The compound microscope is a powerful magnifying tool that is commonly used in scientific laboratories to observe bacteria and other small cell samples. It features at least two convex lenses placed at opposite ends of a tube. The upper portion of the tube (the eyepiece) is raised or lowered, the image of the sample placed under the other end is focused and magnified. Despite its complexity, you don't have to be a scientist to learn how to use it.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Getting to know the microscope
Step 1. Get familiar with the tool
Examine all parts of it by learning its name and function. If you are in class, the teacher should describe it; if you are self-taught, you should find a diagram of the instrument in the package with its instructions.
- Place it on a flat, clean, even surface near an electrical outlet.
- Always carry it with two hands; hold the stand with one and support the base with the other.

Step 2. Turn on the microscope
This means inserting the plug into a suitable socket; the switch is usually located on the base.
- Electricity is needed to power the lighting system inside the compound microscope.
- Make sure the electrical source is suitable for the instrument; typically, a microscope needs a 120 volt power supply.
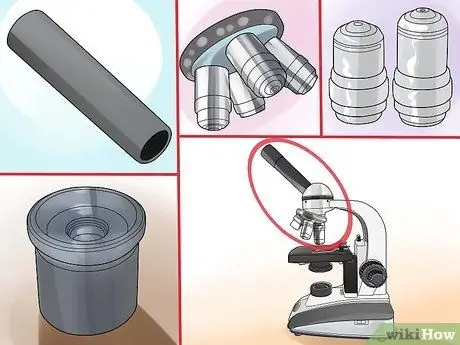
Step 3. Inspect the prism box
This portion contains the optical elements which consist of: eyepiece, eyepiece tube, turret and objectives; some call this part "the body" of the microscope.
- The eyepiece is the element through which you observe the sample placed under the microscope;
- The eyepiece tube is the holder that holds the eyepiece in place;
- The turret holds the objective lenses;
- Objectives are the primary lenses of a compound microscope. There can be three, four, or five, depending on the complexity of the model.
Step 4. Study the tripod
This is the structural element that connects the prism box to the base and there are no lenses inside.
- When carrying a microscope, always grab it by the stand and base.
- The tripod provides a support for the prism box.
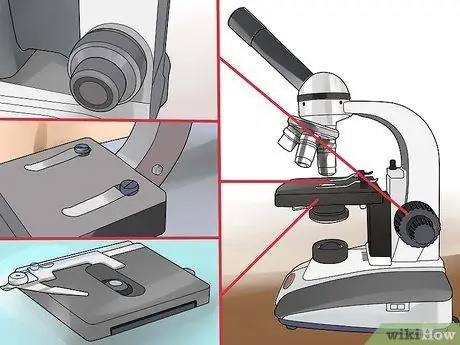
Step 5. Look at the base
It is the surface that supports the weight of the instrument and contains the translating stage which in turn supports the slide; the base is also equipped with focusing screws (coarse and micrometric screws).
- The focus screws can be separate or coaxial (which means that the two screws rotate around the same axis).
- The translating stage is the surface on which the sample rests; when working with high magnification, a mechanical stage is used.
- Slide clips are used when the stage is manually adjusted.
Step 6. Study the lighting system
The compound microscope is equipped with light to ensure optimal observation of the sample; the bulb is placed on the base.
- The light passes through the table thanks to an opening, a hole that allows the illumination of the slide.
- The lamp provides light to the microscope. Typically, this is a low-wattage halogen bulb; the light is continuous and variable.
- The condenser collects and focuses the light coming from the lamp; this element is located under the coffee table and is often equipped with a diaphragm.
- The condenser adjustment screw moves it up and down to adjust the light.
- The diaphragm is located under the stage and together with the condenser controls the amount of light that hits the sample.
Part 2 of 2: Focus the Microscope

Step 1. Prepare the slide
It should always be ready with a coverslip that protects both the specimen you are looking at and the objective lenses, preventing them from coming into contact.
- Place the sample between the two components to form a slide.
- Insert the slide in the center of the stage just above the hole.
- Move the two clips over the slide to secure it in place.
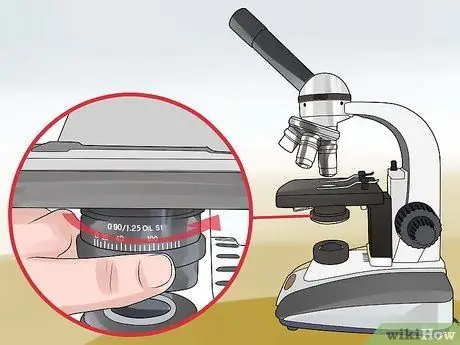
Step 2. Make sure the diaphragm is open
This element is usually found under the coffee table; at this stage you need as much light as possible.
- You shouldn't use the aperture to control the light, but to optimize the level of contrast and resolution to get a more defined image.
- In this process, the minimum magnification is usually used.

Step 3. Adjust the rotating turret and screws
Start with the smallest zoom level that allows you to select the most interesting part of the sample; once located, you can increase the magnification to observe it better.
- Rotate the nosepiece until the shorter lens (4x) is above the specimen. You should feel a "click" and notice some resistance when the lens is in place. The shorter lens is also the least powerful and represents the best magnification level to start with.
- Turn the coarse screw (the larger one) on the base so that the stage rises towards the lens. Make this adjustment without looking into the eyepiece; you must make sure that the slide does not come into contact with the objective. Stop just before the sample touches the lens.

Step 4. Focus the tool
Adjust the lamp and iris while viewing the specimen through the eyepiece to achieve the optimum light level; move the slide so that the image is in the center of the field of view.
- Arrange the lamp until the lighting level is comfortable; the brighter the light, the better the image.
- Turn the coarse screw in the opposite direction, so that the stage moves away from the lens; always go slowly until the image is in focus.

Step 5. Enlarge the image
Use the coarse screw to observe the sample and then switch to the micrometric screw for fine adjustment; it may be necessary to change the position of the slide to center it in the field of view.
- When using a compound microscope, the correct observation technique is that both eyes remain open: one looks through the eyepiece and the other looks at the outside of the microscope.
- When using the 10x objective it is worth reducing the amount of light to improve the visibility of the image.
- Readjust the lamp and iris as needed.
- Change lens by rotating the turret and selecting the longer lenses.
- Make any necessary focus adjustments.
- Once you have a clear image, switch to a higher magnification. It should be a simple procedure that requires minimal use of the focusing tools.
- If you are unable to make the sample image defined, repeat the steps described above.
Step 6. Put the tool away
Dust causes severe damage to the compound microscope; it can scratch delicate lenses, block the adjustment screws, and alter the images you view through the eyepiece.
- Always turn off the power after each use.
- Lower the stage, remove the slide and cover the instrument with a dust cover.
- Do not touch the lenses or the slide with your fingers.
- Always carry the microscope with two hands.
Advice
- As the sample is viewed through various lenses, its image is reversed. You have to move the slide up to bring the sample to the bottom of the eyepiece's field of view.
- Please deposit a smaller sample than you think is necessary. When you place the coverslip on the slide, the contents expand and are pressed to the sides.
- Check if the model in your possession is equipped with a locking screw for the translating stage; if not, you must pay attention that the lens does not touch the slide to avoid breaking it.
Warnings
- Do not place it on an uneven surface; you cannot bring the image into focus properly and the microscope may sway and fall.
- Always carry the compound microscope with two hands; one should grab the stand and the other should support the base. This tool is delicate and expensive.
- Do not touch the lenses with your fingers, you could damage them and make them unusable.
- Keep both eyes open while looking through the microscope; even if only one inspects the sample, you may fatigue it by closing the other.






