This article shows you how to troubleshoot internet connection issues caused by DNS (acronym for "Domain Name Server") errors. The DNS is actually a server reachable via the web, whose task is to translate the URLs of the requested pages into an IP address that can then be used by the browser and the computer to establish the connection and view the related contents. If the IP address to which a certain URL corresponds were to change and it was not possible to update the one stored in the computer cache or if the DNS server, for any reason, was no longer reachable, the internet browser would no longer be able to connect to a specific website or a group of sites, even if the internet connection is fully functional. However, it is possible to solve all the problems related to the DNS service by carrying out simple checks on the internet connection currently in use, forcing the update of the DNS cache of the computer, disabling network connections that are not used, manually modifying the DNS server that will have to use the system's network connection or by restoring the factory default settings of the router that manages the internet connection.
Steps
Part 1 of 5: Troubleshooting
Step 1. Try connecting to the required website using a different device
If using a smartphone, tablet or computer other than the original one on which the problem arises, you are able to view the requested web page, it means that the malfunction is related to the first device and not to the router or internet connection.
- However, even if with the second device you are unable to connect to the requested website, it is not necessarily true that the cause of the problem is the router that manages the internet connection.
- If you're having trouble accessing a single website, try connecting using a mobile device's data connection. If the problem persists, it is very likely that the site itself is having problems.
Step 2. Try using a different internet browser
This is one of the easiest and quickest ways to find out if your DNS server connection is working. Download a free internet browser like Firefox or Chrome and try using it to access the unreachable web page. If the problem persists, you can eliminate the internet browser from the possible causes, since it is most likely the DNS server set in the network connection that is not responding.
Conversely, if the problem is resolved, try uninstalling and reinstalling the first browser you used. In this way the malfunction should never recur
Step 3. Restart your modem and network router
In this way, the cache of the devices will be cleared and updated, so if the cause of the problem is the latter, the DNS service should start working properly again. To perform this step follow these instructions:
- Turn off the router and the network modem and disconnect both devices from the electrical network;
- Wait about 30 seconds so that the capacitors in the devices are completely discharged;
- Reconnect the modem's power cables, turn it on and wait for it to complete the start-up phase;
- Now reconnect the power cable of the network router, turn it on and wait for it to complete the startup phase.
Step 4. Connect the computer to a network port on the router using an Ethernet cable
If you are already using a wired network connection, you can proceed directly to the next step.
- If you are able to access the offending website or web page using the Ethernet network cable, it means that the problem is most likely limited to the router. To fix it you will need to "reset" the device.
- If even using a wired network connection you are unable to access the desired website, then the problem is most likely with the DNS service.
Part 2 of 5: Delete the DNS Cache Contents
Windows

Step 1. Access the "Start" menu by clicking the icon
It features the Windows logo and is located in the lower left corner of the screen. Alternatively, you can press the ⊞ Win key on your keyboard.
Step 2. Perform a search using the "Start" menu and command prompt keywords
This way, the computer will search the entire system for the "Command Prompt" application.
Step 3. Select the icon
of the "Command Prompt".
It should have appeared at the top of the search results list.
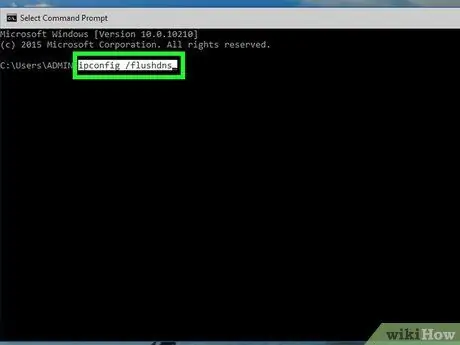
Step 4. Type the command ipconfig / flushdns inside the "Command Prompt" window and press the Enter key
In this way, all the data present in the cache of the DNS service will be deleted. At the next attempt to access a website, a new DNS record for the corresponding URL and IP address will be generated.
Step 5. Now restart your internet browser
This way the program cache will be updated with the new data. If you are now able to reach the specified website, the problem is resolved.
