit numbers, at this point you have to add the two numbers you have obtained so far. The result you will get will correspond to the final product of the two initial values.
Concluding the previous example, you will need to add 66 and 880 to get 946, which is the product of 22 x 43
Method 2 of 2: Manage the Carryover
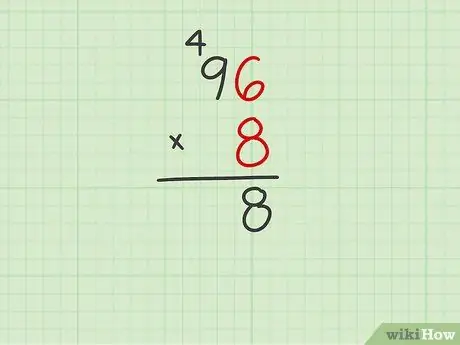
Step 1. When you get a number greater than 9 as the product of multiplying two digits, you need to manage the carryover
If by multiplying two digits of the multiplication factors you get a partial result greater than 9, you have to put the digit corresponding to the tens above the multiplying. Remember to write the carry value above the multiplying figure corresponding to the tens.
For example, if you multiply 96 by 8, when you do the calculation 6 by 8 you will get 48 as the partial result. Instead of putting the number 48 on the result line, just write the value 8, returning the number 4 for the next operation

Step 2. Now do the multiplication by the tens and add the carry over to the result
Continue by multiplying the figure of the multiplier corresponding to the units with that of the multiplying corresponding to the tens, just as you would normally do, then add the number you have reported from the previous calculation to the value obtained.
Continuing with the initial example, 96 x 8, multiply 8 by 9 to get 72, to which you will then have to add the previous carry which is equal to 4, to arrive at the correct partial product of 76. At this point, you will have obtained the result of the original multiplication which will be equal to 768
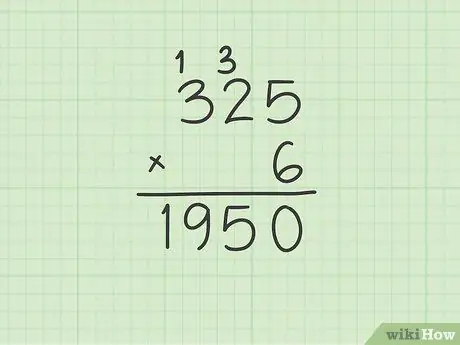
Step 3. If necessary, continue practicing doing multiplications that plan to use carry
If one of the two factors of the multiplication is composed of more than 2 numbers, continue to calculate the partial products using the single digits (units, tens, hundreds, etc.) of the multiplier and the multiplier, as indicated in the article, being careful to keep consider carrying over, where necessary, until you have done all the calculations to arrive at the final result.






