Hard drives are devices created for data storage used on computers to store the operating system, programs, applications, and files. You can install a new hard drive on a computer to increase its storage space or to simply replace the existing one. This article explains how to install a hard drive on a desktop or laptop computer.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Desktop Computer
Step 1. Make sure you have a computer with a Windows operating system
While it's technically possible to replace an iMac's hard drive, doing so is very complicated and could void your manufacturer's warranty. On the contrary, all Windows computers are conceived and designed to make these routine maintenance operations much easier and faster.
If you need to install a hard drive on a Mac, you can contact an Apple certified service center where you will find highly qualified and trained personnel to perform this operation
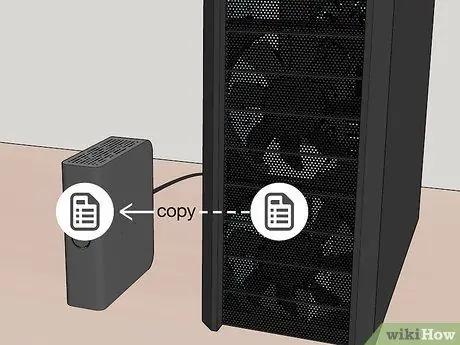
Step 2. Back up the data on your computer
If you need to replace an existing hard drive, you'll need to start by backing up all the data it contains so you can restore it once you've installed the new storage drive.
If you want to install a new hard drive alongside the existing one, read this article for more information
Step 3. Make sure you can install a new hard drive on your specific computer
Before buying the new memory unit you need to be sure that you can then install it inside your computer. If you have chosen to install a second hard drive on your desktop PC, make sure there is a free bay that can accommodate it. If you have an "all-in-one" PC, check that the hard drive installed inside the monitor is replaceable.

Step 4. Purchase a hard drive that is compatible with your PC motherboard
Most modern hard drives adopt SATA connectors, however many of the latest generation motherboards support the use of M.2 SSD memory drives which turn out to be very small, and often faster, than normal SATA hard drives (if the memory unit and motherboard support NVMe protocol).
- SATA drives are produced in two formats, 3.5-inch ones being the most popular and used on desktop computers. Some "all-in-one" PC models can use 2.7-inch SATA disks.
- M.2 SSD memory drives are produced in various formats. The physical dimensions of these memory units are encoded using a 4-digit number. For example, if a unit is marked with the abbreviation 2280 M.2, it means that it is 22 mm wide and 80 mm long; while a 2260 M.2 drive is still 22mm wide, but 60mm long. In order to install an M.2 SSD you need to check that your PC motherboard has an M.2 connector and know what the maximum memory capacity it can handle. The 2280 drives are the most popular and used in desktop computers. In this case, you must also check if the M.2 slot of the motherboard is type M or B. An M.2 SSD with an M connector cannot be inserted into a slot intended for type B connectors. Check your motherboard user manual to find out if it supports the use of M.2 SSD memory drives and to see if it is compatible with the specific model you want to purchase.
-
Solid state memory drives (SSDs) versus traditional hard drives (HDDs):
Standard hard drives are devices that include moving mechanical parts within them. For this reason they are slower in accessing data, but they are also much cheaper. Solid state drives, on the other hand, have no moving mechanical parts and are therefore much faster and quieter, but also more expensive. There are also hybrid drives on the market that consist of a standard hard drive that includes an SSD drive inside. This type of disc is marked with the abbreviation "SSHD".
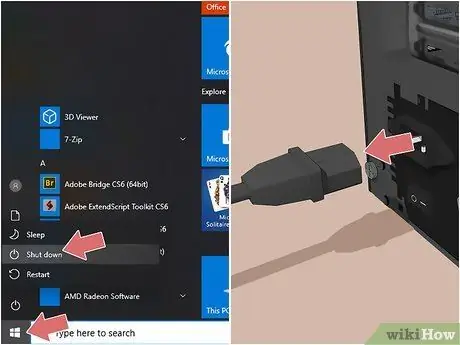
Step 5. Turn off your computer and disconnect it from the mains
Go to the Windows "Start" menu, then click on the "Shutdown" icon. At this point click on the option Shut down the system to turn off the computer. Alternatively, you can press and hold the PC shutdown button located directly on the computer case. Now unplug the power cord and press the power button again to discharge the residual voltage inside the PC components.

