If you have to write your thesis for a master's degree, you will already know that you have to start from a central question and give it a meaningful answer. The master's thesis is the most important text you will ever write during your academic career and will serve you to culminate it. A pertinent thesis statement forms the backbone of this essay and makes it interesting and innovative, and never banal.
Steps
Part 1 of 5: Choose a Topic

Step 1. Think about the goals of writing a thesis
You will spend a lot of time on this project, so choosing a topic wisely is essential. Typical objectives are (in order of importance, from most popular to least common):
- To get a degree - the subject should be difficult enough, but also manageable;
- To appreciate the work - a subject you are particularly interested in, so as to avoid getting bored during the writing;
- To get a job later - if you already know what you would like to do after your studies and which company to turn to, it might be useful to choose a specific topic that can help you reach that type of milestone;
- To be useful - a thesis could actually be useful in helping you make the world a better place to live.
Step 2. Generate ideas for the thesis
Start thinking about your field in its entirety. Where are the gaps in the literature? What kind of new analytics can you offer? Then think about what you particularly like in your field of study and what you have learned in an educational way. Try to connect the two to create a thesis that is enjoyable for you to write and relevant to your studies.
- Try thinking about your favorite subject or subject of study - it can be a particular author, a theory, a historical period, and so on. Imagine how you could deepen the study of this issue.
- You might consider taking a look at the essays you've written for your graduate courses and see if you always tend to choose a certain type of topic.
- Consult with faculty members or your favorite professors. They may give you some good suggestions which you can then develop. Generally, you are required to meet your supervisor at least once before starting work.
- Consider consulting with industry partners. Your favorite company may have some jobs that could be developed as a master's thesis. This could also help you get a job at that company later and perhaps some form of pay for the dissertation.
- If you aim to help make the world better, you may want to consult a local non-profit or charity or do an online search to find possible topics for writing a dissertation.
Step 3. Choose the right topic
Based on the potential topics generated in the previous step, find the one that best fits the goals set in the first step, especially the ones you're most interested in. Make sure you have a specific, detailed and organized program on how to write a thesis that you will be able to defend.

Step 4. Define the focus of the thesis
Carefully consider the questions to be answered in the essay. They should generate important research and questions for members of the academic community and their clients. In the master's thesis, you need to answer the main question with conviction and clarity. Explain it in the presentation of the thesis itself and then in the conclusion. First, however, propose it to those in charge to make sure it goes well.
- Make sure that the question and the answers provided offer original content to an ongoing research, in order to enrich it. A forward-looking thesis will keep the research precise, organized and interesting.
- Once you have determined the topic and direction of the questions, try to formulate 5-10 questions around your research. This forces you to think flexibly about the topic and visualize how small changes in sentence composition can change the direction of your search.
Step 5. Conduct the search
To answer the central question of the thesis, you need to carry out relevant research. Read the texts, organize experiments, do whatever it takes to answer the main question. This allows you to understand if you should continue with the project or if there are intrinsic problems to be solved. In addition, it will help you gather all the information you need to gradually follow the various steps.

Step 6. Choose the speaker and the co-rapporteur
Usually, the student must let himself be guided by two professors in drafting the thesis: the supervisor and the co-supervisor. It is important to contact two teachers you get along with, who have enough time to devote to your project and whose field of interest is relevant to the work you intend to develop.
- Usually, these figures will be determined before formally starting your thesis. Both of them can guide you and offer you input to develop in the project, so the sooner you can do it the better.
- Nothing is more frustrating than a thesis that does not progress due to a professor who has too many commitments to find the time to see you.
Part 2 of 5: Choosing the Sources

Step 1. Analyze the literature of the sector
Make a selection of the texts that have been written and of the research currently available relevant to the topic of the thesis. This literature review must be comprehensive to make sure the final text is original and non-repetitive. It is important that the idea behind the thesis is innovative and relevant. To make sure this is the case, you need to be aware of the context of the research, the views expressed by other subject matter experts, and general ideas about the topic. As you read, take notes on basic information about the subject and the people discussed in the materials available.

