The NT file system (used in most versions of Windows) has several features, including 'journaling', which make it very resistant to errors. However, it is not immune to problems, and in case of errors (in most cases) it is possible to perform a repair using the tools provided by the operating system itself. Repair is feasible only if the problem does not prevent the operating system from starting normally. Let's see together how to proceed.
Steps
Step 1. Try to start your computer to be able to run the 'Scandisk' program and proceed with automatic repair of bad sectors
You can do this by choosing one of the following strategies:
-
Use Safe Mode:

Fix Ntfs Error Step 1Bullet1 Start your computer in safe mode by repeatedly pressing the 'F8' function key while the computer is starting up. Then select 'Safe Mode' from the menu that appeared
-
Use the installation CD-DVD:

Fix Ntfs Error Step 1Bullet2 Insert the operating system installation media into your computer. When you turn on your computer, the installation procedure will automatically detect the presence of an installation and will allow you to access the recovery console by simply pressing the 'R' key. At this point it will be sufficient to follow the instructions on the screen until the recovery console appears

Step 2. Insert the hard drive into a different computer
Remove the hard drive from your computer and install it on another computer. This way you will be able to access the contents of the hard drive using the operating system of the second computer.
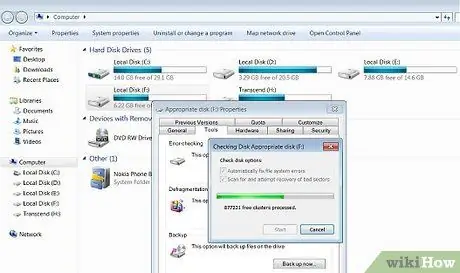
Step 3. Run the 'Scandisk' program
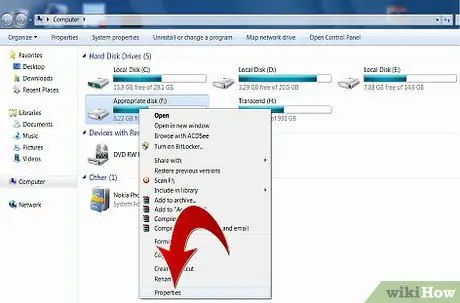
Step 4. If you have the possibility to access the graphical interface follow these instructions:
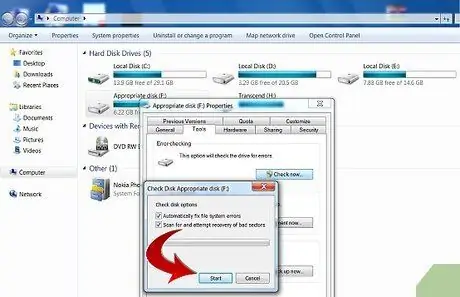
select the 'Computer' icon, then locate the hard drive to be analyzed and select it with the right mouse button. Select the item 'Properties' from the context menu that appeared. Select the 'Tools' tab and press the 'Run Scandisk' button. Check 'Automatically fix file system errors' and 'Scan for bad sectors and attempt recovery'.
Step 5. If you are faced with the recovery console, type the following command 'chkdsk c:
'(without quotes). Where 'C:' is the hard drive or partition to be scanned. If not, replace it with the drive letter you want to check.
Step 6. To be able to repair any errors found, repeat the previous step using the following command:
'chkdsk c: / r' (without quotes). Depending on the speed of the system, and the size of the drive to be scanned, this process may take some time.