On the contrary, if the problem persists, it means that the cause is most likely the network connection, so continue reading the next method of the article
Mac
Access the Spotlight field by clicking the icon
Step 1.
. It is located in the upper right corner of the screen.
Step 2.
Alternatively, you can press the key combination ⌘ Command + Spacebar
Type the terminal keyword into the Spotlight search field. This will perform a search for the "Terminal" app within the Mac.
Click the icon
to open a "Terminal" window. It should appear at the top of the search results list.
Type the following command in the "Terminal" window:
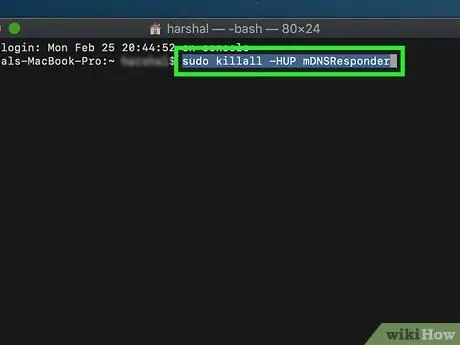
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
At this point, press the Enter key.
In this way, the cache of the DNS service will be cleared, an event that will force it to update.
Before you can run the given command, you will likely need to provide the computer administrator account password
At this point restart the internet browser. This way, the program cache will be updated with the new data. If you are now able to reach the specified website, the problem is resolved.

Part 3 of 5: Disable Additional Network Connections
Step 1. Access your computer's network settings
-
Windows systems:
open the menu Start selecting the icon
choose the item Settings clicking the icon

Windowssettings select the option
Network and Internet and finally click the link Change card options.
-
Mac:
access the menu Apple clicking the icon

Macapple1 choose the option System Preferences and finally click the icon Network.
Step 2. Review all existing network connections
You should disable all network connections that are not currently in use, including Bluetooth and wireless connections.
One of the most common causes of DNS service failure is the presence of the "Microsoft Virtual WiFi Miniport Adapter" network connection
Step 3. Select an unused network connection
To do this, use the left mouse button by clicking once on its icon.
- On Windows systems, each icon in the "Network Connection" window represents a network connection.
- If you are using a Mac, all configured network connections are listed in the left panel of the window that appears.
Step 4. Delete unused connections
To do this, follow these instructions:
- Sui Windows systems, push the button Disable Network Device placed at the top of the window.
- Sui Mac, press the minus button (-) located in the lower left part of the "Network" window.
Step 5. Try to access the offending website again
If the requested page is displayed correctly, the problem has been resolved. Otherwise, continue reading the article.
Part 4 of 5: Manually Set Up the DNS Server
Windows
Step 1. Select the name of the currently active network connection
It is listed inside the "Network Connections" window. To do this, click it once with the left mouse button.
Step 2. Press the Change Connection Settings button
It is located at the top of the window along with all other available options. Pressing it will display the properties window of the selected connection.
Step 3. Select the "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4)" item
It is located inside the "Connection uses the following items" box of the "Network" tab of the "Wi-Fi Properties" window that appears.
If you can't locate the option under consideration, make sure the Net in the "Wi-Fi Properties" window is checked.
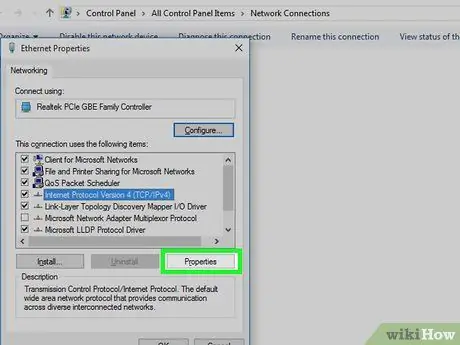
Step 4. Press the Properties button
It is located at the bottom of the window.
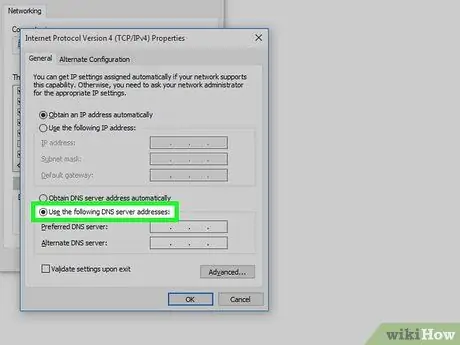
Step 5. Select the radio button "Use the following DNS server addresses"
It is located at the bottom of the newly appeared window.
