This article shows how to create a simple macro using an Excel worksheet. Read on to find out how.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Enabling the Use of Macros
Step 1. Launch Microsoft Excel
The procedure to follow to enable the use of macros in Excel is the same on versions of Excel 2010, 2013 and 2016. However, there are some slight differences, if you are using Microsoft Excel on OS X or macOS systems, which will be described in the article.
Step 2. Go to the File tab of the menu
On OS X and macOS systems, you need to access the "Excel" menu
Step 3. Select the Options item
On OS X and macOS systems select the "Preferences" item
Step 4. Choose the Customize Ribbon option
On OS X and macOS systems, select the "Ribbon and toolbar" item located in the "Editing tools" section
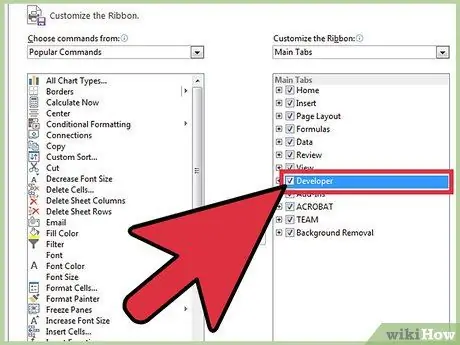
Step 5. Select the Development check button in the list on the right
On OS X and macOS systems you will find the "Development tab" item in the "In the ribbon, show" section
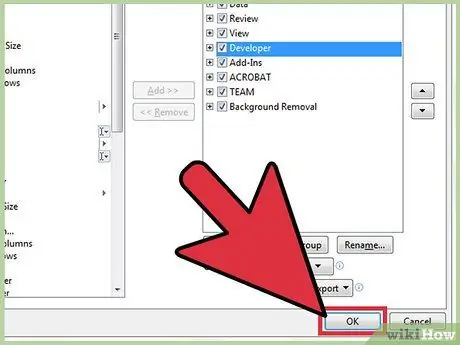
Step 6. Press the OK button
You will see the new "Developer" tab appear on the right side of the ribbon, at the end of all the tabs already present.
Part 2 of 3: Creating a Macro
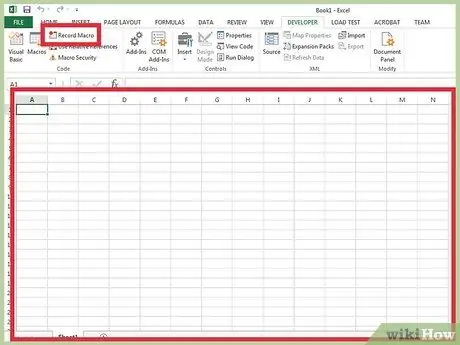
Step 1. Practice the sequence of operations that the macro should perform automatically
When a new macro is recorded, whatever action is performed (a mouse click, insertions and deletions of rows or cells, etc.) is stored, so a single mistake can compromise the entire work. Before creating the actual macro, practice a couple of times in carrying out the entire sequence of operations that will have to be recorded as a macro, in order not to have hesitations and not to make mistakes during the recording.
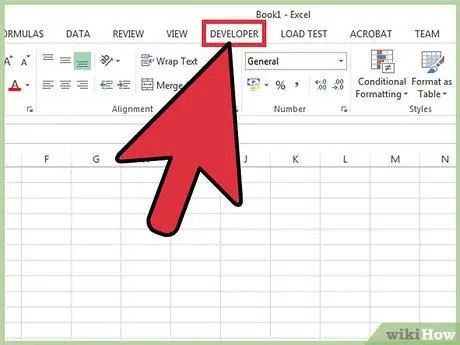
Step 2. Go to the "Development" tab
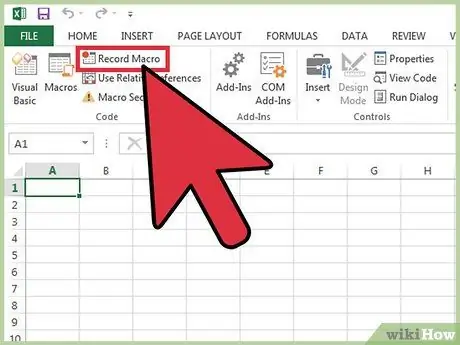
Step 3. Press the Record Macro button
It is located in the "Code" section of the ribbon. Alternatively, you can use the hotkey combination Alt + T + M + R (on Windows systems only) to start recording a new macro.
