Minitab is a statistical program that allows you to quickly enter your data and then perform many different analyzes on that data. You can quickly prepare graphs and calculate regression, and data entry is very similar to Excel. Minitab can save you a lot of hard work for your statistical calculations.
Steps
Part 1 of 4: Entering the Data
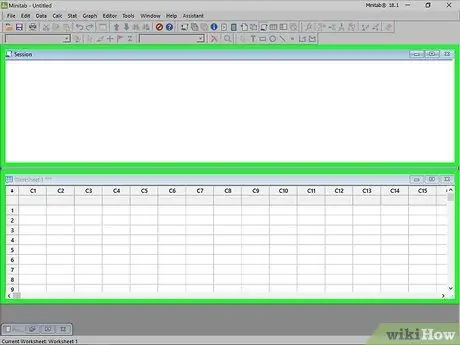
Step 1. Familiarize yourself with the Minitab layout
When you first open Minitab, you will see two main windows: the Session window and the Worksheet window. The Session window will show the results of the analyzes, while in the Worksheet window you will need to enter the data. The worksheet is very similar to that of Excel.
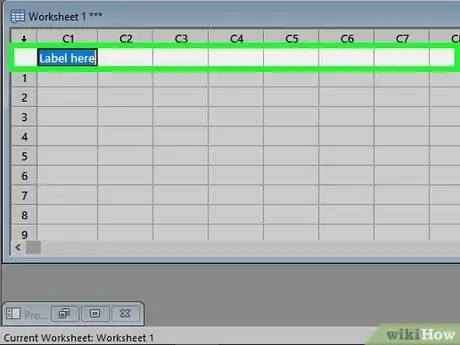
Step 2. Enter the data labels in the second row of the Worksheet
The first row of the sheet is reserved for labels C1, C2, C3, etc. that Minitab assigns to the columns. The second row is dedicated to column labels, which you can enter manually. Just click on one of the empty cells in the second row and type the label for that column.
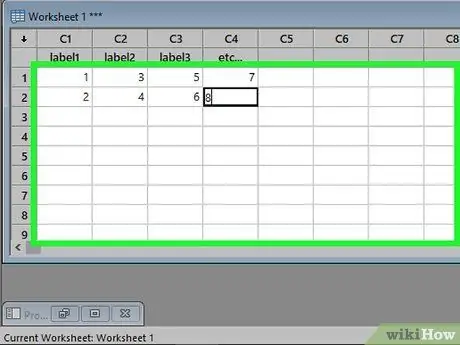
Step 3. Enter the data in the columns
Once you've labeled the columns, you can start entering data. Pressing Enter will take you to the cell below the current. If you click on the small arrow in the upper left corner of the Worksheet, you will be able to change the direction of insertion, so that pressing Enter will take you to the next column on the same row.
- If the data is saved in an Excel worksheet, copy and paste it into Minitab. Select the dataset saved in Excel. Right click with the mouse and select Copy. Go to Minitab and click on the first cell under C1. Right-click with the mouse and select Paste Cells.
- Each column should represent a data type. For example, if you are entering information about a football team, one column could contain Goals, one Attendance and one Yellow Card.
Part 2 of 4: Viewing Descriptive Statistics
Step 1. Learn about descriptive statistics
These statistics summarize a series of data using many important values. Some descriptive statistics include:
- Mean - arithmetic mean value of the data in the column
- Standard deviation - measure of data dispersion
- Median - the central value of a series
- Minimum - the smallest value in a series
- Maximum - the largest value in a series.
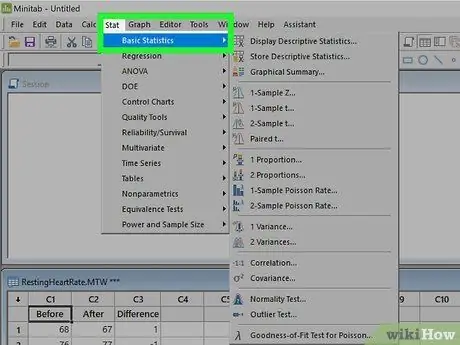
Step 2. Click on the Statistics menu
After entering the data series, click on the menu Statistics at the top of the window. Move your mouse over "Basic Stats".