Step 2. Choose your primary sources
Primary sources are those written by the person who conceived the idea, story, theory or experiment. They form a basis of important facts that you will use in the thesis, especially if it is analytical.
For example, a novel written by Ernest Hemingway or an article published in a scientific journal documenting new findings for the first time ever are to be considered primary sources

Step 3. Choose secondary sources
The secondary sources were written on the basis of the primary ones. It is important to include them in the thesis because you will need to demonstrate that you have a solid understanding of the critical context of the topic and that you understand what the greatest scholars in the field have to say about the subject.
For example, an essay written on an Ernest Hemingway novel or an article published in a scientific journal examining the findings of someone else's experiment can be considered secondary sources
Step 4. Organize the citations
Depending on your field, you could enter most of the research directly into one of the first chapters of the thesis or include sources throughout the entire document. Either way, you'll generally need to keep track of many different quotes. You may want to write them down as you write, do not try to add them all once you have completed the writing.
- Use the textual citation format intended for your discipline. The most common are the MLA, the APA and the Chicago.
- Each source you cite in the text of the document or in a footnote must then be included in the bibliography or in the list of works cited.
- You could use a software to organize quotes like EndNote, Mendeley or Zotero. They allow you to insert and move citations into the word processor and will automatically create a list of cited works or a bibliography, without your intervention.
Part 3 of 5: Planning a Schedule

Step 1. Know the requirements of your field or department
A thesis in literature has different requirements and formats than a thesis in chemistry. There are two types of master's theses:
- Qualitative. This type of thesis involves the completion of an exploratory, analytical or creative project. Usually, it is a text required for students of the humanities.
- Quantitative. This type of thesis involves carrying out experiments, measuring data and recording results. Usually, it is a text required for students of scientific subjects.

Step 2. Define the idea of the thesis precisely
Prepare a clear statement to express the main question you intend to answer with your research. Being able to explicitly and clearly state the underlying idea is fundamental. If you have trouble defining it, you may need to rethink the whole project.

Step 3. Sketch a structure
The structure is useful for keeping the process under control as you progress gradually with the project. It also allows the speaker and co-supervisor to get an idea of the goal you want to achieve and how you intend to do it.
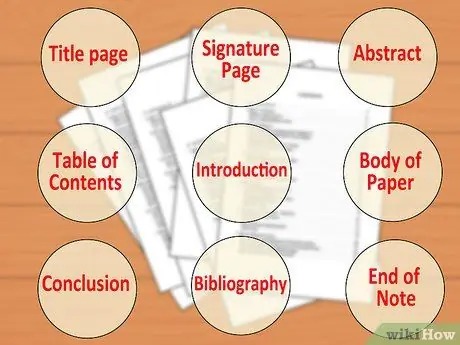
Step 4. Determine the items to include
You should check with the university secretariat for the exact requirements, but most master's theses should include the following parts:
- Frontispiece
- The title must be indicated on the title page; furthermore, this page must be signed by you and the supervisor before delivery to the secretariat.
- Abstract, or a description or summary (of about one paragraph) that summarizes the research carried out in the thesis.
- Table of contents or index (with page numbers)
- Introduction
- Body of the text
- Conclusion
- Works cited or bibliography
- Any necessary appendices or endnotes
Part 4 of 5: Organizing the Writing Process
Step 1. Organize a schedule
One approach that works for many is to use a reverse calendar. This method allows you to plan backwards the writing of the thesis from the date of delivery to the first day. If you know how much time you have to complete the project and break it down into manageable parts with individual expiration dates (knowing these dates can only be of use to you or reminding you when you have to deliver the various chapters to the supervisor and co-supervisor), it will be more difficult for you to scope of the project overwhelms you.

Step 2. Write a little every day
Writing 30 pages accurately in two weeks is a daunting task, but if you write 500 words a day you will be able to meet the deadline calmly. Try not to get frustrated and put off work, as it will build up and become unmanageable.
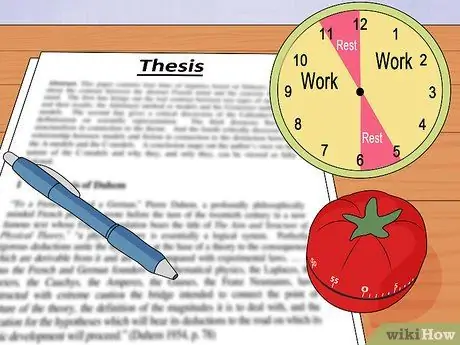
Step 3. Try the "Pomodoro Technique"
Many people who have problems motivating themselves and writing their thesis productively find this strategy useful. The idea behind this tactic? You need to work with full concentration for 25 minutes, then take a five-minute break. This breaks down the work into manageable chunks, so it can ease the anxiety that often accompanies a large, long-term project.

Step 4. Take breaks to unplug
Every now and then, it's important to give your brain a break, especially when you're working on a large project. It is impossible to consistently maintain optimal levels of concentration and attention without running the risk of sacrificing the quality of the content. Plus, having a chance to distance yourself from your ideas for a couple of days will keep you coming back to the text with a fresh mind. You will catch mistakes you haven't seen before and come up with new answers you haven't thought of.

