Gimp is a software package with many features similar to Adobe Photoshop, but has a much smaller price tag - it's free!
Steps
Method 1 of 5: Install GIMP

Step 1. Download the latest version of GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program)
You can do this for free from the developer's website. Click the Download GIMP X. X. X link under the GIMP for Windows title. The installation file will begin downloading within seconds.
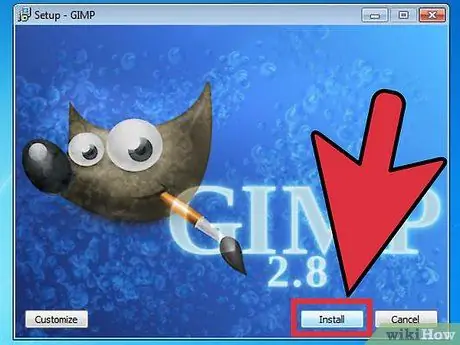
Step 2. Run the installation program
Windows will ask you if you want to run the file. Verify that you have downloaded GIMP from its developer. Select your language to proceed with the installation.
- The GIMP installation program will open. To install GIMP in the default folder, click the "Install" button. To change the installation settings and to choose the additional components to install, select Customize.
- GIMP will automatically associate itself with GIMP image files. To set up to open other file types, select the Customize option. You will be given an option to change file associations.
Method 2 of 5: Start GIMP
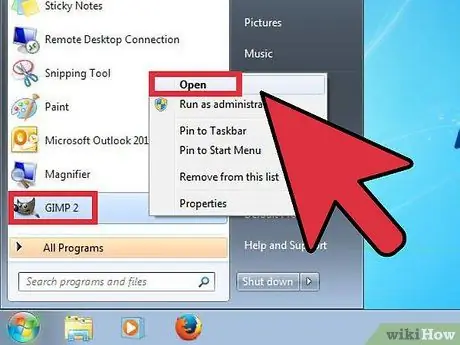
Step 1. Launch the installed program
When GIMP opens, it has to load several data files. This may take a few minutes. Once loaded, several windows will appear. On the left is the Toolbox. On the right is the Levels menu. The window in the middle is where the images will open.
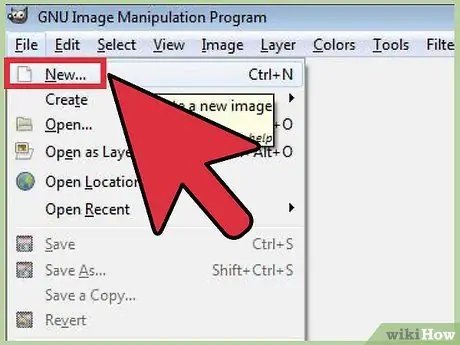
Step 2. Create a new image
To start with a blank image, click the File menu in the center of the window and select New. The Create a new image window will open, asking you for the desired size. You can set the size manually or select from predefined templates using the drop-down menu.
Click OK and the new image will open. The cursor turns into a pen and you can start drawing. Use the Layers and Brushes menu to change the brush type
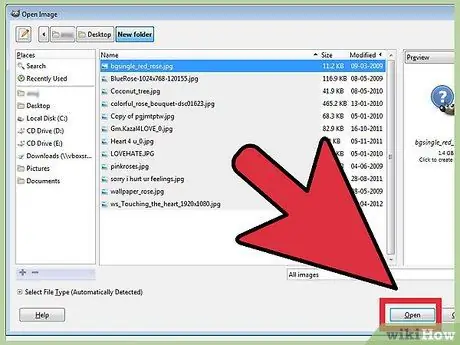
Step 3. Open an existing image
Click File, then Open. Search for the image you want to edit. Once the file is selected, the image will open in a new window.
Method 3 of 5: Cropping an Image
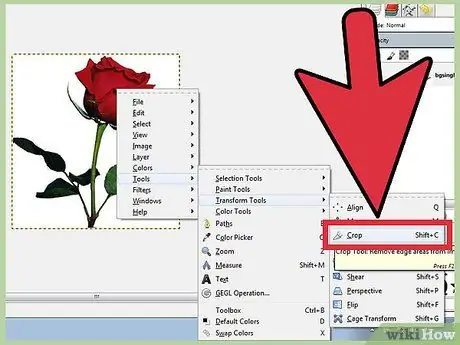
Step 1. Open the image you want to crop
Right-click on the image and select Tools, then Transform Tools and Crop and Resize. The cursor changes to the Cut cursor, which looks like a utility knife. You can also select the cutting tool from the Toolbox.

Step 2. Drag a rectangle that includes the one you want to keep
You don't have to be precise, as you'll be able to edit the rectangle manually. Click the rectangles on the corners or sides to edit.
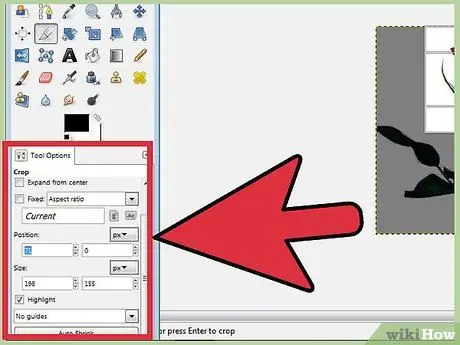
Step 3. Edit the rectangle pixel by pixel
For more precise edits, use Tool Options at the bottom of the Toolbox. You can change the position of the rectangle on the image by changing the numbers in the Position fields. You can finalize the size of the rectangle by changing the values in the Size fields.