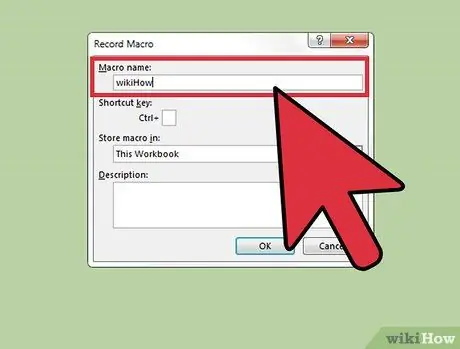
Step 4. Name the macro
Make sure you use a descriptive name, which allows you to identify it quickly and easily, especially if you need to create and use more than one macro.
It is also possible to add a brief description indicating the functions performed by the macro
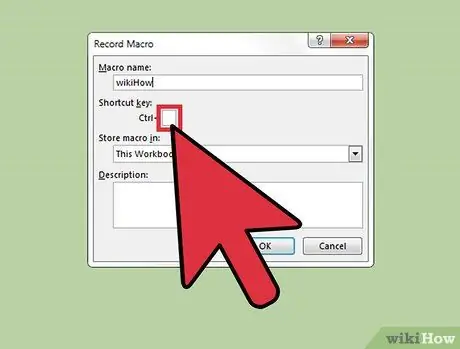
Step 5. Click inside the Hotkey text box
You can assign a shortcut key combination to the macro so you can quickly execute it by pressing a few simple keys. However, this is an optional step.
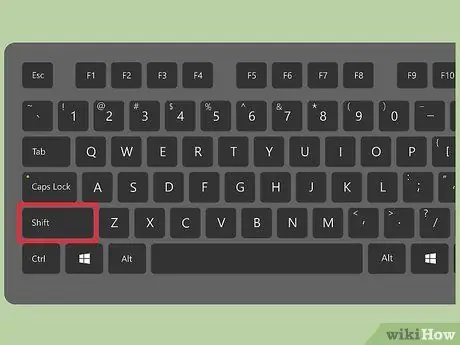
Step 6. Press the ⇧ Shift key, then type a letter
This way you can use the hotkey combination Ctrl + ⇧ Shift + Choice_Letter to execute the macro directly from the keyboard without using the mouse.
On OS X and macOS systems, the hotkey combination to use is ⌥ Opt + ⌘ Command + Choice_Letter
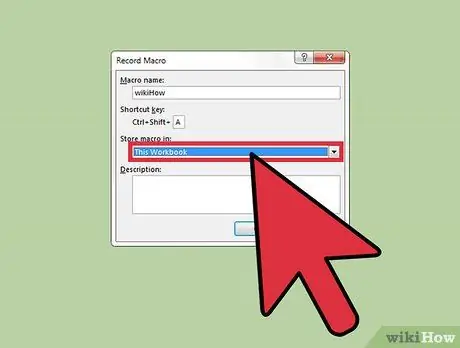
Step 7. Enter the Store macro in menu
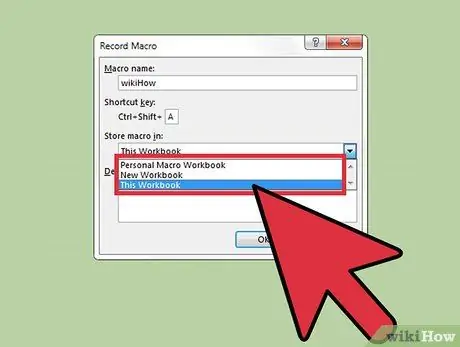
Step 8. Choose the folder where you want to store the macro
If you are going to use the macro in question only on the current worksheet, you can leave the default location "This Workbook". On the contrary, if you want to make it available for all Excel sheets, select the item "Personal macro folder".
