Heat management is an important element to consider when assembling or maintaining a computer. Too much heat can spell death for sensitive components, and if you're overclocking, that's an added problem. Knowing how to apply thermal paste correctly is one of the fundamentals for proper computer cooling. Follow this guide to learn how.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Surface Preparation

Step 1. Choose the right thermal paste
Most of the basic compounds in thermal grease contain silicone and zinc oxide, while the more expensive compounds contain excellent heat conductors, such as silver or ceramic. The advantage for silver or ceramic thermal grease is that it will have more efficient heat transfer. However, the basic thermal grease suits the needs of most people sufficiently.
If you are thinking of overclocking your computer, try to get thermal paste composed mainly of gold, silver and copper. These are the most conductive metals that thermal paste can be made of

Step 2. Clean the surfaces of the CPU and heat sink
Lightly wipe the surface with a cotton swab or cotton swab moistened with isopropyl alcohol. The higher the alcohol percentage, the better: 70 percent is fine, but 90 percent will be even better if you can find it.

Step 3. Sand the heat sink and processor surfaces if necessary
Ideally, if the two touching surfaces were perfectly flat, there would be no need for thermal paste. If the base of your heatsink was rough, you could sand it down by dampening it and then buff it to make it smoother. This isn't always necessary, unless you're aiming for maximum cooling performance.
Thermal paste is designed to fill in gaps and imperfections on the surfaces that are joining. Since modern manufacturing techniques cannot make surfaces flawless, thermal paste will always be needed
Method 2 of 3: Apply the Thermal Paste on the Circular Base Fans
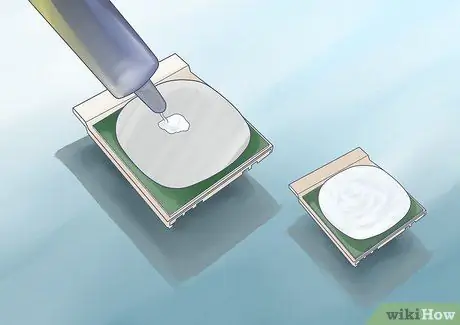
Step 1. Place a small drop of thermal paste in the center of the cooler base
The drop of pasta should be smaller than a grain of rice. If you've read that it should be the size of a ball or pea, it will be way too much and you'll end up with glue on your motherboard.
There is no need to spread the paste for the circular fans, because the pressure applied will spread it evenly over the entire surface
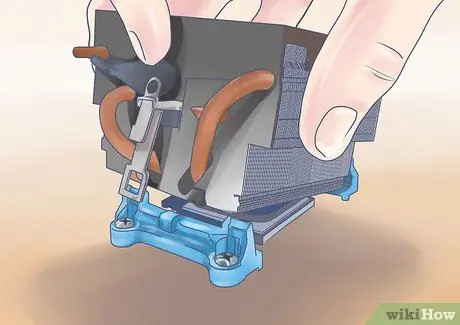
Step 2. Attach the heat sink to the processor
Install the fan with even pressure from all sides: the drop of paste you placed on the surface will spread over the entire contact area. This will create a thin, even layer that will fill any gaps, but will prevent excess buildup.
When heat is applied, the paste will become thinner and more distributed towards the edges. This is why it is important to use a small amount of pasta, as it spreads a little
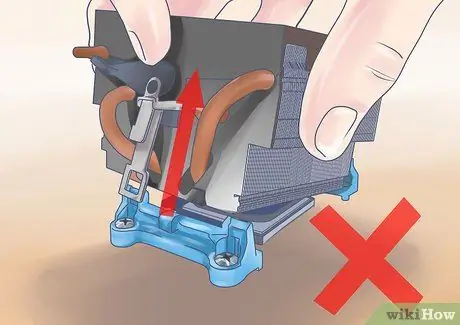
Step 3. Avoid removing the heat sink after installation
It can be difficult to check if the paste has been applied correctly. If you break the seal that is created when you install the heatsink, you will need to start over, first cleaning the old paste and then reapplying it.
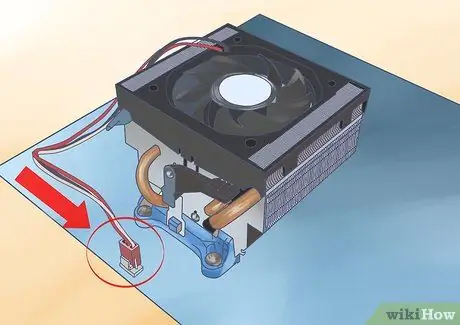
Step 4. Reconnect the fan to the motherboard
The CPU fan wire should be connected to its specific socket, because it mainly has the PWM function, which allows the computer to automatically adjust the fan speed, without changing the voltage.
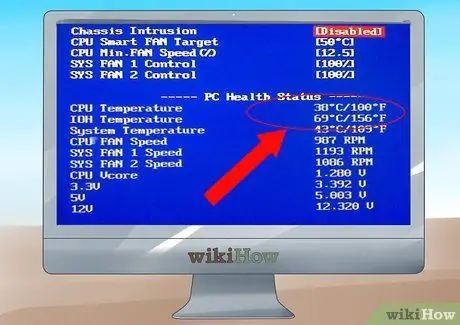
