Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a high-level programming language that allows you to write programs to automate functions and tasks within Microsoft Office. This article shows you how to secure your VBA code so that other users cannot modify or copy it.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Password Protect the VBA Code
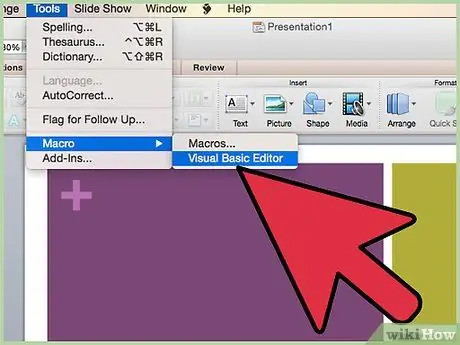
Step 1. Open the Visual Basic Editor
Normally you can do this by accessing the "Tools" menu and choosing the "Macro" option (in Access, depending on your computer configuration, you may need to be inside the database window to access the editor).
-
Go to the "Tools" menu of the Visual Basic Editor and choose the "Properties" option.

Protect VBA Code Step 1Bullet1
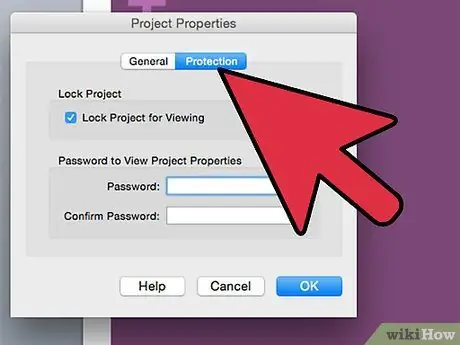
Step 2. Go to the "Security" tab
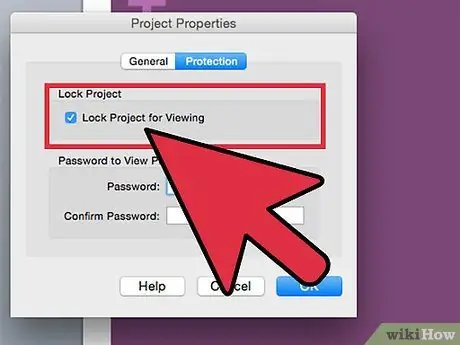
Step 3. Select the "Lock project for viewing" check button
If you do not tick this checkbox, your code will not be hidden and protected from prying eyes.
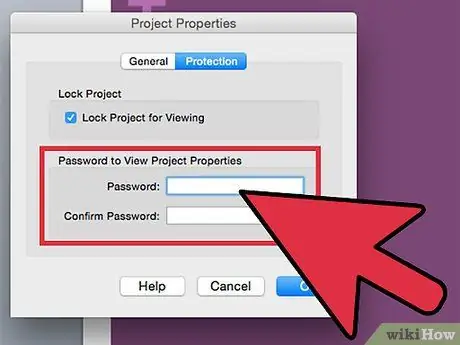
Step 4. Create a login password using the appropriate fields, then enter it again for confirmation
Step 5. Save your changes and restart your program for the new settings to take effect (in Microsoft Excel 2007 and later versions, you may need to save your work in "XLSM" format for your code to work correctly)
Method 2 of 3: Hide VBA Code in Read Only Files Using Access 2007
Step 1. Go to the "Database Tools" tab
Step 2. Locate the "Database Tools" group
Step 3. Choose the "Create ACCDE" option
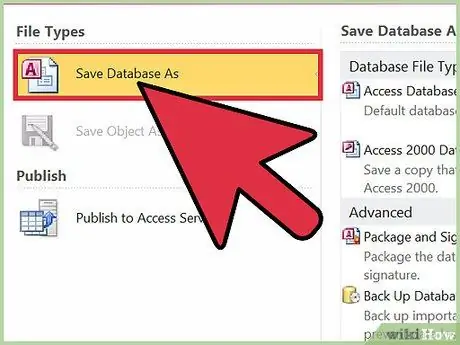
Step 4. Save the file in "ACCDE" format using a different name from the original
The new "ACCDE" file will be created as read-only, in order to make the necessary changes to your work you will therefore need to have the original file as well.