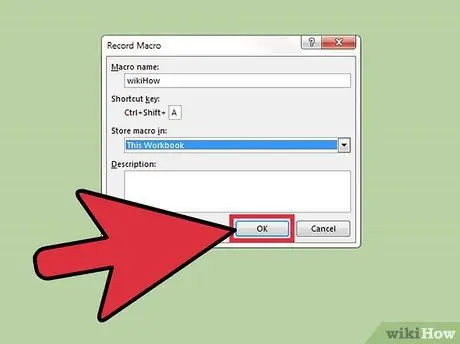
Step 9. Press the OK button
Recording of the new macro will begin.
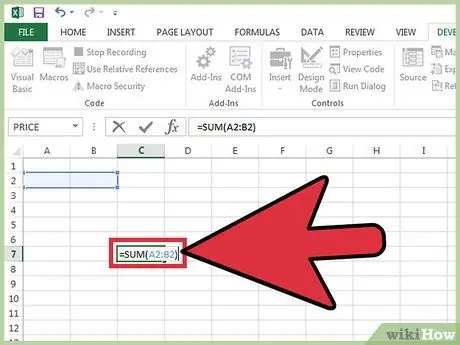
Step 10. Perform the sequence of operations you want to assign to the macro
Once you get to this point, you will need to be very careful what you do because any action will be recorded and added to the macro. For example, let's say we create a macro that sums the contents of cells A2 and B2 and places the result in cell C7. Executing it in the future will always carry out the same series of operations: the sum of the data present in cells A2 and B2 will be displayed in cell C7.
Macros are a powerful and flexible tool, but they can also become very complex to manage. You can also use a macro to open other Office package programs. When recording a new macro is enabled, any action performed within Excel will be inserted into the macro
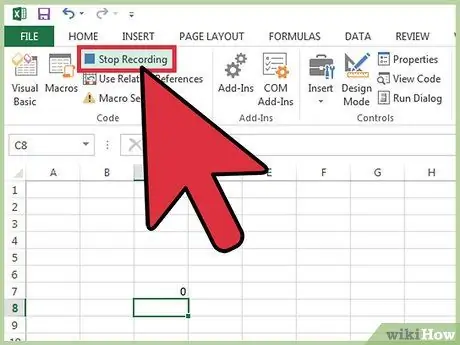
Step 11. Once the recording is complete, press the Stop Recording button
In this way, the registration procedure of the operations to be assigned to the macro in question will be interrupted and all the activities carried out will be stored inside it.
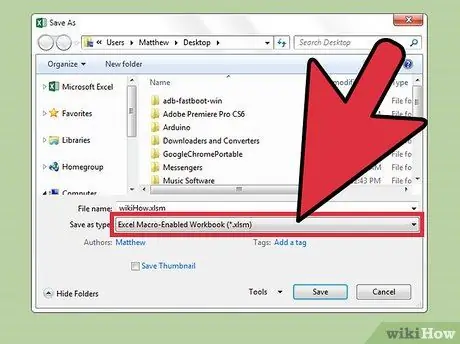
Step 12. Save the file in a format that allows macros to run
To properly use macros within a worksheet, you need to save its file in a format that supports macro execution:
- Access the "File" menu, then choose "Save as";
- Select the "File type" drop-down menu under the "File name" field;
- Choose the Excel file format "Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (*.xlsm)".
Part 3 of 3: Using a Macro
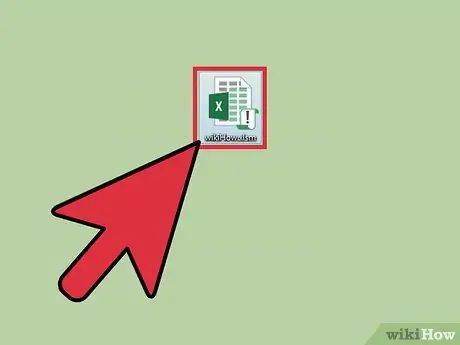
Step 1. Open a macro-enabled worksheet
If you closed your Excel file before running the macro, you will be prompted in the future to enable the use of the contained code.
