Losing information stored in a Word file can be really frustrating. Microsoft Word has a native data recovery feature that can help recover information contained in a corrupt document. However, there are other methods to restore a damaged document, which can be used both before and after using this feature, for example if the latter has not had the desired effect. The steps in this guide show you how to recover the information contained in a Word document and, if necessary, how to restore it.
Steps
Step 1. Back up your document
Even if the file is corrupt, making a copy of it gives you a chance to recover the information within it, in case the procedure you want to use to recover the document accidentally destroys the file. Keep the backup file on a USB storage device.
If you have an older version of the document, you may want to back up this file as well, and then try to open it on the same computer or on a second machine. If the final version of the document, which is currently corrupted, differs only in some detail from the previous version in your possession, you will find it much easier to replicate the changes
Step 2. Try opening another Word document on the same computer
Your Word file may not be corrupt. If the second document also doesn't open, it's likely the problem lies with your Word installation and not your document.
Step 3. Look for other copies of your document
If you have a copy of the file on another computer or if you have emailed it to someone, you should have a working copy of your work.
- If you have a copy of the document on another computer, search by creation or modification date. If the file looks identical to the 'corrupt' one, but on the second computer you can open it without problems, it could mean that your PC has an operating system or hard drive problem.
- If you recently emailed a copy of your document, check the 'Sent Items' folder of your email client you sent the email message with. Then download the attached document in a different folder from the one where the corrupt file resides, or even on a different computer, and check if Word can open the new file.
Step 4. Use the 'CHKDSK' system utility
This program allows you to check your hard drive for errors at the file system level. If the application does not find any errors, the problem is limited to the Word document. If any errors are found, CHKDSK may be able to repair your document.
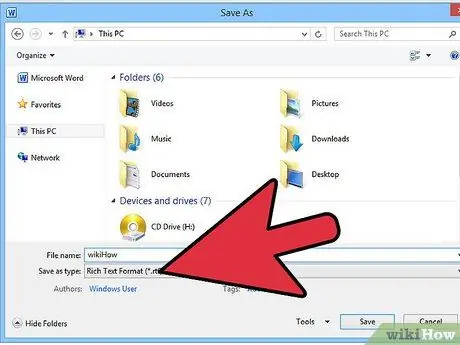
Step 5. Save the document using a different file format
If you are able to open the document with the version of Word installed on your computer, save it in '.rtf' (Rich Text Format) or '.txt' (ASCII text document) format. Doing so may eliminate corrupt code present in '.doc' or '.docx' file formats. After opening the new file, you can safely save it again in '.doc' or '.docx' format to check if the problem has been solved.
- Be careful if you decide to use the '.txt' file format, as it does not support text formatting, for example in the case of using the 'Bold', 'Italic' or 'Underline' style. If your document uses text formatting functions, it is best to create a new file in '.rtf' format to preserve all information regarding the formatting of the text.
- Also remember that some Word documents could be damaged even if saved in different formats, in this case the program would not be able to open them anyway.

Step 6. Try extracting the text using a second text editor
If you are unable to open the document using Microsoft Word, try using a different program that can handle '.doc' or '.docx' file formats. Some of these text editors may allow you to retrieve the information contained in the document.
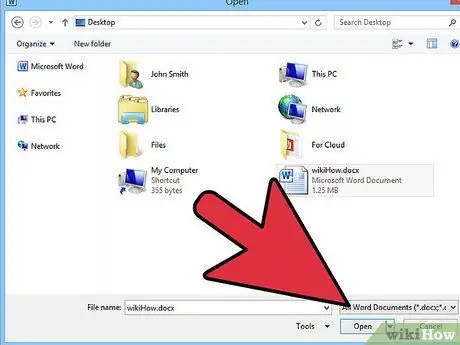
Step 7. Use Word's native function for text conversion
If your Word document was saved in an old '.doc' format, you may be able to recover the stored text using Word's 'Recover Text from Any File' feature. The method by which to use this feature varies based on the version of Word you are using.
- In Word 2003, choose the 'Open' option from the 'File' menu.
- In Word 2007, press the 'Microsoft Office' button located in the upper left corner of the window, then choose the 'Open' option from the 'File' menu.
- In Word 2010, select the 'File' tab, then choose the 'Open' option from the 'File' menu.
- From the dialog box that appeared, relating to your version of Word, select the item 'Recover text from any file' from the 'Files of type' drop-down menu. Then select the file to convert. The program should be able to recover the text present in the document, but any text formatting or graphic objects will be lost. Text in the header or footer should be recovered, but will appear within the body of the converted document text.
- After using this functionality in Word, return the value of the 'Files of type' field of the 'Open' dialog to a commonly used file format, so as not to take advantage of the 'Recover text from any file' function when it is not needed.
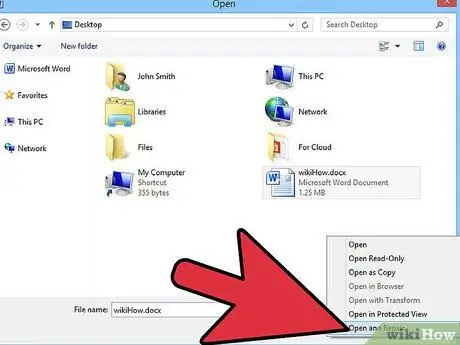
Step 8. Use Word's 'Open and Repair' feature
This feature restores (or at least attempts to restore) a Word document upon opening. To take advantage of this feature, use the following procedure:
- Select the 'Open' option for the version of Word you are using, as described in the previous step.
- Select the file you want to restore using the dialog that appeared.
- Select the button with a down arrow next to the 'Open' button. Then choose the 'Open and Repair' option from the appeared menu.
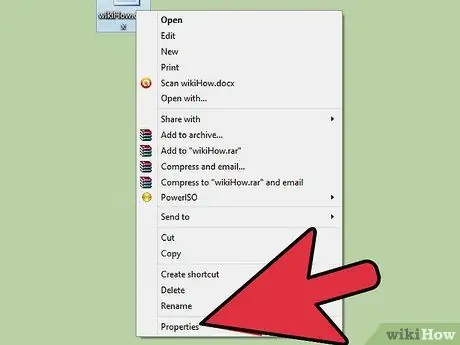
Step 9. Use a 'Shadow' copy of the document
Windows Vista and Windows 7 have the ability to create 'shadow copies' of some files. Check if there are any system copies of your Word document. To do this, select the file with the right mouse button, then choose 'Properties' from the menu that appeared. Select the 'Previous Versions' tab from the displayed property panel, then select one of the available document versions.
- The 'Previous Versions' tab only appears if your computer's hard drive is formatted with the NTFS file system.
- Before you can use the 'shadow copies' feature, you will need to activate and configure it.
- Be careful because 'shadow copies' do not create a complete copy of the system like a backup does.
Step 10. Rebuild the file header by taking the necessary data from the header of another Word file
You will need to open several working Word documents using an advanced file editor in order to identify the header section. This way you can compare the header of the different files with the header of the corrupt file to use the correct one. Once you have found the right header, use it to replace the corrupt file header, repairing it.
Step 11. Use a third party program to restore damaged files
If none of Word's native functionality for recovering damaged documents was successful, try using a third party application, such as 'OfficeRecovery' or 'Ontrack Easy Recovery'. Unfortunately, if your file is severely damaged, even this solution may not solve your problem.






