This article tells you how to remove the echo from an audio file using Audacity, a free audio editor for Windows and Mac. Sometimes it happens that the room where you record an audio file creates an echo or background noise. Most audio editors, such as Adobe Audition, have similar tools that can reduce echo and background noise. These methods are most efficient when used on a track with a single voice or musical instrument. In complex tracks with different voices and instruments it is more difficult to isolate the background noise and remove it.
Steps

Step 1. Open Audacity
The program icon represents an audio waveform between two blue headphones.
To download Audacity, visit https://www.fosshub.com/Audacity.html and click on the link for your computer's operating system. After downloading it, double-click the installation file and follow the instructions
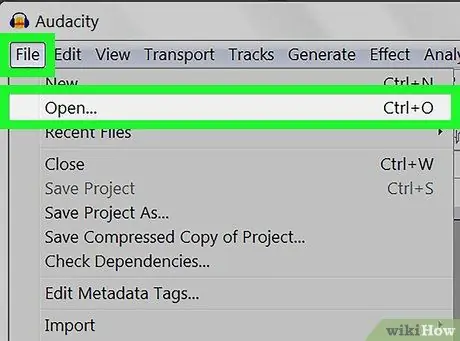
Step 2. Open the audio file
Audacity supports most audio formats, including mp3, wav, aiff, flac, ogg, and ffmpeg. To open an audio file:
- Click on File.
- Click on You open.
- Search and select an audio file.
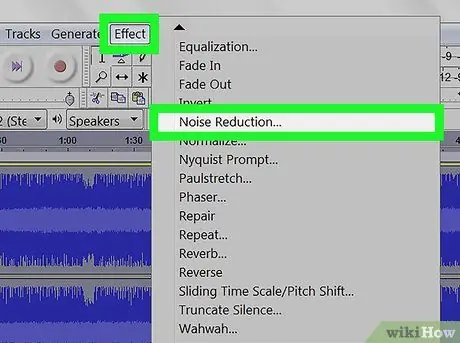
Step 3. Apply noise reduction
To apply it, select all the audio waveform by pressing Ctrl + A on PC or ⌘ Command + A on Mac. Then click on "Effects" in the top bar and choose "Noise Reduction". Increase noise reduction (dB) by moving the slider to the left; this will reduce echo and other background noises. Click on "Preview", in the lower left corner, to listen to the result; when you are satisfied, click on "Ok" to apply the effect.
This process will reduce the volume and alter the pitch of the audio file
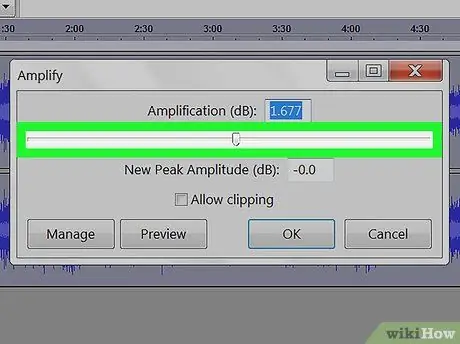
Step 4. Apply amplification
Amplification increases the volume of the audio file. It's at the top of the "Effects" menu list on Audacity's top bar. Drag the amplification slider to the left to turn up the volume as needed. Do not turn it up too much or the sound will be distorted. Click on "Preview" to listen to the result and, when you are satisfied, click on "Ok" to apply the effect. If necessary, re-apply amplification throughout the process.
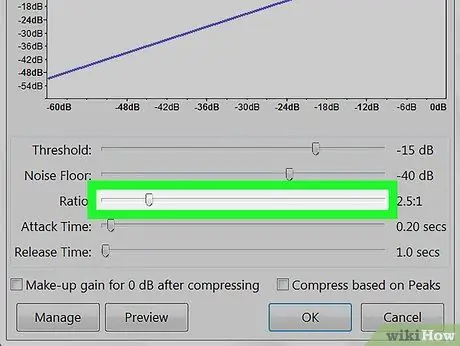
Step 5. Apply compression
Compression reduces the distance between the high and low peaks of the audio wave. To apply compression, click on "Effects" and then on "Compression", drag the slider relative to the "Ratio" item, so that the graph above the sliders drops slightly with respect to its initial position. You can also reduce background noise and threshold. Click on "Preview" to listen to the result and, when you are satisfied, click on "Ok" to apply the effect. This will reduce the volume. If necessary, re-apply compression throughout the process.
