A simple addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are enough to convert Fahrenheit degrees to Celsius and vice versa. The next time you are given temperature data with the wrong scale in a physics assignment, you will be able to convert it in an instant!
Steps
Method 1 of 6: Fahrenheit to Celsius
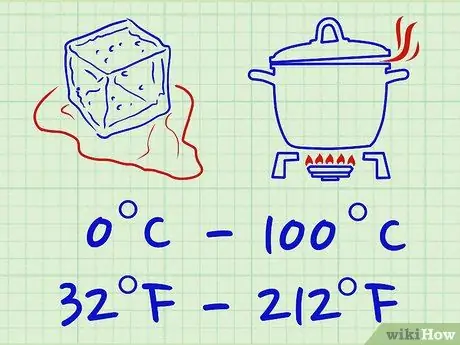
Step 1. Understand the stairs
The Fahrenheit and Celsius scales start with a different number. In the first the freezing point of the water is equal to 32 ° F, in the second it is 0 ° C. In addition to having a different "zero" value, the two scales maintain a different subdivision. For example, the range between the freezing point and the boiling point on the Celsius scale is 0-100 ° C, while for the Fahrenheit scale it is 32-212 ° F.

Step 2. Subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit value
Since the freezing point of water for Fahrenheit is 32 ° F and for Celsius it is 0 ° C, then you need to start the conversion by subtracting 32 from the Fahrenheit value.
For example, your starting temperature in Fahrenheit is 74 ° F, so run: 74 - 32 = 42
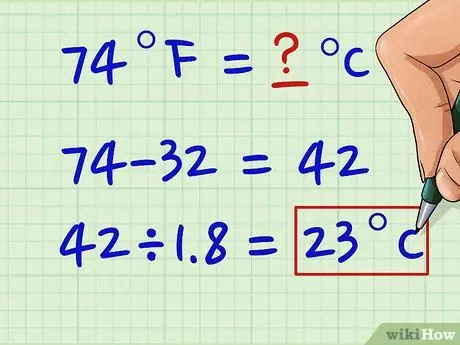
Step 3. Divide the result by 1, 8
The range between the boiling and freezing point on the Celsius scale is 0-100 while on the Fahrenheit scale it is 32-212. This means that every 180 ° on the Fahrenheit scale corresponds to 100 ° on the Celsius one. We can express this relationship with the ratio 180/100 which, simplified, is equal to 1, 8. For this reason you have to divide the difference found previously by 1, 8.
- According to our example, you simply have to do the division 42: 1, 8 = 23 ° C. Therefore 74 ° F corresponds to 23 ° C.
- Note that 1, 8 is equivalent to the fraction 9/5. So, if you don't have a calculator or you prefer to work with fractions, you can use this value instead of 1, 8.
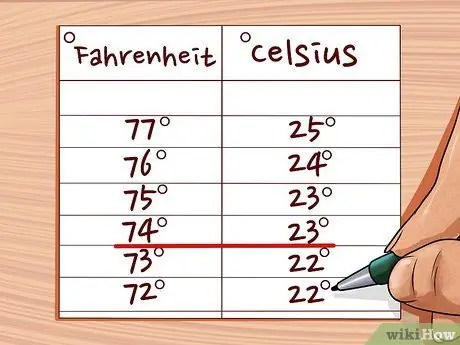
Step 4. Check the result
Here are some reference conversions so that you compare. If your results do not match those shown in this diagram, check the calculations. you may have forgotten some steps, perhaps the initial subtraction.
| ºFahrenheit | ºCelsius (approx.) |
|---|---|
| -40 | |
| -18 | |
| 0 | |
| 16 | |
| 38 | |
| 66 | |
| 100 |
Method 2 of 6: Celsius to Fahrenheit
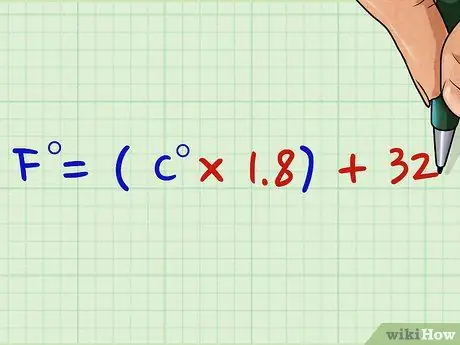