Method 3 of 3: Protect the VBA Code By Creating an Add-on
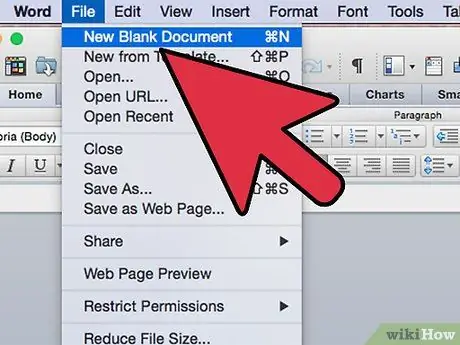
Step 1. Create an empty Office file, of the same type as the one that the VBA code will use (for example if your code works on an Excel sheet, create an empty Excel file)
Step 2. Copy the VBA code into the Visual Basic Editor of the new file
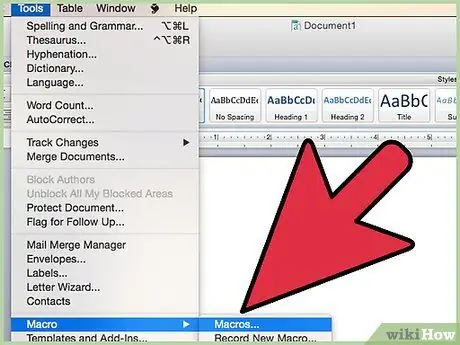
Step 3. Open the "Macro" window, normally available in the "Tools" menu
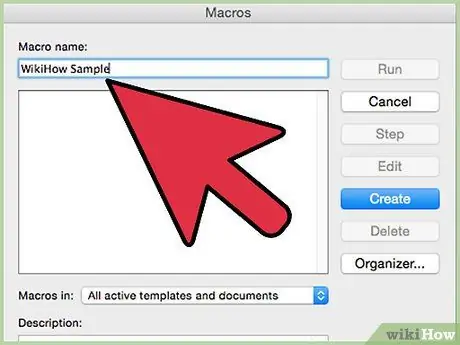
Step 4. Test your code again using debug, making sure everything is working correctly
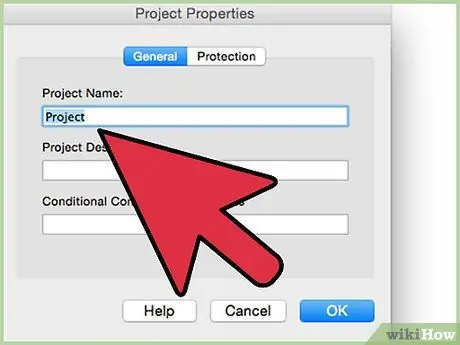
Step 5. Delete any data entered in the new file to be able to test the VBA code
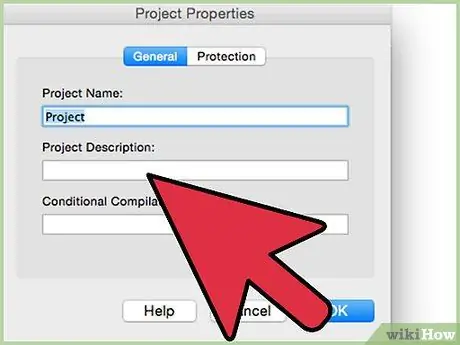
Step 6. Add a description to the macro that your add-on will run (you may need to select the "Options" item for your macro to be able to enter a description)
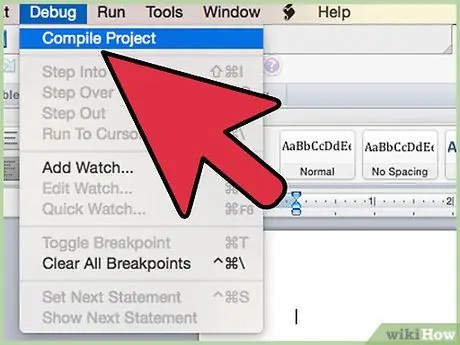
Step 7. Compile the VBA code (from the Visual Basic Editor window, access the "Debug" menu and choose the "Compile VBA project" option)
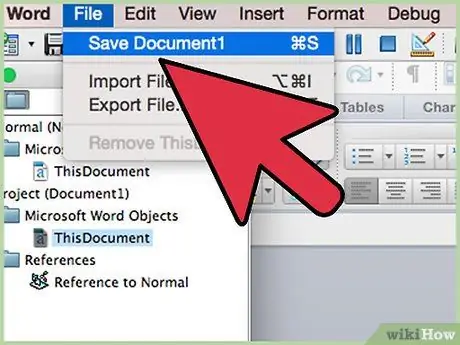
Step 8. Save a copy of the file in its standard format
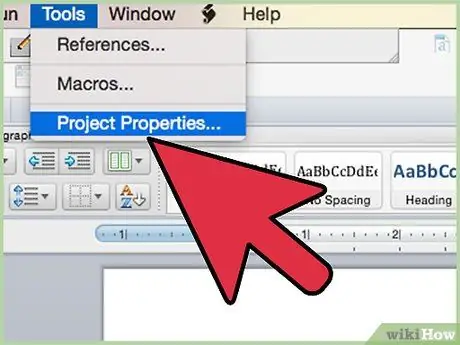
Step 9. Access the "Tools" menu of the Visual Basic Editor window and choose the "Properties" option
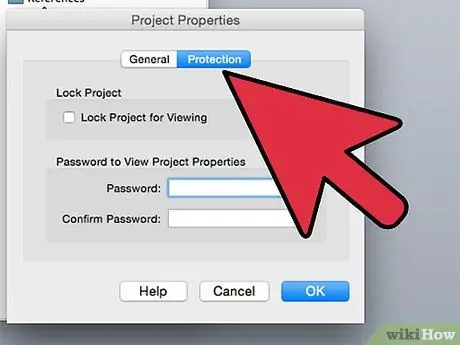
Step 10. Select the "Security" tab
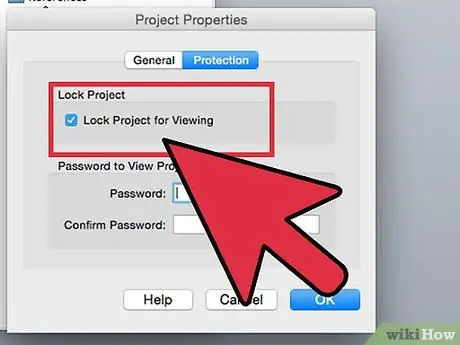
Step 11. Check the "Lock project for viewing" checkbox (depending on the file format you are working on and the settings of Microsoft Office and your computer, you may need to create a login password)