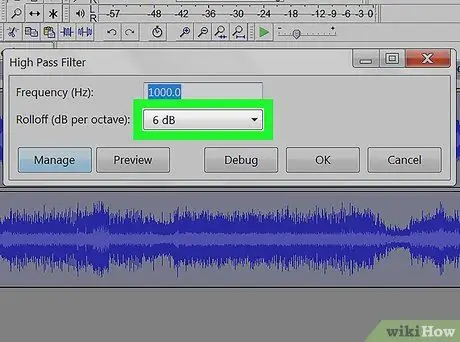
Step 6. Apply Low Pass Filter or High Pass Filter
Depending on how the audio file sounds, you may need to apply low-pass or high-pass filter. If the sound has a high pitch and a lot of hiss, apply the low pass filter. If the sound is low and muffled, apply the high pass filter. You can find both in the "Effects" menu. Use the drop-down menu to choose the roll-off range (dB per octave) from options between 6 dB and 48 dB. Click on "Preview" to listen to the result and then on "Ok" to apply the effect.
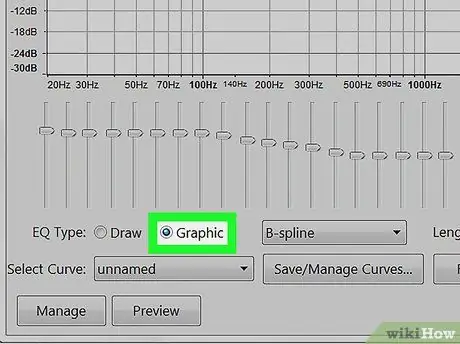
Step 7. Apply Graphic Equalization
To apply graphic equalization choose "Graphic EQ" on the "Effects" menu. Use the sliders to change the equalization. The bars on the left modify the low tones, those on the right modify the high tones, the middle ones the intermediate tones. Click on "Preview" to listen to the result and then on "Ok" to apply the effect.
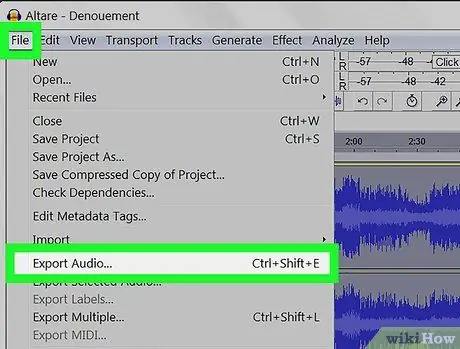
Step 8. Export the audio file
When you are satisfied with the sound of your audio file, you can export it in such a way that you can play it with a media player. To export it:
- Click on File in the top bar.
- Select Export.
- Click on Export as MP3.
- Click on Save.
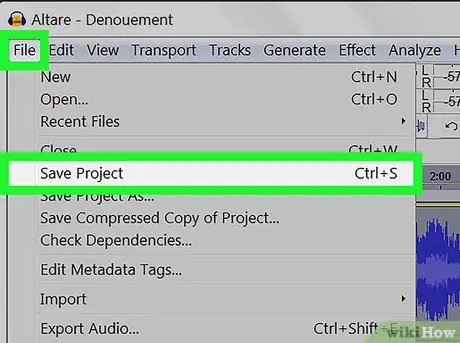
Step 9. Save the project
If you anticipate that you will edit the audio file again in the future, you should save the project. To do it:
- Click on File in the top bar.
- Click on Save project.
- Click on Ok in the popup menu.