Step 1. Understand the stairs
Since the relationships between the two scales do not change, to switch from Celsius to Fahrenheit degrees you have to proceed with the reverse procedure to that explained in the first method.
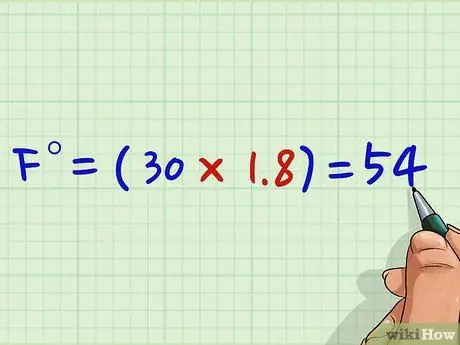
Step 2. Multiply the temperature in degrees Celsius by 1.8
It basically involves applying the opposite process, multiplying the value in degrees Celsius by 1, 8.
Step 3. Suppose you have a temperature of 30 ° C
For example, if you are considering the value of 30 ° C, you simply need to multiply 1.8 x 30 = 54. Instead of 1, 8 you can use the fraction 9/5.
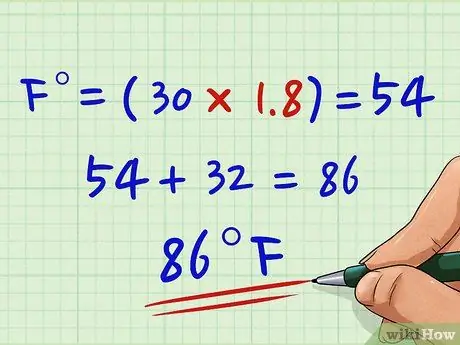
Step 4. Add 32 to the result
Now that you have corrected the difference between the two scales, you also need to realign the starting points. To do this, add 32 to the product you found in the previous step, so you found the temperature expressed in degrees Fahrenheit.
Then add the number 32 to the value you found in step 2 (54): 32 +54 = 86 ° F. The temperature of 30 ° C equals 86 ° F
Step 5. Check the result
Here are some reference conversions so that you compare. If your results do not match those shown in this diagram, check the calculations. You may have made a mistake. Remember to multiply x 1, 8 before adding 32.
| ºCelsius | ºFahrenheit |
|---|---|
| -40 | |
| 32 | |
| 59 | |
| 86 | |
| 140 | |
| 212 | |
| 392 |
Step 6. Make a general comparison
A more general way to compare the two values is to realize that a variation of 5 ° C corresponds to 9 ° F:
| ºCelsius | ºFahrenheit | ºCelsius | ºFahrenheit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -58 | 32 | |||
| -49 | 41 | |||
| -40 | 50 | |||
| -31 | 59 | |||
| -22 | 68 | |||
| -13 | 77 | |||
| -4 | 86 | |||
| 5 | 95 | |||
| 14 | 104 | |||
| 23 | 113 | |||
| 50 | 122 |
Step 7. Understand the conversion
Since the conversion factor is 1, 8 we will have that to each degree ° C of difference correspond 1, 8 ° F, with that idea highlighted in the range between 10 and 15 ° C:
| ºCelsius | ºFahrenheit | ºCelsius | ºFahrenheit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30, 2 | 50, 0 | |||
| 32, 0 | 51, 8 | |||
| 33, 8 | 53, 6 | |||
| 35, 6 | 55, 4 | |||
| 37, 4 | 57, 2 | |||
| 39, 2 | 59, 0 | |||
| 41, 0 | 60, 8 | |||
| 42, 8 | 62, 6 | |||
| 44, 6 | 64, 4 | |||
| 46, 4 | 66, 2 | |||
| 48, 2 | 68, 0 |