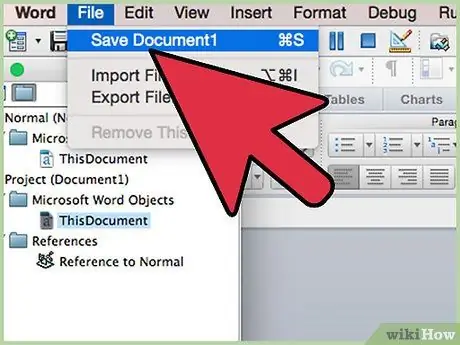
Step 12. Open the "Save As" or "Save a Copy" dialog box
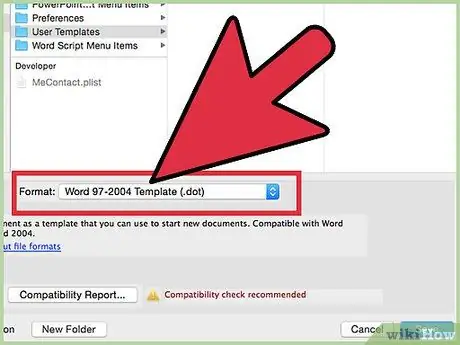
Step 13. Access the file format drop-down menu and choose the appropriate one for the type of add-on you created
- If you have created an add-in for Microsoft Word, use the "DOT" file format (if you want the add-in to run when Word starts, save it in your Office Startup folder).
- If you have created an add-in for Microsoft Excel, use the "XLA" file format.
- If you have created a Microsoft Access add-in, use the "MDE" file format to protect your VBA code (Microsoft Access add-ins can also be saved in "MDA" format, but in that case the VBA code will not be hidden).
- If you have created a Microsoft PowerPoint add-in, use the "PPA" file format. In this case, you will be the only user who can view and edit the VBA code.
Step 14. Close and reopen Microsoft Office
You should now be able to use the add-on you created.
Advice
- If you can't locate the VBA Editor or Add-ons Manager, make sure it is installed on your system. Otherwise, most likely, you will need to use the Microsoft Office installation disc to proceed with adding the programs in question.
- Your Microsoft Office configuration and related settings can change where components and functions are located within each program. If you can't find a specific function, try a quick search in the "Help" using the name of the function in question.