Step 6. Remove the computer case panel
To do this, you will most likely need a Phillips head screwdriver. Remove the side panel of the case. In some cases you may need to remove both side panels of the case.
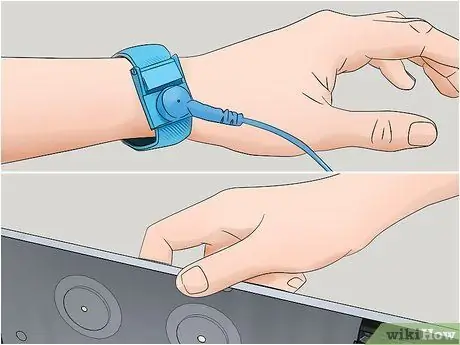
Step 7. Discharge the static electricity in your body to the ground
This will prevent a discharge of static electricity from your body from damaging the delicate internal components of the computer. You can perform this simple step by touching a metal part of the computer case or by wearing an antistatic wrist strap while working inside the computer.
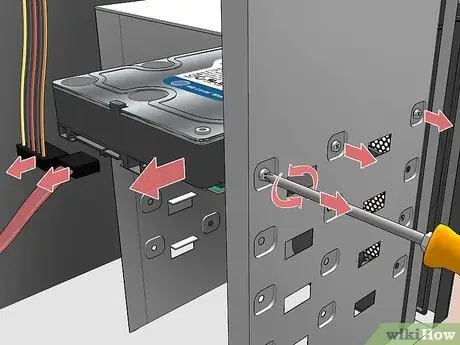
Step 8. Unmount the old hard drive
If you have chosen to replace your computer's current hard drive, make sure you have disconnected both the motherboard data cable and the power cable that comes from the PC's internal power supply. If the hard drive is secured in the hard drive bay with security screws, you will need to unscrew them before you can remove it.
In some cases, in order to gain access to the hard drive slot, you may need to disconnect additional cables or temporarily uninstall cards

Step 9. Remove the current hard drive from its enclosure to be able to mount it on the new one (if necessary)
Some houses adopt a special metal structure in which the hard disk is inserted and then fixed in its slot. If this is your case, you will need to unscrew all retaining screws, remove the old hard drive, install the new one, and retighten all screws.
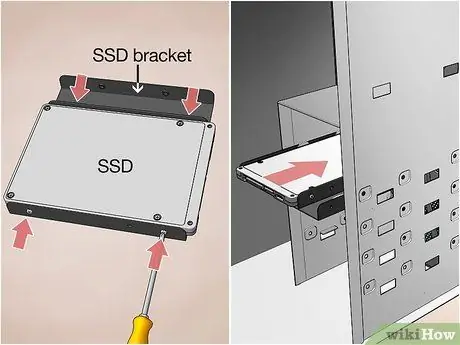
Step 10. Insert the new hard drive into its bay
Install it in the same slot where the old disk was. If, on the other hand, you are adding a new drive to increase system storage space, the new hard drive will need to be installed in a separate bay.

Step 11. Secure the hard drive in place
After installing it in its housing, use the supplied screws to secure it in place. There are usually two screws on each side. If you do not fix it properly, it could vibrate during operation, causing noise and in severe cases physical damage to the internal magnetic platters.
Tighten the screws firmly, but do not use excessive force, as this could still cause damage
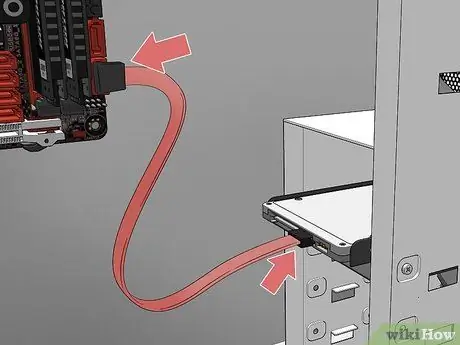
Step 12. Connect the motherboard data bus cable to the hard drive
Modern hard drives use a SATA cable. This is a very thin cable similar to a regular USB cable. Use the SATA cable that came with the drive to connect it to the corresponding port on the motherboard. SATA connectors do not have to be inserted in a specific direction to make the connection.
- If you need to install an M.2 SSD, simply insert it into the slot at a 30 ° angle, then gently push the opposite end of the drive down and secure it to the motherboard with the retaining screw.
- If you are installing the primary hard drive, the connecting SATA cable should be plugged into the first SATA slot on the motherboard. It is usually characterized by the abbreviation "SATA0" or "SATA1". Refer to the motherboard documentation for more information on how to connect correctly.
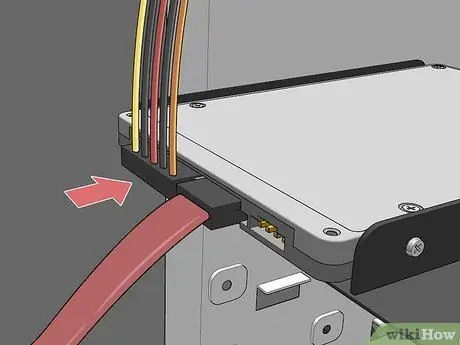
Step 13. Connect the power cable to the hard drive
Modern power supplies have SATA power connectors, while older models only have Molex (4-pin) connectors. If the latter is your case and you need to install a SATA hard drive, you will simply need to purchase a Molex to SATA adapter.
Make sure all cables are firmly connected by moving their connectors slightly