Step 8. Round the values to the nearest whole number
If you round the values expressed in Fahrenheit, the difference between 5 and 10 ° C has the pattern 2, 4, 5, 7:
| ºCelsius | ºFahrenheit (rounded) |
|---|---|
| 41 = 41+0 = 41-0 | |
| 43 = 41+2 = 50-7 | |
| 45 = 41+4 = 50-5 | |
| 46 = 41+5 = 50-4 | |
| 48 = 41+7 = 50-2 | |
| 50 = 50+0 = 50-0 | |
| 52 = 50+2 = 59-7 | |
| 54 = 50+4 = 59-5 | |
| 55 = 50+5 = 59-4 | |
| 57 = 50+7 = 59-2 | |
| 59 = 59+0 = 59-0 |
Method 3 of 6: Celsius to Kelvin

Step 1. Understand the stairs
Scientists claim that the Celsius scale derives from the Kelvin scale. Although the difference between the Kelvin and Celsius scale is greater than that between Celsius and Fahrenheit, both still respect the same interval between one degree and another. If the ratio of Celsius to Fahrenheit is 1: 1.8, that of Celsius to Kelvin is 1: 1.
If it seems strange that the freezing point for the Kelvin scale is such a large number (273.15 K) it is because this system of measurement is based on absolute zero, which is 0 K
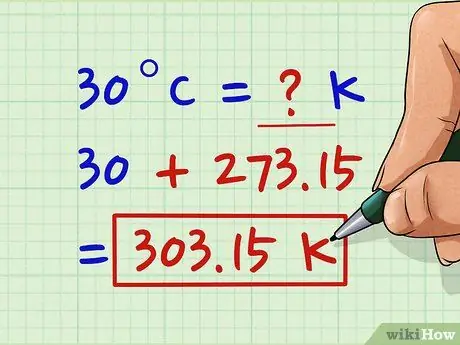
Step 2. Add 273.15 to the value in Celsius
Since 0 ° C is the freezing point of water, scientists put it equal to 273.15 K. Furthermore, the two scales have an equal subdivision, so to transform a temperature expressed in Celsius into a Kelvin value just add 273, 15.
For example, if you are considering the value 30 ° C, add it to 273, 15. 30 + 273, 15 = 303, 15 K
Check the results. Here is a rough scale so that you can compare the values you get from your calculations. Note how the Celsius and Kelvin scale have the same rate of increase, so the difference between the two values is always 273, 15.

- If you start with an integer value of degrees Celsius, your result in Kelvin will end with the decimal, 15.
- The lowest possible value for a temperature is -273, 15 ºC = 0 K. If you get negative values in Kelvin, you have miscalculated or are using values that are not possible.
| ºCelsius | Kelvin |
|---|---|
| 173, 15 | |
| 223, 15 | |
| 273, 15 | |
| 323, 15 | |
| 373, 15 | |
| 473, 15 | |
| 773, 15 |
Method 4 of 6: Kelvin to Celsius

Step 1. Understand the stairs
Since the ratio between these two scales is 1: 1, we can apply the procedure of the previous method but in reverse. You just have to remember the value 273, 15 and use the reverse math operation to go from Celsius to Kelvin.
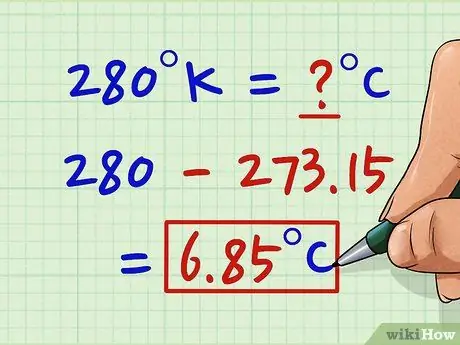
Step 2. Subtract 273, 15 from the value in Kelvin
Reverse the process of Method 3 and subtract this number from the temperature in Kelvin. If you need to convert 280 K to Celsius, then: 280 K - 273.15 = 6.85 ° C.

Step 3. Check the results
If the two values obtained do not correspond to the pattern described in this table, check the calculations.
- If you start with an integer value for Kelvins, the results in degrees Celsius will end with the decimal, 15 (for negative degrees Celsius) or.85 (positive Celsius).
- Notice how the difference between Kelvin and Celsius becomes less important for higher values. When you come to deal with numbers with at least six digits, the difference is often within the margins of error.
| kelvins | ºCelsius |
|---|---|
| -273, 15 | |
| -268, 15 | |
| -223, 15 | |
| -73, 15 | |
| 226, 85 | |
| 726, 85 | |
| approx. 99, 700 | |
| very close to 10 million |
Method 5 of 6: Kelvin to Fahrenheit

Step 1. One of the most important things to remember in this equivalence is the relationship between the two scales
Since the Kelvin scale respects a ratio of 1: 1 to the Celsius scale, then it will have the same ratio to the Fahrenheit that the Celsius maintains. This means that for each Kelvin degree corresponds 1, 8 ° F.
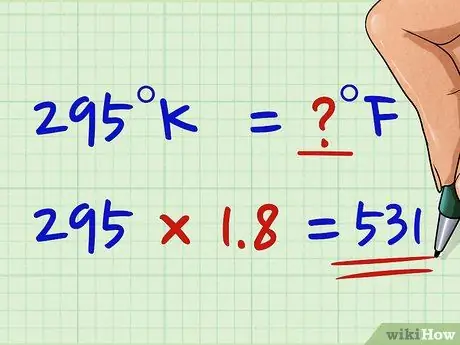
Step 2. Multiply the Kelvin value by 1, 8
To realign the split between the two scales you must first multiply the Kelvin degrees by 1, 8.
Let's consider the value of 295 K. Now multiply it by 1, 8: 295 x 1, 8 = 531
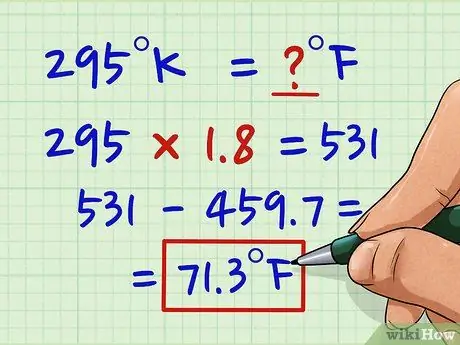
Step 3. Subtract 459, 7 from the result
At this point we have to realign the "zeros" of the two scales. To go from Celsius to Fahrenheit we added 32, to go from Kelvin to Fahrenheit we have to add -459.7 because 0 K = -459.7 ° F. Since it is a negative number, the sum turns into a subtraction.
We proceed with the calculations and remove 459.7 from 531. 531 - 459, 7 = 71, 3 ° F. So 295 ° K = 71.3 ° F