Step 5. Find the perfect time to write
Some work better in the morning, while others are able to concentrate more effectively in the evening. If you're not sure when you're most productive, try different approaches and see which one seems right for you.

Step 6. Write your introduction
Probably, the thesis proposal you sent to the supervisor is a useful springboard for writing the introduction. You may want to copy and paste parts of the proposal for the introduction principle, but remember that it is possible to change your mind in light of the progress made. You may want to revisit and revise several points of the introduction throughout the writing process, perhaps even every time you finish a long section or chapter.

Step 7. Incorporate the literature review
If you have been asked to write a critique of the sources before starting your thesis, good news: you have already completed almost an entire chapter! Again, it may be necessary to reformulate the work and correct it. Additionally, you will likely have the opportunity to add ideas to the review as you go about writing the text.
If you haven't already written a review of the sources, now is the time to do the right research. Sorting the literature in practice involves making a summary of all existing studies on the topic you have chosen, with enough direct citations taken from the primary and secondary sources you refer to

Step 8. Contextualize the work
After analyzing an existing study, you should explain the contribution your work makes to these sources. In other words, you have to explain why the thesis will enrich the topic.
Step 9. Write the thesis
The body of the text varies a lot depending on the field. A scientific thesis involves the use of few secondary sources, because the main body of the text requires the description and presentation of the results of a study. A literary thesis, on the other hand, often constantly cites secondary sources in an attempt to carry out an analysis or reading of one or more particular texts.

Step 10. Write an effective conclusion
The conclusion should indicate in detail the importance of the thesis in the scientific community. It could suggest a direction that can be followed by future researchers to continue to offer information relevant to the discipline.
Step 11. Add disclosure information
Make sure you include relevant tables, charts, and images. At the end of the work, you could also attach appendices relevant to the research, but marginal for the central thesis. Remember that all parts of the text must be formatted according to the guidelines provided by the institution and the discipline.
Part 5 of 5: Concluding the Thesis

Step 1. Review the draft in light of the university's requirements
The formatting rules provided for theses and dissertations are notoriously tedious and complicated. Make sure that the documents adhere to all the requirements indicated by the department (in general) and by the chair of the subject (specifically).
Many departments or programs provide a document to follow as a template for theses and dissertations. If you have one, it would be easier to use it from the start of work (as opposed to copying and pasting your text into it)

Step 2. Reread the entire thesis to correct it
Once you have finished writing, unplug and, if possible, do not read the thesis for a week. Then, reopen it with a fresh mind to catch any grammatical and spelling errors. When you're into the writing process, it's easy to read what you meant instead of what you actually wrote. Consequently, it is important to take a step back so that you can evaluate your work and writing more effectively.
Alternatively, ask a trusted colleague or friend to read the thesis to help you catch any minor grammatical, spelling, and punctuation errors
Step 3. Follow all the guidelines regarding printing indicated in the university regulations
You will have to pay for copies of the thesis out of your own pocket. Generally, you have to deliver one to the secretariat, one to the supervisor and one to the co-supervisor. If you want, it also prints copies for you. Make sure you adhere to these rules to avoid possible hitches in this final step.

Step 4. Prepare for the thesis defense
After completing the drafting of the text, you will have to participate in the discussion to present the ideas explained in the thesis to the members of the commission. This is a great opportunity to demonstrate what you have learned in the process and give professors a chance to ask you questions or raise concerns. Usually, this is more of a conversation than a defense of your point of view, so don't be fooled by the word "discussion".
Step 5. Submit the thesis
Universities usually have very specific guidelines in this regard. Most of them require you to deliver a hard copy and an electronic copy to the secretariat before a certain expiration date. In addition, you will be required to sign a disclaimer regarding the consultation of the thesis. Make sure you stick to the university's rules in this regard.
- To avoid problems, try to stick to the format for hard copy and electronic copy. On the university website you will find all the guidelines in this regard. If you are not sure, ask for specific instructions in the secretariat.
- Write down the due date for the submission of the thesis, which often occurs at least one month before the discussion. Late deliveries may force you to postpone the discussion date, which could adversely affect your job search or further education.
Advice
- A thorough review of the literature and research available on similar topics will save you corrections that will take a long time to submit.
- Remember why you are writing the thesis and the audience who will be interested in reading and using the material. The master's thesis is written for members of a scientific community, so keep in mind that they have vast knowledge and experience on the subject. Don't bore them with useless information.
- Choosing the perfect thesis before starting your search will prevent frustration and save you time. Strictly striving to find the perfect topic is one of the most important steps in learning how to write a master's thesis.
- Consult other people who have written a master's thesis and who have completed this path. It can be a long and exhausting process, so having the support and advice of someone who has been through it before you can be invaluable.