Step 14. Close the computer case
Mount the side panels of the case, secure them with the appropriate screws and reconnect any cables you have disconnected to be able to work in a better position on a more suitable work surface.
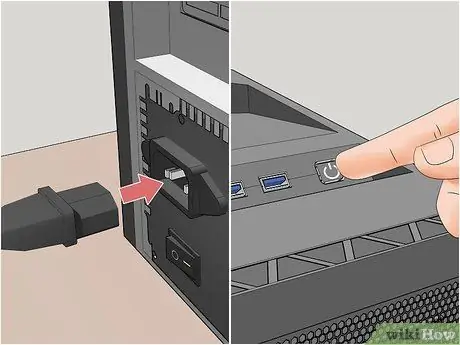
Step 15. Now, plug your computer into the power cord and turn it on
You should immediately hear the classic sound of the hard drive's magnetic platters starting to spin.
If you hear a beeping or grinding clicking noise, immediately shut down your computer and check the hard drive connections
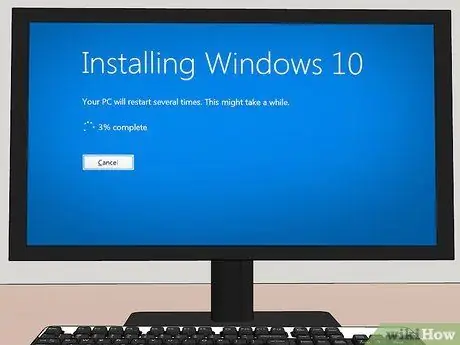
Step 16. Install the operating system
If you've replaced your computer's primary hard drive, the first step will be to install the operating system, as hard drives are completely blank when purchased.
Method 2 of 2: Install a Laptop Hard Drive

Step 1. Back up the data on your computer
If you need to replace your computer's existing hard drive, you'll need to start by backing up all the data it contains, so you can restore it once you've installed the new storage drive.

Step 2. Make sure you can install a new hard drive on your specific laptop model
Before purchasing the new memory unit for your laptop, check the user manual or physically disassemble the lower case cover to make sure you can replace your current hard drive or install a second one. In most cases there will not be a second slot for adding a second disk. On some modern laptops the hard drive is soldered directly to the motherboard, so it may not be swappable quickly and easily.

Step 3. Purchase a hard drive that is compatible with the laptop model you own
Most modern laptops use SATA hard drives. Look for a disk model that is functional for your computer, then buy the one that seems to suit your needs best. Most laptops are equipped with 2.7-inch SATA hard drives. Most modern laptops use M.2 SSDs which have a smaller physical size and are much faster than regular SATA drives.
- M.2 SSD memory drives are produced in various formats. The physical dimensions of these memory units are encoded using a 4-digit number. For example, if a unit is marked with the abbreviation 2280 M.2 it means that it is 22 mm wide and 80 mm long; while a 2260 M.2 drive is still 22mm wide, but 60mm long. In order to install an M.2 SSD, you need to check that the motherboard of your PC has an M.2 connector and know what is the maximum memory capacity it can handle. The 2280 drives are the most popular and used in desktop computers. In this case, you also need to check if the M.2 slot of the motherboard is type M or B. An M.2 solid-state drive with an M connector will not fit into a slot intended for type B connectors. the motherboard user manual to find out if it supports the use of M.2 SSD memory drives and to check if it is compatible with the specific model you want to purchase.
-
Solid state memory drives (SSDs) versus traditional hard drives (HDDs):
Standard hard drives are devices that include moving mechanical parts within them. For this reason they are slower in accessing data, but they are also much cheaper. Solid state drives, on the other hand, have no moving mechanical parts and are therefore much faster and quieter, but also more expensive. There are also hybrid drives on the market that consist of a standard hard drive that includes an SSD drive inside. This type of disc is marked with the abbreviation "SSHD".
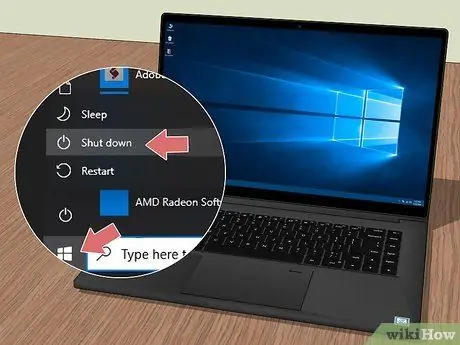
Step 4. Turn off the laptop
Unplug the power cord from your computer, then press and hold the power button until it turns off completely. Alternatively, you can use the menu options to shut down your computer:
- Windows - Click on the Windows "Start" button, click on the "Shutdown" icon and finally on the option Shut down the system.
- Mac - click on the "Apple" menu, click on the option Switch off… and finally on the button Switch off when required.