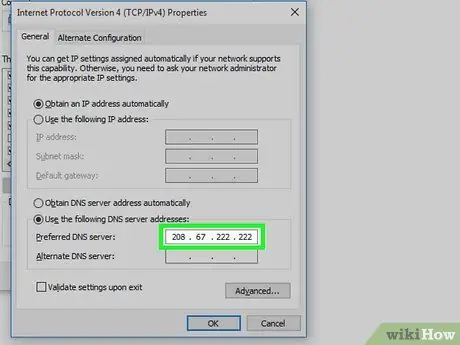
Step 6. Enter the IP address of the DNS server you want the network connection to use
To do this, use the "Preferred DNS Server" field at the bottom of the window. The most secure and reliable DNS servers are:
- OpenDNS - Enter the IP address 208.67.222.222;
- Google - Enter the IP address 8.8.8.8.
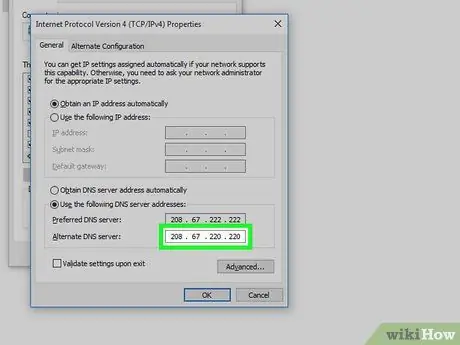
Step 7. Set up an alternate DNS server
To do this, you will need to use the "Alternate DNS Server" field below the previous one. Based on which DNS server you have chosen as your favorite, use the other as an alternative:
- OpenDNS - Enter the IP address 208.67.222.222;
- Google - Enter the IP address 8.8.8.8.
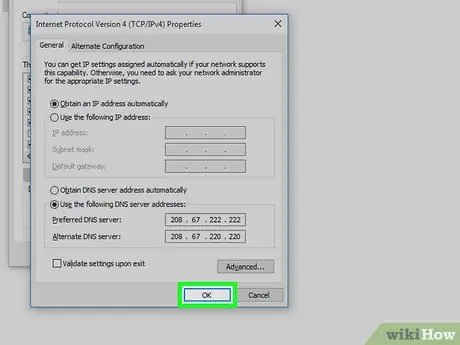
Step 8. Press the OK button
This way the network settings related to the DNS server will be saved and applied.
Step 9. Press the Close button
It is located at the bottom of the window.
Step 10. Restart your computer
At the end of the reboot try to test the correct functioning of the network connection. If the problem is resolved, it means that the cause was the malfunctioning DNS server.
- If you can now access the specified website, consider calling the customer support of your internet connection provider to point out that their DNS servers are malfunctioning.
- If the problem persists, continue reading the article.
Mac
Step 1. Enter the "Apple" menu by clicking the icon
It is located in the upper left corner of the screen.
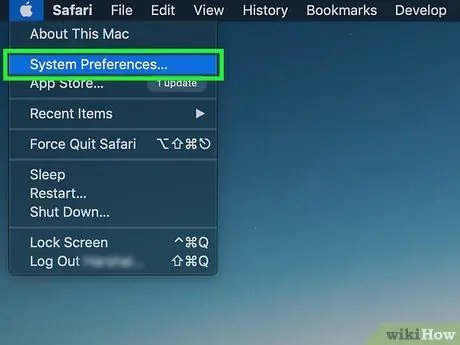
Step 2. Choose the System Preferences option
It is located at the top of the drop-down menu that appeared.
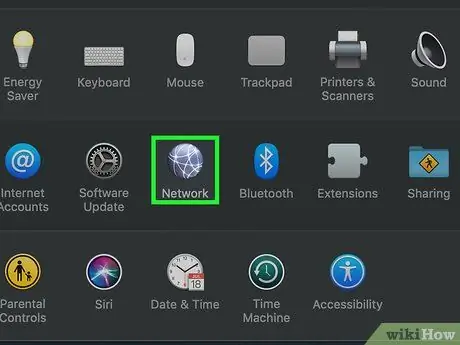
Step 3. Click the Network icon
It is characterized by a globe and positioned in the central part of the "System Preferences" window that appears.