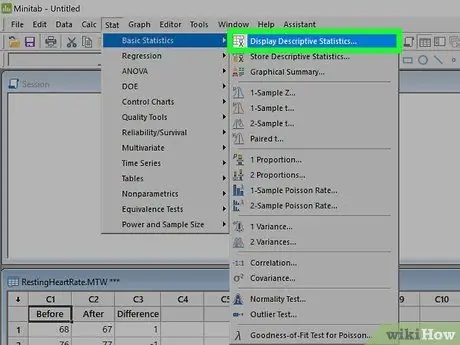
Step 3. Select "View Descriptive Statistics"
The Descriptive Statistics View window will open, showing all columns in a list on the left, and the Variables pane on the right.
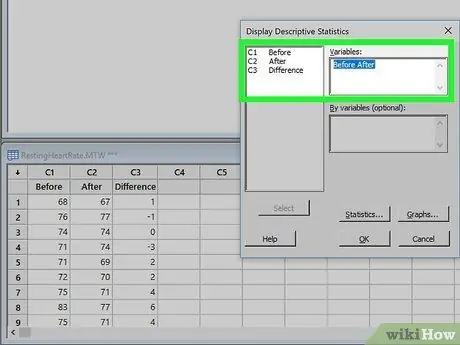
Step 4. Double click on the variable to analyze
The variable will appear in the Variable box on the right side of the window.
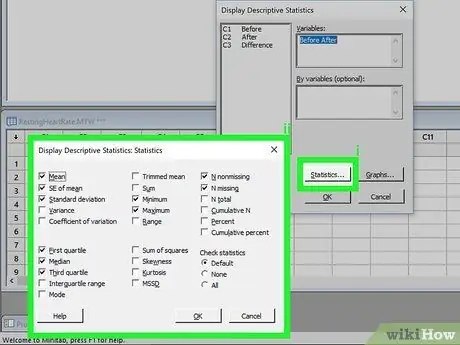
Step 5. Choose the statistics to view
Click Statistics… to select which statistics to display. You can tick the boxes you prefer. Click OK when done.
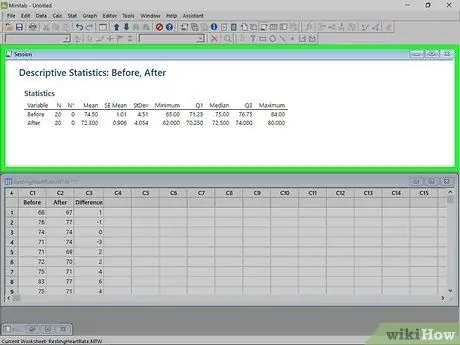
Step 6. Read the result
Click OK in the View Descriptive Statistics window when you are satisfied with the data and statistics options. The descriptive statistics you have selected will appear in the Sessions window.
Part 3 of 4: Creating Graphs and Tables
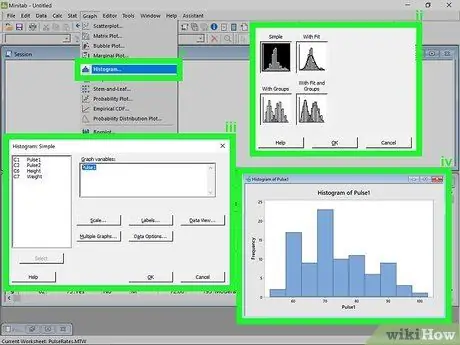
Step 1. Create a histogram
The histogram represents the frequencies in relation to the categories. It allows you to view how often a variable repeats.
- Click on the Graphs menu. After entering the data series, click on the menu Graphic at the top of the window. Select "Histogram…".
- Choose the type of chart. You have 4 options to create a histogram: "Simple", "With Fitting", "With Description and Groups", and "With Fitting and Groups". Select "Simple".
- Choose the data series. You will be able to view the list of available data. Double-click on the one you want to use to create the histogram, then click OK. The histogram will be created and you can view it in a new window.
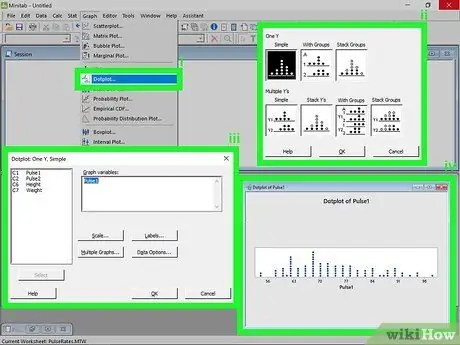
Step 2. Create a dot chart
A dot chart is similar to a histogram in that it shows which values fall into which categories. It is suitable for small data series.