Step 5. Turn the laptop over
Close the computer screen, then turn it upside down so that the underside of the laptop faces up.

Step 6. Remove the bottom cover of the computer
The procedure to follow varies according to the model of the laptop, but in general you will have to unscrew the fixing screws. Once you've unscrewed all the screws, use a small plastic tool to pry along the edges of the case and gently pry the bottom panel off the rest of the computer.
- In many cases you will have to use specific screwdrivers to be able to unscrew the fixing screws, for example the Pentalobe or Tri-wing models.
- Some laptop models, for example Macs, have several fixing screws even along the edges of the case.
- Be careful when lifting the bottom panel of the computer, as there may be cables (regular or ribbon) connected directly to the motherboard and to the panel itself. If this is the case for you, make a note of the precise location where the cables are connected to the motherboard or anywhere else on the computer, then unplug them very carefully.

Step 7. Discharge the static electricity in your body to the ground
This will prevent a discharge of static electricity from your body from damaging the delicate internal components of your computer. You can perform this simple step by touching a metal part of the computer case or by wearing an antistatic wrist strap while working inside the computer.

Step 8. Remove the battery if possible
In most cases, you will have the option to disconnect the battery from the laptop to prevent an accidental power discharge from hurting you when replacing the hard drive.
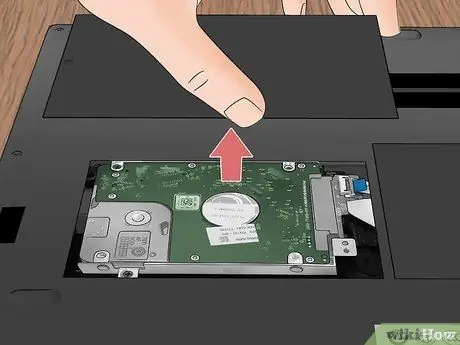
Step 9. Remove the hard drive bay filler panel (if present)
In some cases, the computer hard drive may be inserted into a special bay protected by a panel. The latter is usually identified with a small stylized hard drive printed on it. Typically you will need a small Phillips screwdriver to be able to unscrew the retaining screw and remove the panel.
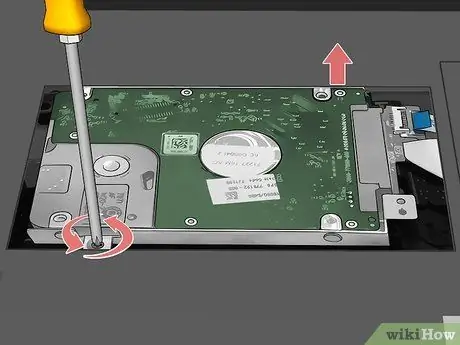
Step 10. Unscrew the hard drive retaining screws
Depending on the laptop model, the hard drive may be fixed in place with some screws. In this case, unscrew them all before removing the hard drive.
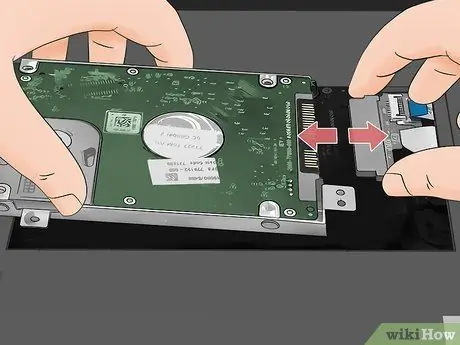
Step 11. Remove the laptop's current hard drive (if needed)
Slide it to the side opposite to where the port it is connected to is. There may be a safety tab that you will need to pull or lift in order to disconnect the hard drive from its port. The memory drive should slide back about an inch allowing you to remove it from its slot.