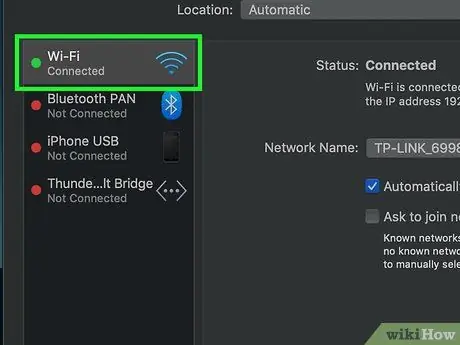
Step 4. Select the Wi-Fi network connection currently in use
It is located inside the left panel of the "Network" window.
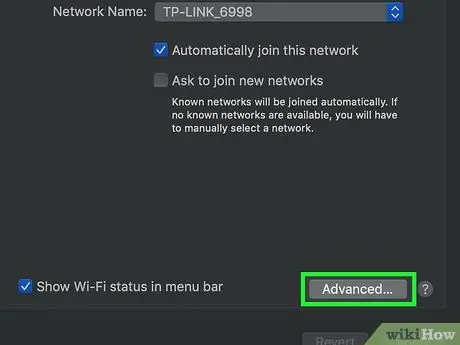
Step 5. Press the Advanced button
It is located in the lower right part of the "Network" window.
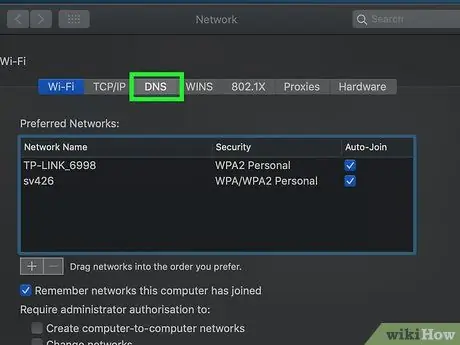
Step 6. Go to the DNS tab
It is located at the top of the newly appeared window.
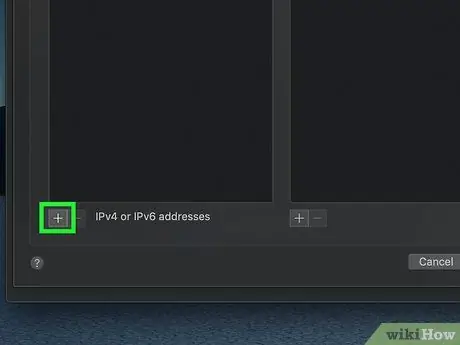
Step 7. Press the + button
It is located below the "DNS Server" box.
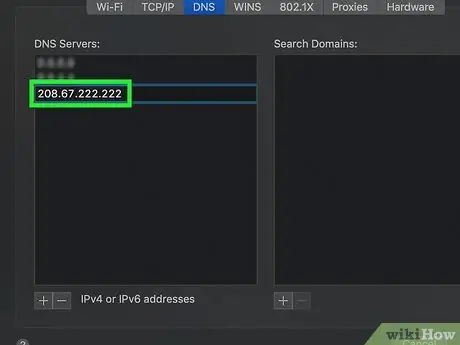
Step 8. Enter the IP address of the DNS server you want the network connection to use
The most secure and reliable DNS servers are:
- Google - Enter the IP address 8.8.8.8 or 8.8.4.4;
- OpenDNS - Enter the IP address 208.67.222.222 or 208.67.220.220.
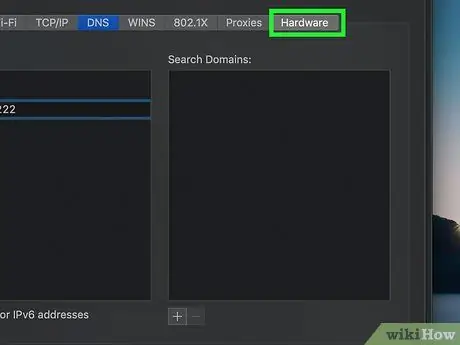
Step 9. Go to the Hardware tab
It is located in the upper right part of the window.