- Click on the Graphs menu. After entering the data series, click on the menu Graphic at the top of the window. Select "Dot Chart…".
- Choose the type of chart. You have seven options when you create a dot chart. Select Simple for now, to create a chart from a single column of data.
- Choose the data series. You will be able to view the list of available data. Double click on the one you want to use to create the dot chart, then click OK. The graph will appear in a new window.
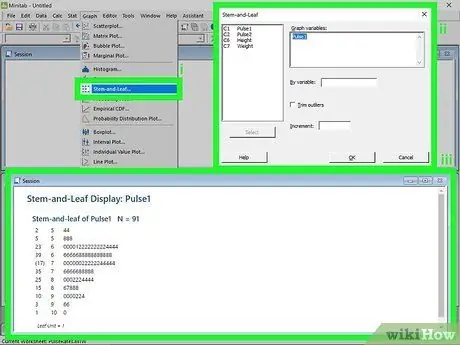
Step 3. Create a stem and leaf chart
This graph is also similar to a histogram. Shows how often a value occurs. It shows the numbers in each category, and contains no visual aspects.
- Click on the Graphs menu. After entering the data series, click on the menu Graphic at the top of the window. Select "Stem and Leaf…".
- Choose the data series. You will be able to view the list of available data. Double click on the one you want to use to create the stem and leaf chart, then click OK. The graph will appear in the Session window.
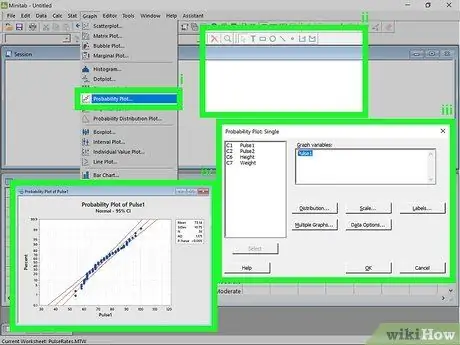
Step 4. Create a probability chart
This graph allows you to quickly identify extreme values and other deviations from the normal curve.
- Click on the Graphs menu. After entering the data series, click on the menu Graphic at the top of the window. Select "Probability Graph…".
- Choose the type of chart. You will have two options for this chart. Choose Single for now.
- Choose the data series. You will be able to view the list of available data. Double click on the one you want to use to create the probability graph, then click OK. The graph will appear in a new window.
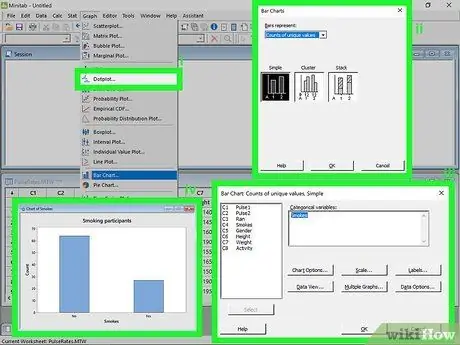
Step 5. Create a bar chart
A bar chart allows you to visually represent your data. It differs from a histogram in that each column of a histogram represents a quantitative variable, while the columns of the bar graphs represent categorical variables.
- Click on the Graphs menu. After entering the data series, click on the menu Graphic at the top of the window. Select "Bar Chart…".
- Choose what to represent with the bars. Use the drop-down menu to choose what to represent with the bars: single value count, function of a variable or values of a table.
- Choose the type of chart. Typically you will choose the Simple chart.
- Choose the data series. You will be able to view the list of available data. Double click on the one you want to use to create the chart. You can add labels to the chart by clicking the Labels… button. Click OK to create the bar chart in a new window.
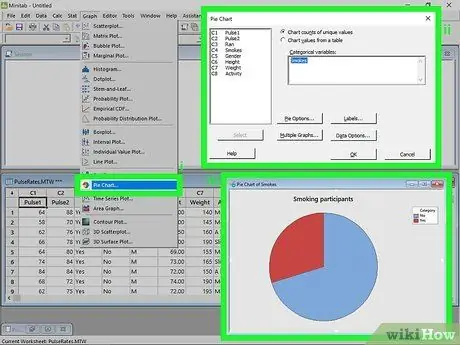
Step 6. Create a pie chart
A pie chart is similar to a bar chart in that the slices of the pie represent categorical variables.