Step 4. Cut the image
Once all the changes have been made, crop the image by clicking the center of the rectangle. Everything around the image will be erased, leaving only what is contained in the rectangle.
If you are not happy with the cut, you can undo the action by pressing Ctrl + Z
Method 4 of 5: Flip and Rotate an Image
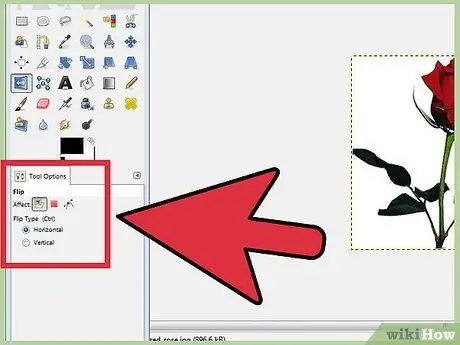
Step 1. Rotate an image
Right-click the image and select Image, then Transform, then Horizontal Rotation or Vertical Rotation. Alternatively, you can click the Rotation icon in the Toolbox. In Tool Options you can choose whether to rotate horizontally or vertically.
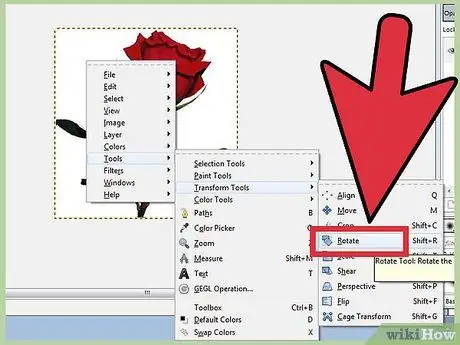
Step 2. Rotate an image 90 °
To perform basic rotations, right-click the image and select Image, then Transform: select whether you want to rotate 90 degrees clockwise, counterclockwise, or 180 degrees.
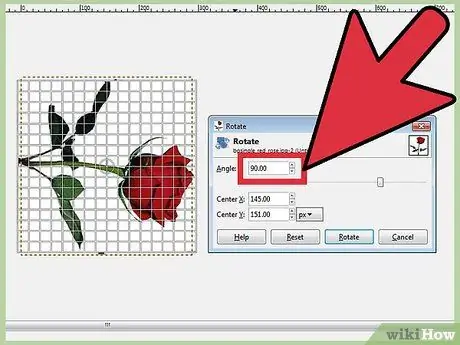
Step 3. Rotate an image to a predefined angle
If you prefer to rotate the image to a predefined angle, right-click the image, then select Tools, Transform Tools, then Rotate. This will open the Rotation tool, where you can set the angle of rotation, by making use of the slider or by entering a number. You can also move the rotation center point by entering coordinates or dragging the circle in the figure.
Method 5 of 5: Gain Mastery of other Basic Functions
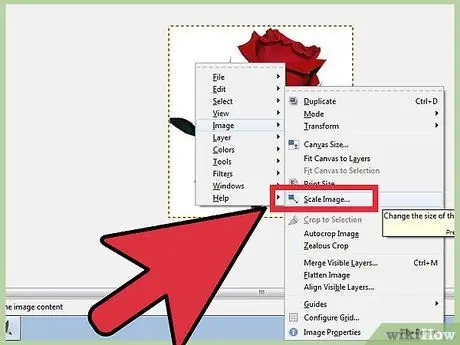
Step 1. Change the size of an image
Right-click on the image. From the menu select Image, then click Scale Image. The Image Scale window will open, and you can change the size of the image. Enter a new value for the width or height and the image will be modified.
- GIMP will automatically keep the same aspect ratio by locking the width and height values. This means that if you change one, the other will also be changed automatically to prevent the image from being stretched or squashed. You can disable by clicking on the chain symbol between the two boxes.
- If you are satisfied with the settings, click Scale to change the image size.

Step 2. Draw a straight line
Select a drawing tool, such as Pencil or Brush. Click the image to create a point from which to start drawing the line. Hold down the Shift key and move the mouse where you want the line to end. You will see a line appear that connects the starting point with the ending point. Click to draw the line. Keep holding Shift to add new lines, each starting where the previous one ended.
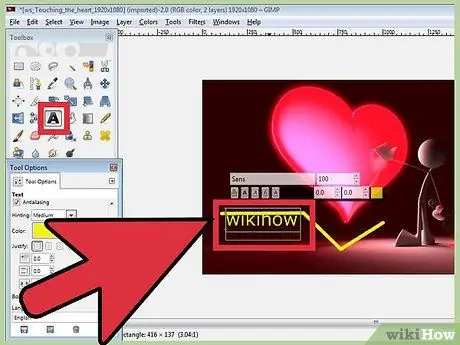
Step 3. Add text to an image
Press T on your keyboard and click where you want to start typing. This will open the Text Toolbox. You can write and the text will appear above the image. Use the toolbox to edit fonts and text effects.
Advice
- The site, www.gimp.org, distributes only the GIMP source code (the building blocks). However, you can download executable versions by following the instructions that can be downloaded.
- There are several support sites on the net for users unfamiliar with the building blocks of free Unix-based graphics software. Note that the www.wiki.gimp.org website has been closed. It is assumed that the site has been relocated, but it is not known where.
- At the bottom of the gimp.org page is a "contact us" link which leads to several other support links, discussions and forums and a wealth of information on the latest versions of GIMP.
- GIMP stands for GNU Image Manipulation Program. GIMP originally stood for General Image Manipulation Program and can be downloaded for free from www.gimp.org. As with all downloadable software, please read carefully to make sure the Operating System is compatible. GNU is a Unix-like operating system developed by the GNU project for the purpose of having a "Unix compatible software system" consisting solely of free software.