Step 5. Boot the system
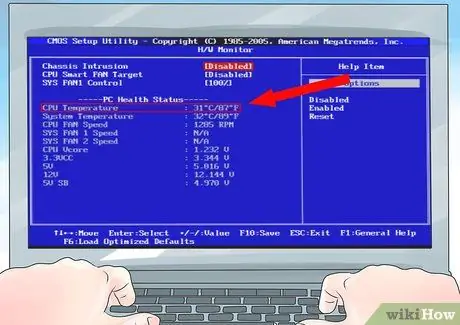
Check that the fan is spinning. Enter the BIOS by pressing the F1 or Del key during POST. Check if the CPU temperature is normal: it should be below 40 ° C when idle; the same goes for the GPU.
Method 3 of 3: Apply the Thermal Paste on the Square Base Fans
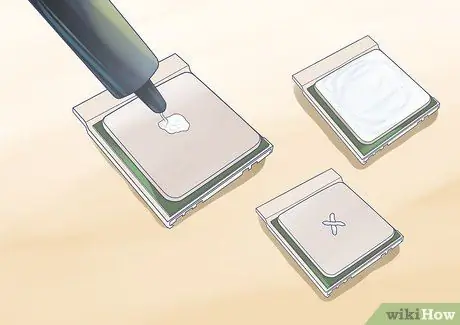
Step 1. Apply the paste to the base of the heatsink
Applying the paste on a square cooler is a little more challenging than a round one, simply because putting a dot on it and applying pressure will not result in full coverage. There are several approaches that people are used to, so we will review some of the more popular ones:
- The line method. Place two thin lines of thermal compound on the base of the heatsink. The line should be parallel and spaced so that each is one-third the width of the processor. The lines should also be about a third of the processor's length in length.
- The cross method. This is very similar to the previous method, but the lines are crossed in an "X" pattern, rather than parallel. The length and thickness of the lines should be similar to the previous method.
- The diffusion method. This is one of the most popular and most effective methods, but it requires a little more effort. Put a small amount of thermal paste on the base of the fan. Using a plastic finger protector or plastic bag, use your fingers to spread the paste evenly over the entire surface. Make sure to cover the entire surface that will come into contact with the processor and not to apply too thin a layer of paste. In most cases, the paste should barely hide the underlying metal.
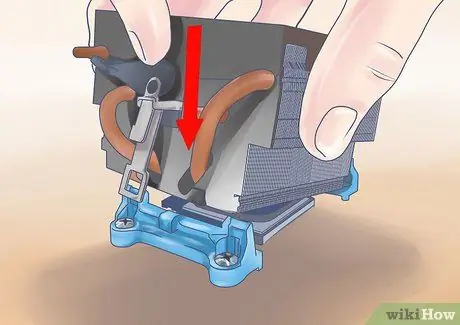
Step 2. Install the heat sink
If you are using one of the line methods, apply even pressure to the heat sink when you install it to make sure the paste covers the entire surface. If you are using the diffusion method, you need to install the heatsink at a slight angle to avoid bubble formation - this is because the paste is usually spread too thinly to compensate for bubbles after applying pressure.
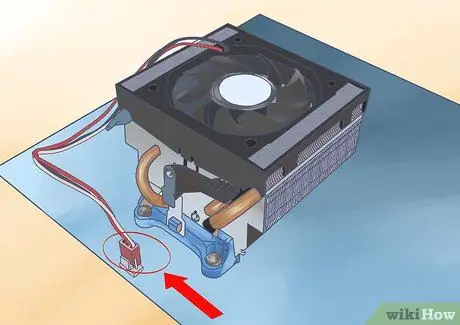
Step 3. Reconnect the fan to the motherboard
The CPU fan wire should be connected to its specific socket, because it mainly has the PWM function, which allows the computer to automatically adjust the fan speed, without changing the voltage.
Step 4. Boot the system
Check that the fan is spinning. Enter the BIOS by pressing the F1 or Del key during POST. Check if the temperature is normal: that of the CPU should be below 40 ° C when idle; the same goes for the GPU.
Advice
- After cleaning the surface with alcohol, do not touch it with your bare fingers. Human skin has its own oils that damage the surface and coolers.
- Keep in mind that what is known as the "impression period" often occurs with thermal paste, in which the paste is more efficient and continues to lower the temperatures. Sometimes this period is very short, but sometimes it could be up to 200 hours.
- If latex gloves are used to spread the thermal paste over the entire designated surface, make sure they are free of talc. If you combine thermal paste and talc, the heat sink will be severely damaged.
- A thin layer of thermal paste is ideal, while a thick one decreases the rate of heat transfer. It serves to bridge the gap between the chip and the heat sink, even that tiny "up and down" in between them.