- Click on the Graphs menu. After entering the data series, click on the menu Graphic at the top of the window. Select "Pie Chart…".
- Choose the data series. You will be able to view the list of available data. Double click on the one you want to use to create the chart. You can add labels to the chart by clicking the Labels… button. Click OK to create the pie chart in a new window.
Part 4 of 4: Performing a Regression Analysis
Step 1. Learn how regression analysis works
A regression analysis models the relationships between random variables. There are two types of variables in regression analysis: dependent variables and predictive variables. The values of the predictive variables are chosen to predict the values of the dependent variables, the regression analysis will determine, among other things, how accurate these predictions will be.
Y usually represents the dependent variable and X usually the predictive variable
Step 2. Create the data series
Insert the variables individually in separate columns. Make sure the columns are labeled correctly in the second row.
- Dependent variables: measured in an experiment.
- Predictive variables: the variables whose values determine the changes of the other variables. They are defined as independent variables.
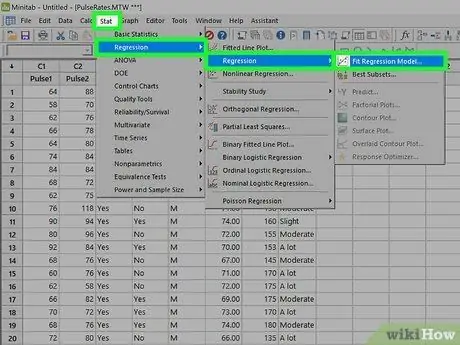
Step 3. Open the Regression Wizard
Click on the menu Statistics and move the mouse to "Regression", then select "Regression…".
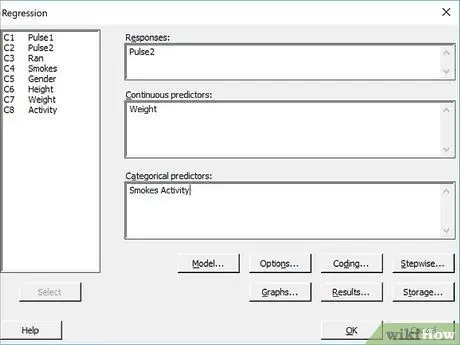
Step 4. Add your variables
Double click on the data set of "dependent" variables. They will be added to the "Answers" field. Then, double click on the predictive variable dataset. They will be added to the "Predictors" field. You can add more variables to the "Predictors" field
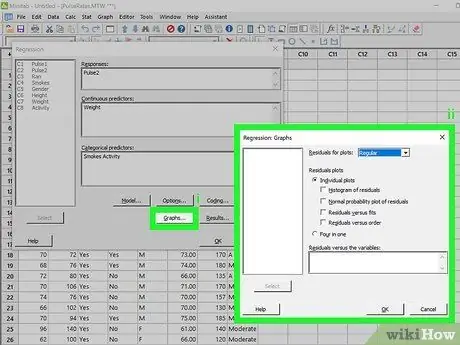
Step 5. Choose any chart
If you want to generate a graph from your analysis, click on the Graphs … button. You can choose the residual graph you want to create. Click OK to complete the selection.
Step 6. Choose to archive the results, as residual and adequate
Click the Archive button to choose which items you want to archive. They will be added in new columns of the worksheet.
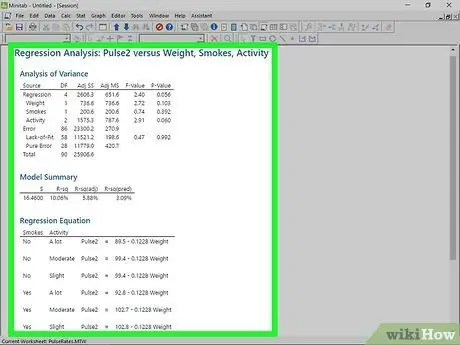
Step 7. Run the regression analysis
When you have finished configuring the options, click OK in the regression window. Minitab will calculate the regression and display the graphs and values you have selected.
- The results of the regression analysis will appear in Minitab's Session window.
- The regression equation gives an approximation of how X predicts Y.
- P-values determine the relevance of predictive variables.
- R-sq describes how well the data fits the model (1 and -1 indicate perfect matches).