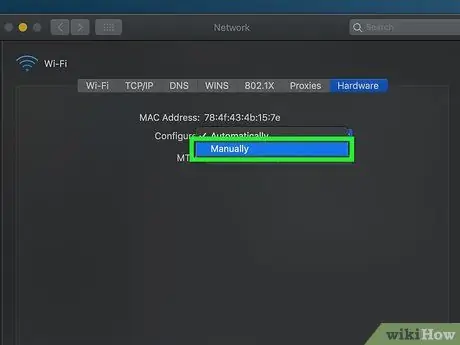
Step 10. Select the "Configure" drop-down menu, then choose the Manually option
It is placed at the top of the card Hardware.
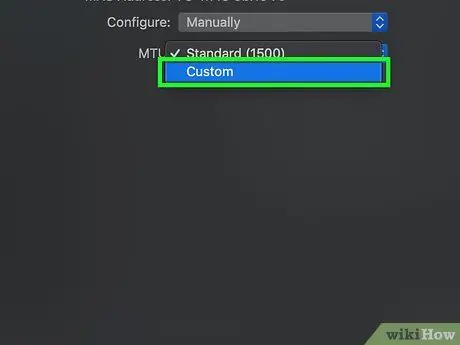
Step 11. Select the "MTU" drop-down menu to choose the Custom option
The "MTU" drop-down menu is located below the "Configure" menu.
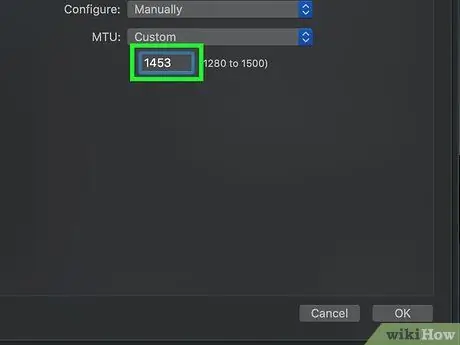
Step 12. Enter the number 1453 into the text field that appeared below the "MTU" drop-down menu
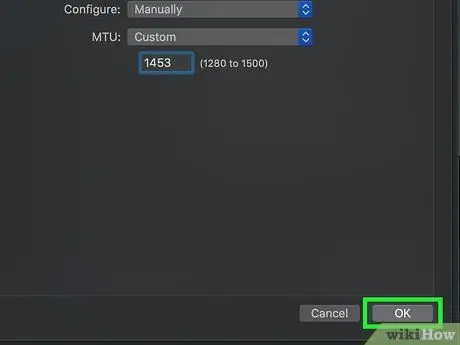
Step 13. Press the OK button
It is located at the bottom of the page.
Step 14. At this point, press the Apply button
This button is also located at the bottom of the page. This way, the new settings will be saved and applied to the currently active Wi-Fi network connection.
Step 15. Restart your computer
After the reboot is complete, try to test the correct functioning of the network connection. If the problem is resolved, it means that the cause was the default DNS server not working.
- If you can now access the specified website, consider calling the customer support of your internet connection provider to point out that their DNS servers are malfunctioning.
- If the problem persists, continue reading the article.
Part 5 of 5: Restore the Network Router's Factory Configuration Settings
Step 1. Locate the router's "Reset" button
It is usually located on the back of the device.
- Most likely, to press the "Reset" button, you will need to use a paper clip, needle or a thin, pointed object.
- Remember that this procedure will disconnect all devices currently connected from the network.

Step 2. Press and hold the "Reset" button
Do this for at least 30 seconds, to make sure the device is reset to factory configuration settings.
Step 3. Connect to your home network
To do this, use the default security password which is normally printed on a sticker on the bottom of the router.
Step 4. Try to access the offending website
If the problem persists, it may be time to contact the customer support of your internet connection provider to report that you are experiencing a DNS service malfunction.






