Excel is a great tool for performing multiple regressions when you don't have access to an advanced statistics program. The process is quick and easy to learn.
Steps
Step 1. Open Microsoft Excel
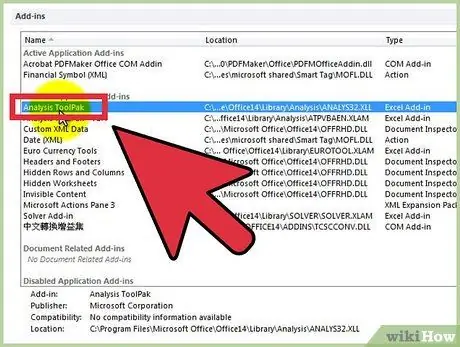
Step 2. Check the presence of the "Analysis tools" by clicking on the "Data" tab
If you don't see the option, you will need to activate the add-on, as follows:
- Open the "File" menu (or press Alt + F) and select "Options".
- Click on "Add-ons" on the left.
- Click "Go" next to the "Manage: Add-ons" option at the bottom of the window.
- In the new window, check the box next to "Analysis tools", then click "OK".
- The add-on is now activated.
Step 3. Enter data or open a document with data
The data must be arranged in immediately adjacent columns and the labels must be in the first few rows of each column.
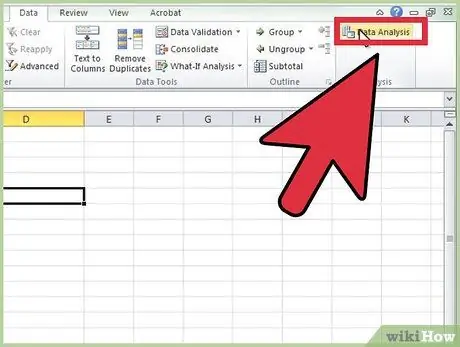
Step 4. Select the "Data" tab, then click on "Data Analysis" in the "Analysis" group (usually on the far right of the screen)
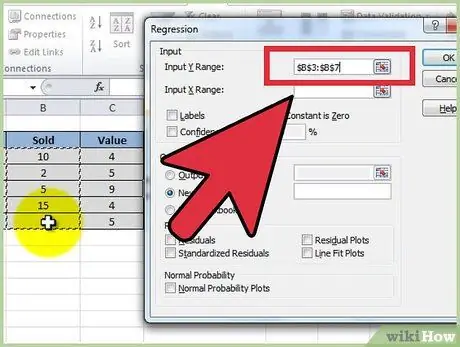
Step 5. Enter the independent data (Y) by placing the cursor in the "Input range Y" field, then highlight the data column
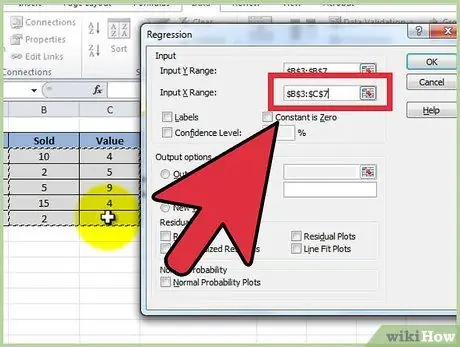
Step 6. Independent variables are inserted by first placing the cursor in the "Input Range X" field, then highlighting multiple columns (for example $ C $ 1:
$ E $ 53).
- NOTE: Independent variable columns MUST be adjacent to each other for the input to work properly.
- If you use labels (which must be in the first row of each column), click on the box next to "Labels".
- The default confidence level is 95%. If you want to change this value, click on the box next to "Confidence level" and modify the adjacent value.
- Under "Output Options", add a name in the "New Worksheet" field.
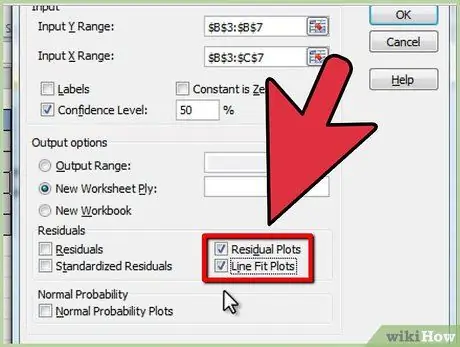
Step 7. Select the desired options in the "Residual" category
Graphical residual outputs are created with the "Residual Paths" and "Lines Fit Paths" options.