- In some cases, you may also need to disconnect a cable from the hard drive before you can remove it.
- It is a good idea to temporarily store the old hard drive in a safe place in case you need to recover data.
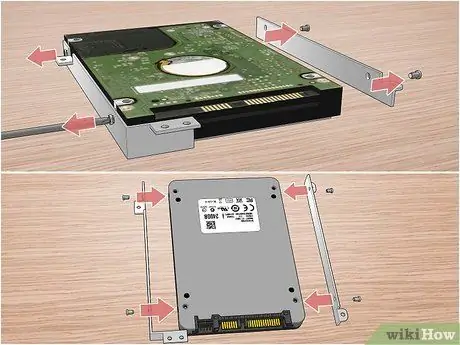
Step 12. Remove the current hard drive from its enclosure to be able to mount it on the new one (if necessary)
Some computers use a special metal structure in which the hard disk is inserted and then fixed in its slot. If this is your case, you will need to unscrew all retaining screws, remove the old hard drive, install the new one, and re-tighten all screws.
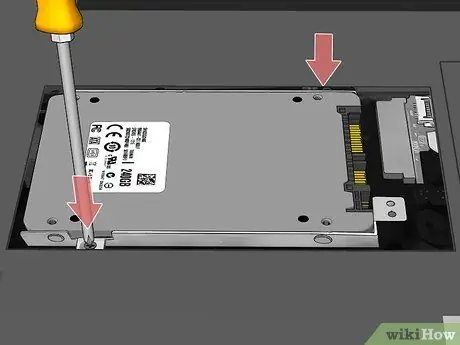
Step 13. Install the new hard drive
Make sure it's facing the right way, then push it firmly towards the connecting door. Do not force the disc if it offers resistance to avoid damaging the connectors.
- If you had to unscrew some retaining screws in order to remove the old drive, use them to secure the new one in place.
- If you need to install an M.2 SSD, simply insert it into the slot at a 30 ° angle, then gently push the opposite end of the drive down and secure it to the motherboard with the retaining screw.
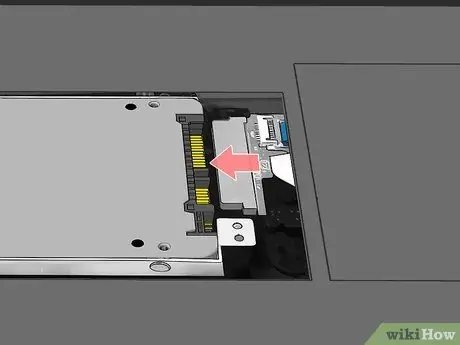
Step 14. Reconnect any cables or electrical wires that you had to disconnect
If you first had to disconnect any cables or wires to remove the original hard drive, reconnect them to the new memory unit.
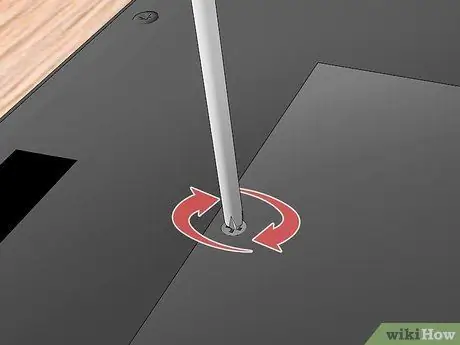
Step 15. Replace the bottom cover of the laptop
Replace the bottom of the computer and secure it using the mounting screws.
If you had to disconnect any connecting cables to remove the bottom panel of your laptop, be sure to reconnect them properly before reassembling the computer
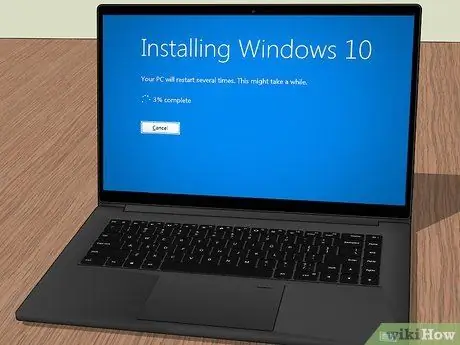
Step 16. Install the operating system
If you've replaced your computer's primary hard drive, the first step will be to install the operating system, as hard drives are completely blank when purchased.
Advice
- All hard drives dissipate heat while they are running. If your computer has multiple bays for installing multiple hard drives, consider leaving an empty slot between each drive to help promote free airflow and optimize cooling.
- Pay close attention to static electricity discharges when you have to work closely with the internal components of a computer. In this case, before starting to work inside the device, you should always wear an antistatic bracelet or touch the screw of a metal plate of a light point (if the electrical system is earthed) or the tap of the bathroom or kitchen