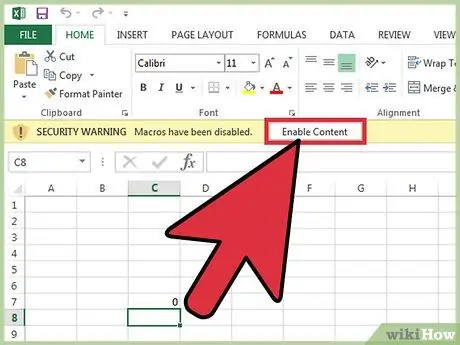
Step 2. Press the Enable Content button
It appears at the top of the Excel sheet inside the "Security Warning" bar. This warning will appear whenever you open a macro-enabled sheet or workbook. In this case, you can enable the use of the contents of the file without any risk, since it is an Excel sheet created by you, but in the case of files with active macros inside and coming from other sources, be very careful before enabling its content to run.
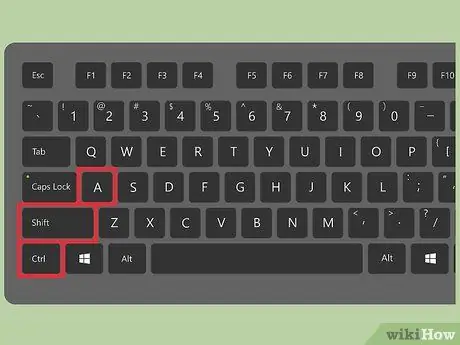
Step 3. Press the key combination to run the macro
When you need to use a macro, you can quickly run it by simply pressing the hotkey combination you assigned it.
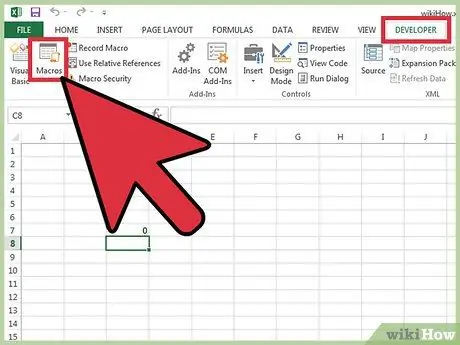
Step 4. Press the Macro button located inside the "Development" tab of the ribbon
The complete list of all macros currently available for the sheet or workbook in use will be displayed.
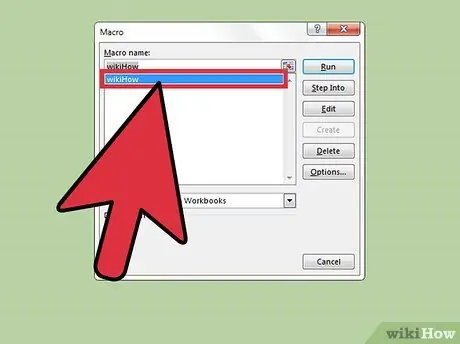
Step 5. Select the macro you want to run
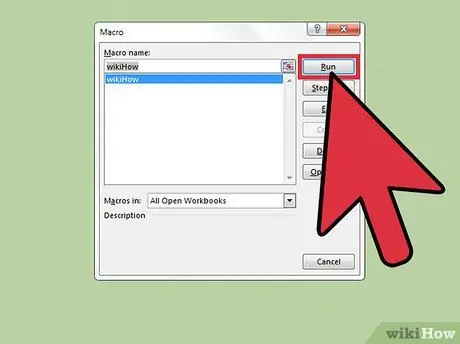
Step 6. Press the Run button
The selected macro will run using the currently selected cell or area.
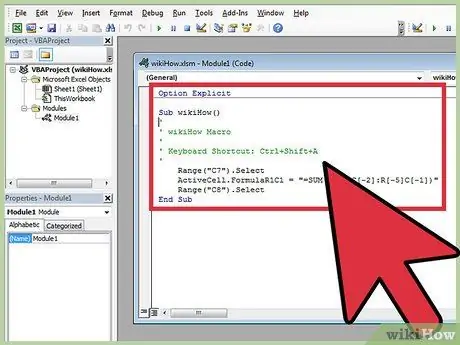
Step 7. View the code of a macro
If you need to know in depth how a macro works, you can view the code that was automatically created by Excel during the recording phase and make any changes you want. Here are the instructions to follow:
- Press the "Macro" button located in the "Development" tab of the ribbon;
- Select the macro you want to review the code for;
- Press the "Edit" button.
- Analyze the code that makes up your chosen macro in the Visual Basic editor window.