Step 4. Check the results
If your conversion does not match the values in the table, please try again. You may have made a miscalculation or forgotten to multiply before subtraction.
- If you start with an integer value in Kelvin, the result in degrees Fahrenheit will end with the decimal, 67 (if ° F is negative) or, 33 (if ° F is positive).
| Kelvin | ºFahrenheit |
|---|---|
| -459, 67 | |
| -450, 67 | |
| -369, 67 | |
| -99, 67 | |
| 440, 33 | |
| 1.340, 33 | |
| approx. 180,000. |
Method 6 of 6: Fahrenheit to Kelvin
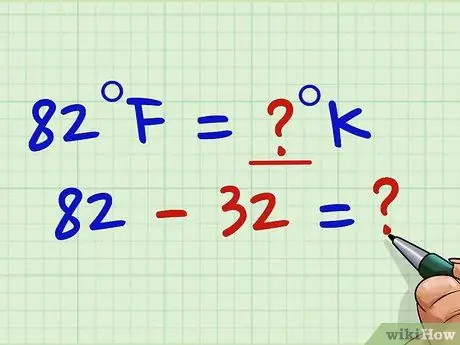
Step 1. Subtract 32 from the temperature in Fahrenheit
In this case, to switch from Fahrenheit to Kelvin it is easier to first convert Fahrenheit to Celsius and then from here to switch to Kelvin. First, then, let's subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit value.
If we are working with the 82 ° F value we execute: 82 - 32 = 50

Step 2. Multiply the result by 5/9
When you go from Fahrenheit to Celsius you have to divide the difference you found by 1, 8 or multiply by 5/9.
50 x 5/9 = 27.7 this is the Fahrenheit temperature value expressed in Celsius

Step 3. Add 273, 15 to this result
Since the difference between Celsius and Kelvin is 273.15, then just add this value to conclude the equivalence.
273.15 + 27.7 = 300.9 So 82 ° F = 300.9 K
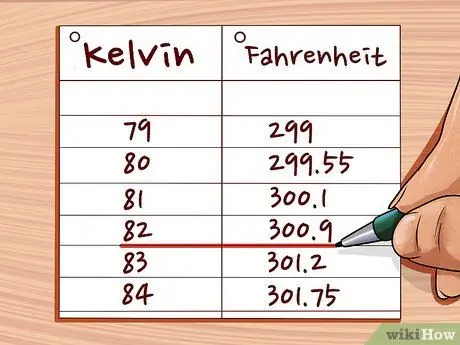
Step 4. Check the results
Compare the obtained values with the following table. If they don't seem to match, try again. Make sure you subtract before multiplying.
| ºFahrenheit | Kelvin (approx.) |
|---|---|
| 241 | |
| 255 | |
| 273, 15 exactly | |
| 294 | |
| 311 | |
| 339 | |
| 373, 15 exactly |
Advice
-
Here are some equivalences worth remembering:
- Water freezes at 0 ° C or 32 ° F.
- Body temperature is usually 37 ° C or 98.6 ° F.
- Water boils at 100 ° C or 212 ° F.
- At -40 both scales are the same.
- Always check the calculations, you will be more sure of your answer.
- When addressing an international audience, do not use the terms 'centigrade' or 'celsius'. Say 'degrees Celsius' instead.
- You can use the formula C = 5/9 (F - 32) to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, e 9 / 5C = F - 32 for the opposite conversion. These formulas are the simplified version of the equation: C / 100 = F-32/180. Since the freezing point on the Fahrenheit scale is 212, we have to subtract 32 ° F from the Fahrenheit value (F-32) and then again 32 from 212 and so we get 180. In this way we realign the two scales in equal intervals.
- Remember that Kelvins are always 273, 15 ° more than Celsius.






